

Volume 60
Published on June 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Literature, Language, and Culture Development
Against the backdrop of globalization and the complex relationship between the Chinese and American film industries, integrating Chinese elements into Hollywood science fiction films has drawn significant attention. This study focuses on the perspective of cross-cultural communication. It takes 15 Chinese audiences who have watched relevant films as the research objects, uses the semi-structured interview method, and combines the Uses and Gratifications Theory and Acculturation Theory for research. The results show that the presentation of Chinese elements in American science fiction films is complex and diverse. The integration of characters shows a polarized trend. The integration of scenes enhances the effect by combining real and artistic scenes. Technology integration showcases China’s scientific and technological achievements and promotes the plot. At the same time, the presentation effect of Chinese elements affects the emotional response and cultural identity of the audience. A positive presentation can enhance the communication effect, while a negative one can hinder it. This study provides empirical support for the development of cross-cultural communication theories and also offers references for film producers.

 View pdf
View pdf


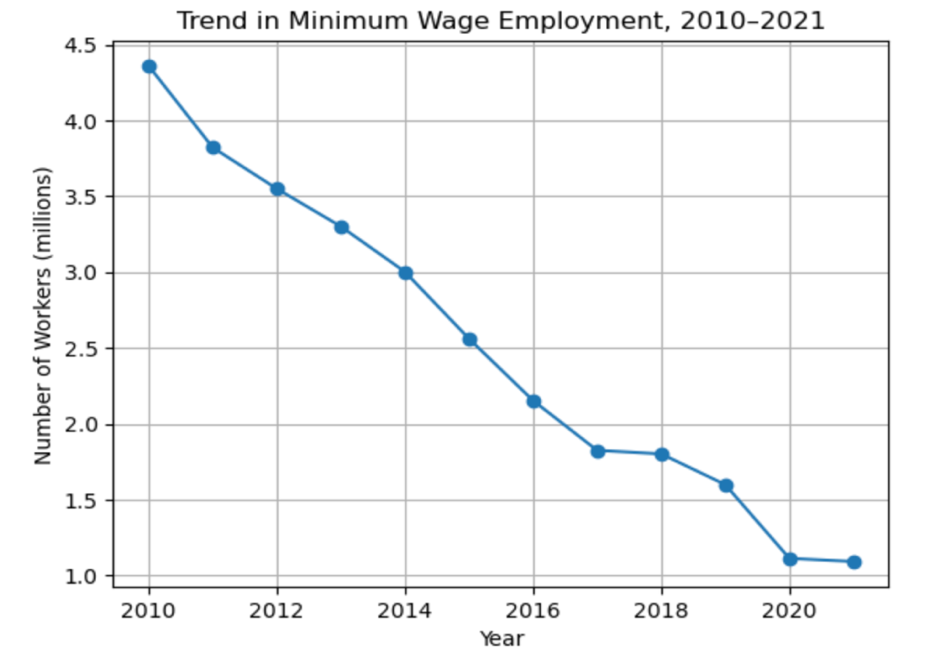
Education is a cornerstone of labor market success, shaping wage levels, job security, and access to diverse income opportunities. This research examines how educational achievement influences the probability of working at minimum wage throughout US states between 2010 to 2021 while studying how education combines with state minimum wage regulations. This analysis uses Current Population Survey data as well as national economic indicators and Integrated Public Use Microdata Series to calculate the difference-in-differences effects with state-year fixed components for analyzing educational impacts on minimum wage standards. Labor statistics show that raising the average years of education decreases minimum wage employment by 0.18 percentage points specifically in states where educational levels are higher after implementing higher minimum wages. The impact of education levels on employment faces crucial modification through state-level labor policies, thereby demonstrating the necessity for combined educational programs and wage reform initiatives. The findings help policymakers distinguish minimum wage employees from other workers while recommending vocational instruction with accessibility to education as a method for boosting socioeconomic opportunities for vulnerable groups.

 View pdf
View pdf


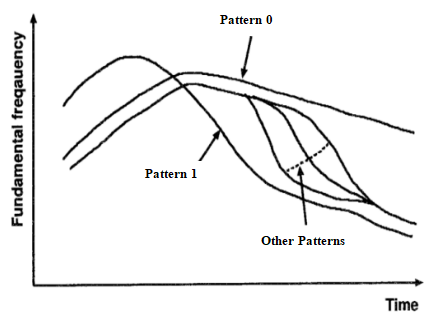
A growing number of native Chinese speakers are enrolling in Japanese language programs, rendering the acquisition of Japanese pitch accent a significant topic in linguistics. Despite extensive research on the perception and production of devoiced vowels, studies on Chinese learners’ perception and production of Japanese pitch accent remain limited. This study examines the perception and production of three-mora Japanese word sequences with devoiced vowels by Chinese native learners of Japanese. The results reveal that learners made fewer perceptual than articulatory errors, who tend to pronounce P0 as P3 and P1 as rising-falling type. Further analysis indicates that compared to native speakers, there is no significant difference in the pronunciation of P0, while the pitch frequency difference for P1 is smaller and for P2, it is larger. In terms of perception, learners are able to recognize the most natural pitch differences, but the perceptual difference for P0 is smaller. Moreover, no significant correlation is found between pitch accent perception and pronunciation in these sequences.

 View pdf
View pdf


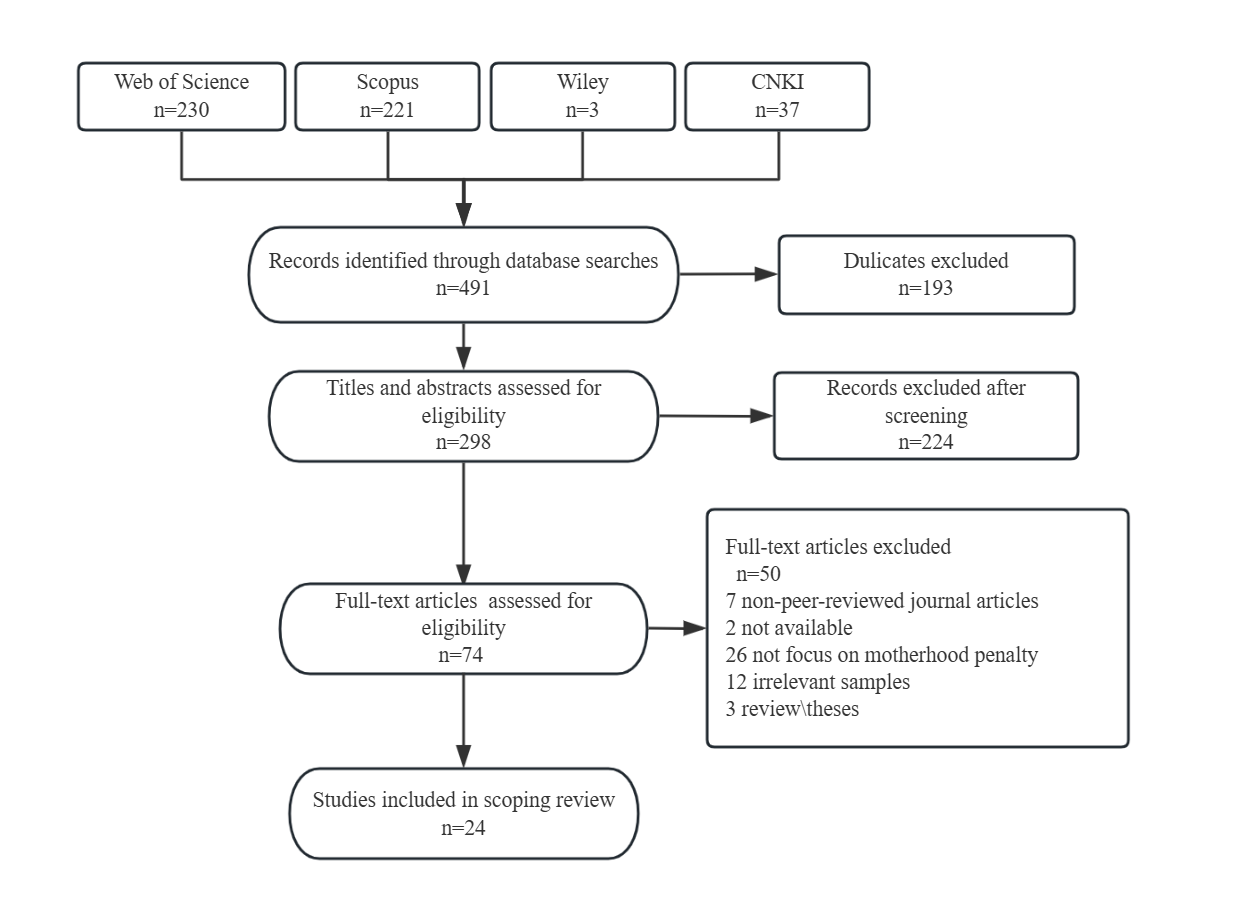
This scoping review explores the phenomenon of the "motherhood penalty" in China, a growing issue within the global gender equality discourse. The motherhood penalty refers to the wage and career disadvantages that women experience in the labor market due to their roles as mothers. Despite global research on this topic, limited studies have examined the specific manifestations and influencing factors of the motherhood penalty in China. This review aims to fill this gap by synthesizing 24 empirical studies published between 2013 and 2024, primarily utilizing quantitative methods. The review follows Arksey and O'Malley's five-step framework to analyze the studies. The review identifies four main manifestations of the motherhood penalty in China: lower income, labor force participation and career interruptions, and restricted career development. Moreover, it examines key factors that contribute to these penalties, including family structure, education, workplace sector, intergenerational support, gender norms, and policy. The study provides a comprehensive overview of the literature on the motherhood penalty in China, highlighting the need for future research and policy intervention to address the issue.

 View pdf
View pdf


China is facing an increasingly serious problem of urban shrinkage, which is embodied in the long-term massive population loss in the northeast and the short-term small population loss in the East. By comparing the characteristics of cities from several dimensions and referring to some successful cases of preventing urban shrinkage, this paper explores urban shrinkage in two different regions and development models within China. Two typical shrinkage cities, Wenzhou and Jixi, are selected as samples for this study, while statistical analyses are conducted with the help of public government information data. The result of this research is that due to varying city development patterns, Wenzhou and Jixi exhibit distinct types of shrinkage. There are different solutions for different types of urban shrinkage. Both cities should actively explore new industries and upgrade existing ones to enhance livability and community vitality, meeting residents' needs for better lives and achieving a win-win outcome.

 View pdf
View pdf


There are multiple factors that influence academic performance. This study examines the relationship between learning motivation and academic performance in A-Level Biology students. A-Level Biology is part of the General Certificate of Education Advanced Level (A-Level) curriculum. A quantitative approach was adopted, with data being collected from 21 students via an online questionnaire. A quantitative approach was used, collecting data from 21 students through an online questionnaire. In this study, learning motivation comprises three dimensions, namely cognitive motivation, extrinsic motivation, and the need for achievement. At a macro level, there is a significant correlation between learning motivation and academic performance. At a micro level, correlation analysis revealed that cognitive motivation had the strongest positive impact on academic performance, while need for achievement showed a moderate correlation. Extrinsic motivation had no significant effect. The research not only reveals a correlation between learning motivation and academic performance but also suggests that fostering intrinsic motivation may be more effective in enhancing academic outcomes in A - Level Biology.

 View pdf
View pdf


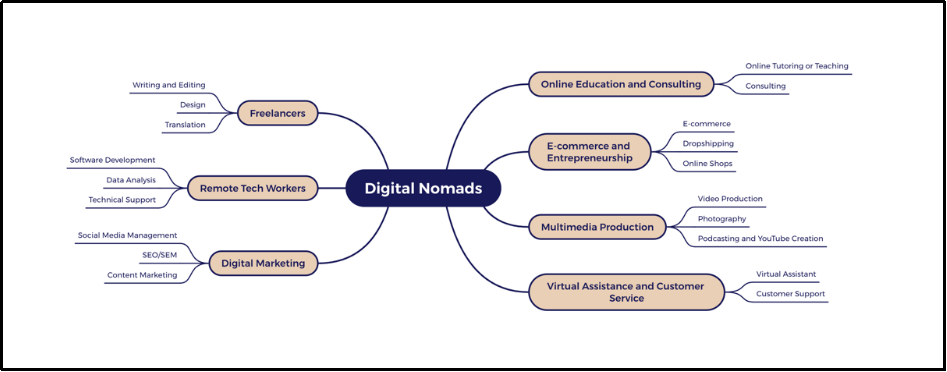
With the rise of digital nomadism as both a lifestyle and a working model, more people are choosing a mobile way of life, breaking away from traditional, location-based living. This study explores the motivations behind digital nomads’ decision to embrace mobility and examines how they develop a sense of belonging despite their constant movement. Using methods such as online ethnography and virtual interviews, the research finds that digital nomads no longer derive their sense of belonging primarily from physical spaces like family homes or local communities. Instead, their sense of belonging is increasingly shaped by their recognition of work value, personal fulfillment, and meaningful social interactions. This paper offers a fresh perspective on how digital nomads construct belonging, arguing that this process is multi-dimensional and constantly evolving. Rather than being tied to fixed geographic locations, a sense of belonging for digital nomads is now centered on self-worth, professional identity, and social recognition in a globalized world.

 View pdf
View pdf


The “Cool Japan” strategy, integral to Japan’s post-war cultural diplomacy, has significantly reshaped its international image and enhanced soft power. This study examines the strategy’s evolution and its role in transforming Japan’s global perception from a militaristic past to a modern, innovative, and culturally rich nation, while also driving economic growth through cultural exports. By integrating anime, cuisine, fashion, and technology into its national brand, Japan has developed a diverse identity that resonates globally. Empirical data, including European surveys and industry statistics, highlight the strategy’s effectiveness: 93% of respondents acknowledge Japan’s cultural richness, while the anime industry recorded revenues of 33.5 trillion yen in 2023, boosting tourism and cross-cultural engagement. The analysis further examines Japan’s leadership in international frameworks such as the CPTPP and initiatives like Data Free Flow with Trust (DFFT), highlighting its role as a mediator in addressing global challenges. However, critiques of cultural exoticization, particularly concerning the 2021 Tokyo Olympics’ cultural representations, expose tensions between globalization and cultural authenticity. The study concludes that while the “Cool Japan” strategy effectively harnesses cultural resources to enhance soft power, future success will depend on balancing promoting popular culture and integrating traditional heritage, fostering bidirectional cultural exchanges, and addressing domestic social issues within Japan’s global narrative.

 View pdf
View pdf


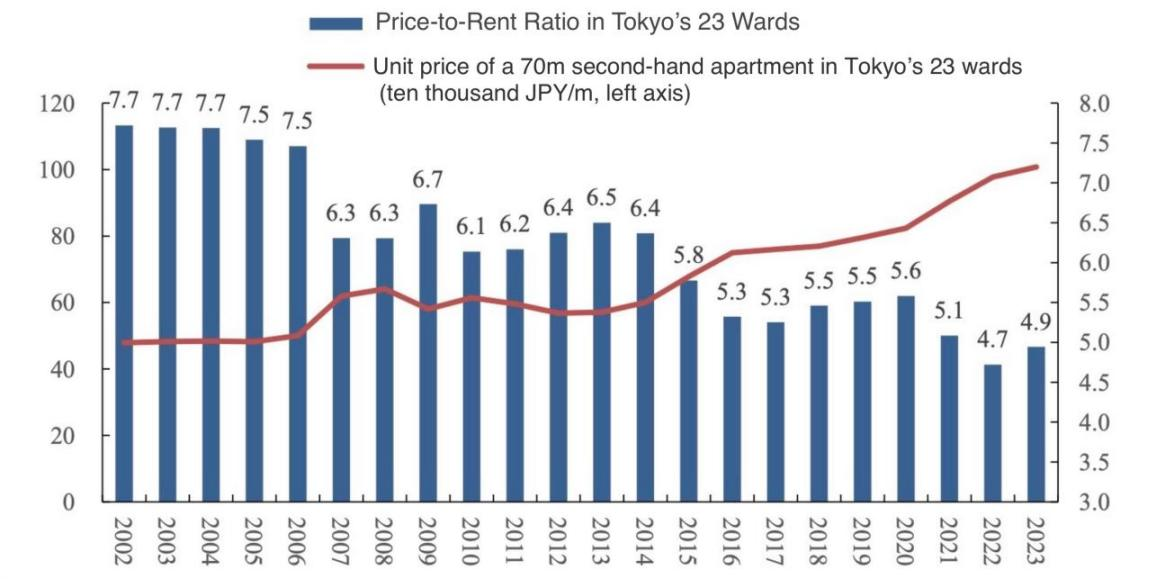
This paper explores the impact of interest rate adjustments on real estate markets in China and Japan, highlighting how monetary policy interacts with institutional structures and supply-demand dynamics, and compares the development trajectories of their real estate markets at the same time. In China, declining interest rates have fueled high property prices and low rental yields due to persistent supply-demand imbalances, particularly in major cities. This has contributed to economic disparities, income inequality, and financial risks. In contrast, rising interest rates in Japan have suppressed real estate activity as higher mortgage costs, and weakened export competitiveness, ultimately prolonged the recovery from its past real estate bubble collapse. This paper concludes that interest rate policies alone cannot resolve structural challenges in real estate markets. A broader policy framework is needed, incorporating industrial restructuring, population mobility, and fiscal measures. In China, key priorities include balancing land supply, enhancing population mobility, strengthening the rental market, reducing fiscal reliance on real estate, and improving housing affordability for low- and middle-income groups. The government must also address speculative risks, market adjustments, and economic overdependence on real estates. In Japan, population policies and property market reforms are the key to support its long-term recovery.

 View pdf
View pdf




