

Volume 64
Published on November 2024Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Global Politics and Socio-Humanities
In the rapidly evolving e-commerce landscape, algorithmic collusion has emerged as a sophisticated method for businesses to engage in anti-competitive behavior without explicit agreements. This paper delves into the complexities of algorithmic collusion, examining how modern information technologies facilitate these covert practices. This study underscores the profound impact on market competition and consumer rights by categorizing the different types of algorithmic collusion and analyzing their implementation mechanisms. Furthermore, it highlights the deficiencies in current antitrust frameworks and the urgent need for legal and regulatory reforms. The paper concludes with strategic recommendations to enhance market transparency and fairness, ensuring that technological advancements do not undermine competitive equity.

 View pdf
View pdf


Under the digital age, the method of learning expanded to the virtual setting. With resources shared through online platforms, digital divide became a new problem in achieving education equality. This paper intends to examine the effect of digital divide on educational system in the U.S. and China from a comparative perspective. This study adopts literature review as its research method. Types of digital divide that occurs in the two countries showcase some similarities, yet the factors attributing to the educational digital divide varies widely. Educational divide exists in different social groups. Systematic and cultural differences are the root behind these factors. In the U.S., digital divide occurred due to differences at multiple levels: race, state, schools, and family SES. In China, digital divide occurs due to geological divergence, generational division, and social class. The root Moreover, mitigating policies from the two countries illustrate how the U.S. and China access the issue from different perspective. The root behind such contrast is the difference in the two countries’ social system and cultural attitudes. The two countries can inspire each other and the world in creating better solutions to solve this new form of education inequality.

 View pdf
View pdf


In a rapidly evolving digital society, the active engagement of adolescents on social media platforms has progressively increased. This study examines the relationships between depression, sleep health, and social media usage mainly among adolescents, along with a subset of undergraduates and working adults to explore other underlying reasons. A questionnaire was designed and distributed via the Questionnaire Star platform, yielding 115 respondents and 111 valid responses. The study utilized the Self-Rating Depression Scale (SDS), Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), and Social Anxiety Scale for Social Media Users (SAS-SMU) to evaluate the three measures. Higher levels of depression are consistently associated with poorer sleep quality and shorter sleep duration; however, the influence of SMU on these variables is neither as direct nor as significant as initially hypothesized. This research provides a preliminary exploration of the concurrent effects of SMU on sleep quality and depression. Future studies should consider additional related variables and undertake longitudinal investigations.

 View pdf
View pdf


The Chinese thriller film, as a specific genre, exhibits unique principles and characteristics in its creation, which is also significant in terms of cultural heritage and creative expression. Nevertheless, the current systematic investigation of the research principles and creative connotations of the sample remains inadequate. The objective of this paper is to analyze the research principles of Chinese thriller-horror films and identify the sources and evolution of the narrative materials underlying them. The analysis employs both the literature analysis method and the case study method. The former is used to examine the expression of the combination of thriller imagery and traditional Chinese cultural symbols in the film, while the latter is employed to explore the cultural elements belonging to the Chinese nation's tradition. Additionally, the analysis considers the distinctive characteristics of the film in terms of artistic scene layout, sound, and color, as well as the significance and role of such films. By examining the fundamental principles of Chinese thriller film-making, it is possible to gain a deeper understanding of the distinctive appeal and artistic nuances of Chinese thrillers, offering insights that can inform and inspire the creation of Chinese films.

 View pdf
View pdf


Based on the theory of second language acquisition, this study employs a mixed-method approach to investigate the impact of language environment on English writing proficiency in higher education institutions. In the quantitative study, data were collected from 184 students with diverse English language learning backgrounds via the online questionnaire platform "Wenjuanxing" at several universities in China and in-depth interviews were conducted to gain qualitative insights. The findings indicate that the frequency and depth of writing practice, parents' education level, and early exposure to English have a notable impact on English writing ability. Students in the advanced training group demonstrated superior performance due to their increased exposure and practice opportunities, whereas students in the standard study group necessitated more structured instruction and writing practice to enhance their proficiency. The study offers a theoretical foundation and practical guidance for teaching English writing, such as the creation of a rich language environment to facilitate students' English writing abilities.

 View pdf
View pdf


The Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st-Century Maritime Silk Road spearheaded by General Secretary Xi Jinping offers a practical framework for fostering a fresh approach to international relations between China and its neighboring countries. This study thoroughly examines how the Belt and Road Initiative contributes to shaping a new form of international relations between China and its neighboring regions from a constructivist viewpoint. This is achieved through qualitative research, literature analysis, and inductive methodologies. Under the constructivist perspective, The Belt and Road Initiative has transformed the dynamic between China and its neighboring nations on various levels. When looking at it from a horizontal perspective, the focus is on highlighting the unique aspects and qualities of international interactions, such as "common development", "mutual respect", and "harmonious coexistence".Looking at things from an aerial viewpoint, the Belt and Road Initiative delves into a fresh approach to China's relationships with its neighboring countries across three levels: national, subnational, and regional. China prioritizes establishing innovative international relations with neighboring countries through the Belt and Road initiative to stabilize domestic growth and navigate foreign relations amidst the changing development scenario. Faced with intricate regional dynamics stemming from recent historical shifts, China must steadfastly advance the "Belt and Road" project to cultivate a conducive neighboring atmosphere, fostering the development of a shared human destiny.

 View pdf
View pdf


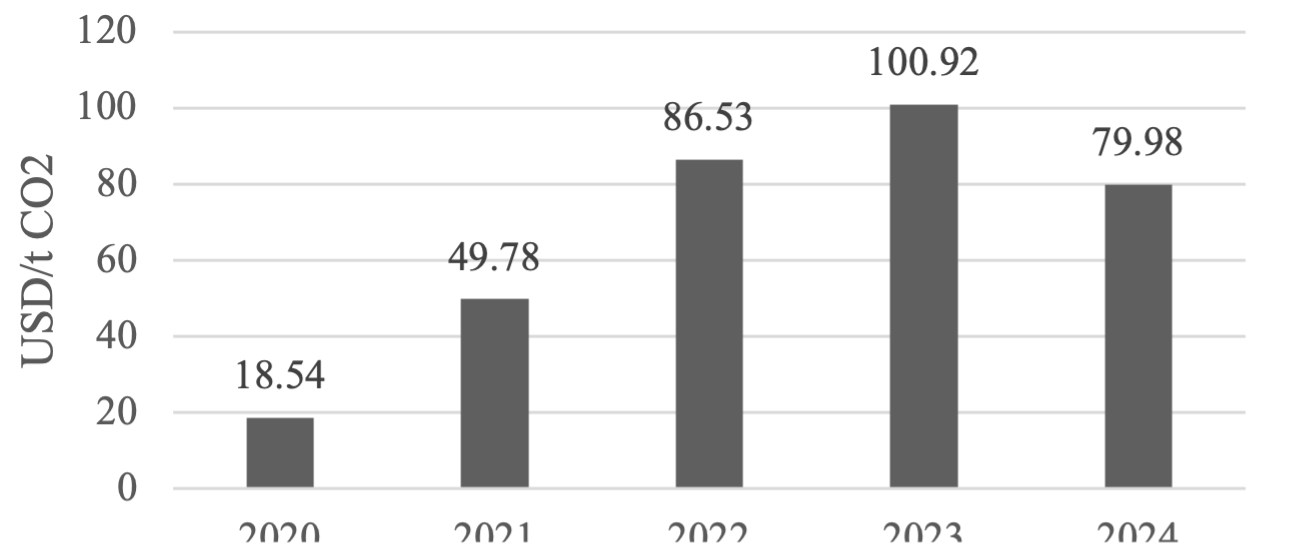
The European Parliament plans to gradually introduce the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism in 2023, with a complete implementation set for 2026. As an essential trading partner of the EU, China will shoulder an additional carbon border tariff due to the lack of low-carbon technology and the dependence on extensive development patterns. These extra costs will undermine the profit margins of China’s carbon-intensive industry sectors, possibly resulting in decreased exports and a restructuring of production. The latest estimate of the exact costs of China’s embedded carbon exports to the EU is a problem that has received limited academic attention. Using the IPCC carbon emission accounting methodology and non-competitive single-region input-output analysis, this research precisely measures the embedded carbon in China’s exports to the EU for the nine most affected industries. Furthermore, this study quantifies the impact of the CBAM on China’s exports of these nine industry sectors. The findings suggest that China should improve the domestic carbon emission trading system and take the initiative to participate in formulating a carbon pricing consultation and dialogue mechanism, mitigating the negative impact of the EU CBAM on exports.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the rapid development of time and technology, the significance of digital game development cannot be underestimated. In today's era, games have permeated thousands of households, encompassing a wide range of genres. They are no longer solely entertainment products but also can be applied in education, medical care, learning, scientific research, and other fields. Research indicates that serious games (games designed to teach knowledge and skills or provide professional training and simulation) can effectively improve mental health. This review discusses the current status and future prospects of serious games in promoting mental health. It presents a comprehensive classification of serious games by integrating several literature resources, synthesizing information and data analysis to investigate their effectiveness in improving mental health outcomes. The findings show that serious games play a certain role in the treatment of mental illness. However, the current body of research is not without limitations, as there exists a dearth of controlled experiments comparing the efficacy of serious games to other types of games and investigating the effectiveness of gamification techniques. To address these gaps, researchers and designers should further prioritize approaches such as emotional design and participatory design. Additionally, leveraging emerging technologies like virtual reality can facilitate the development of adaptable game designs and methodologies that align with evolving societal needs.

 View pdf
View pdf


As global population structures change rapidly, the social rights and welfare of the elderly have increasingly become a focal point of societal concern. Pension policies not only address economic issues but also encompass welfare levels, social equity, citizenship rights, and identity. This paper explores the impact of different pension policies on the citizenship experience of the elderly by comparing the pension systems of China and Japan. The study is based on pension policy documents and related data from both countries and employs a comparative social policy analysis. The comparison is conducted conceptually, focusing on the scope, content, and depth of the pension policies in China and Japan, in order to reflect on the elderly's citizenship experience in both nations. The research highlights that China’s pension policy features a single-tier structure with limited autonomy and marked urban-rural disparities, which restrict the citizenship experience of the elderly. In contrast, Japan’s retirement policy is characterized by mandatory participation, clear responsibilities, and a multi-tiered structure, providing broader coverage and more comprehensive social rights and a sense of identity for the elderly. However, this system also brings about noticeable class divisions.

 View pdf
View pdf


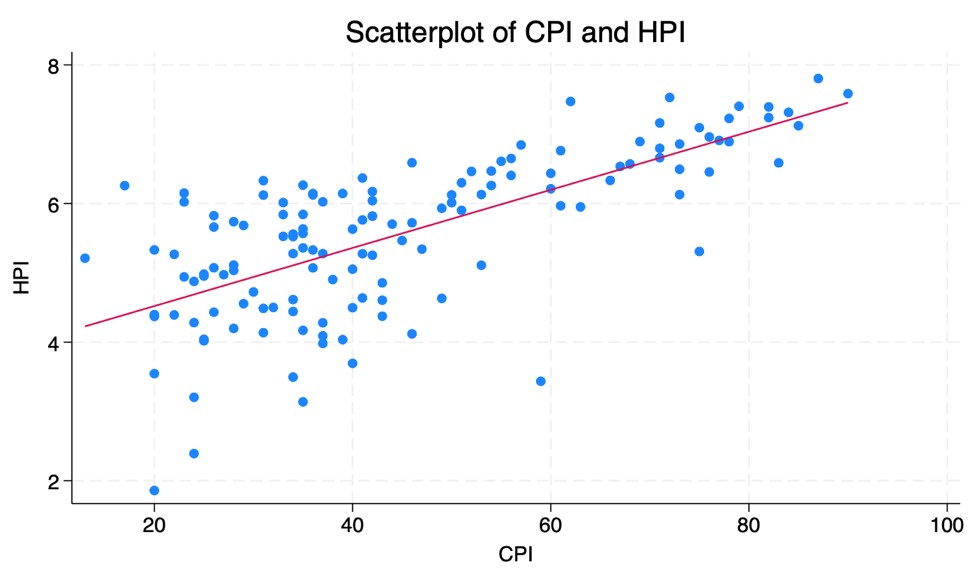
Corruption and subjective well-being are of interest to scholars, governments, and legislators. The study builds on existing literature that explores the interplay between economic, cultural, and political factors and happiness, with a particular focus on the less-examined role of governance quality, as measured by corruption levels. While scholars generally see corruption as a predictor of happiness, the direction of that effect is unclear. Using cross-national data from 133 countries, this paper investigates the impact of corruption on individuals’ happiness. Employing an Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) regression analysis, the research controls for other critical variables such as GDP, democracy index, and education, and tests the hypothesis that lower corruption is associated with higher happiness. The perceived corruption is statistically significant on predicting happiness when it is solely considered, but the situation changed when controlling GDP. The paper reveals that economy plays important role as a intervening variables between corruption and happiness. The paper is a helpful guides for policymakers and governments in making effective anti-corruption measures for enhancing happiness at a national level.

 View pdf
View pdf




