

Volume 129
Published on September 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICBioMed 2025 Symposium: Computational Modelling and Simulation for Biology and Medicine
K-mer analysis is a core technology in bioinformatics, widely used in genome assembly, variant detection, and metagenomic research. With the exponential growth of sequencing data, efficiently processing massive k-mer datasets imposes higher demands on computational performance, memory usage, and system scalability. This paper focuses on implementing k-mer analysis in Python environments, exploring its key challenges in algorithmic efficiency and resource management. Python-based workflows demonstrate strong performance in data compression, graph structure simplification, and feature extraction by incorporating greedy strategies, sorting optimisations, parallel computing, and deep learning methods. With GPU acceleration and cloud platform deployment, this technical approach exhibits potential for scaling to petabyte-scale genomic datasets, making it suitable for high-throughput bioinformatics tasks across multiple scenarios. This methodology not only addresses current computational needs but also provides a reference for the development of bioinformatics computational models.

 View pdf
View pdf


Rhubarb, as an important traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) with a long history, has core active ingredients known as anthraquinone compounds (such as aloe-emodin, rhein, chrysophanol, etc.). These have been confirmed to possess broad biological activities, exerting significant regulatory effects in multiple key systems of the human body, including the digestive, hepatic, renal, and cardiovascular systems. However, clinical precision medication strategies and long-term safety assessments under different preparation forms and individual variability backgrounds still require more substantial data support. This paper systematically summarizes the chemical basis, in vivo pharmacokinetic characteristics, and core pharmacological mechanisms of rhubarb anthraquinones in the digestive, hepatic, renal, and cardiovascular systems. It concurrently evaluates their clinical application efficacy in related indications like constipation and hepatobiliary diseases, alongside potential adverse reaction risks. The review results clearly elucidate the intrinsic relationship between the "structure-metabolism-activity/toxicity" of rhubarb anthraquinones, providing crucial theoretical support for precise and rational clinical medication. The integrated pharmacological and toxicological evidence in this study lays a scientific foundation for the subsequent development of highly effective and low-toxicity rhubarb-derived drugs. Future research needs to focus on in-depth analysis of the pharmacodynamic material basis of anthraquinone monomers, deep exploration of structural modifications of anthraquinones, and the construction of long-term toxicity prediction models based on metabolomics, to promote the high-quality development and international application of rhubarb resources within the modern TCM system.

 View pdf
View pdf


A polyphenolic compound curcumin, which is extracted from turmeric, has been proven to have dual effects of inhibiting tumor cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis. Prostate Cancer (PCa) which in the male urinary and reproductive systems was recognized as the most common malignant tumors, seriously affects men's daily lives. At present, there is still a lack of highly effective and low-side-effect clinical drugs. Current research indicates that curcumin significantly stops the PCa from growing by regulating miRNA and key enzyme activities, controlling the androgen receptor (AR) signaling pathway. Particularly, nanocarrier technology can greatly enhance its bioavailability and targeting. However, the current research still lacks large-scale clinical validation, standardized dosing regimens, and the ability to overcome the problem of its low bioavailability. This article systematically reviews the research progress on the molecular mechanism of curcumin in the prevention and treatment of PCa and the clinical efficacy data, providing a basic direction and feasibility for future research, and also creating a mechanistic blueprint to guide drug development against PCa.

 View pdf
View pdf


Acne, a common skin disorder, is prone to causing erythema and pigmentation. It has a high prevalence rate and is prone to recurrence. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has a long history and rich experience in treating acne, with methods such as syndrome differentiation and treatment, acupuncture, TCM decoctions, and facial masks. The treatment approaches are unique and effective. This article, through analyzing the common combinations of TCM in the treatment of acne, found that the proportion of Salvia miltiorrhiza in the combinations of TCM preparations is significant. The research discovered that the active ingredients in Salvia miltiorrhiza have a remarkable effect on the treatment of acne. This article explores the inhibitory effect of tanshinone on androgen and the combined effect of Salvia miltiorrhiza and Scutellaria baicalensis in killing Propionibacterium acnes, and analyzes the mechanism of action of tanshinone in the treatment of acne. At the same time, it also investigates the research progress in improving the pigmentation caused by acne. However, in the treatment of acne, TCM mainly proves the effectiveness of treatment through practical means such as the review and summary of clinical results, with relatively few experimental explorations. Therefore, future research should focus on the exploration of the effective components and action mechanisms of TCM, as well as the investigation of new treatment methods.

 View pdf
View pdf


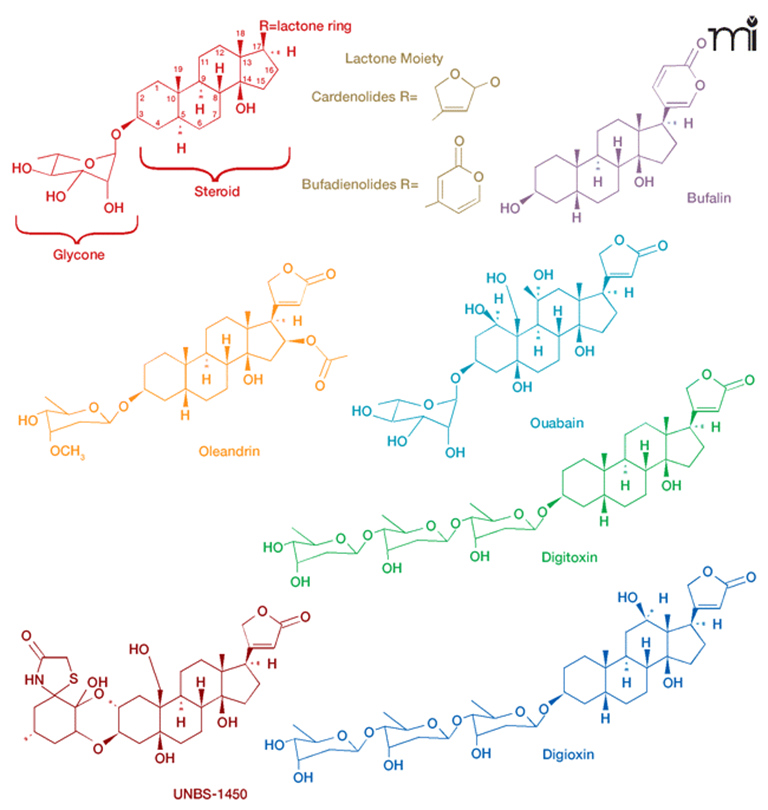
Cardiac glycosides (CGs), traditionally used for the treatment of cardiac diseases, have recently garnered widespread attention due to their unique antitumor effects, making them important candidates for drug repurposing strategies. This review systematically illustrates the diverse mechanisms of action of CGs in antitumor activities, including inhibition of Na⁺/K⁺-ATPase-mediated signaling, downregulation of key transcription factors such as HIF-1α, and induction of G2/M cell cycle arrest. Studies have shown that CGs exhibit minimal cytotoxicity against normal cells at therapeutic concentrations (0.5–2.0 nM) and exhibit excellent selectivity against various tumor cell types. Clinical data demonstrate a 20%–30% reduction in cancer incidence in patients receiving long-term digoxin therapy. Furthermore, the combination of CGs with chemotherapeutic agents significantly enhances tumor inhibition and reduces cardiotoxicity. Chemical modification and nanoformulation optimization have further enhanced the anticancer efficacy of CGs, such as by reducing the IC50 of fluorinated digoxin against MCF-7 cells to one-third of the original drug. Combination with anti-PD-1 antibodies has also demonstrated enhanced immunotherapy synergy. In summary, CGs are expected to serve as an important part of comprehensive tumor treatment and provide new treatment options for cancer patients.

 View pdf
View pdf


In some breast cancers, HER2 genes are overexpressed, which leads to HER2+ BC. Historically, HER2+BC was associated with a more aggressive disease course, faster growth and higher risk of recurrence compared to HER2—BC. Therefore, it used to be a threat to women’s health. Currently, diverse treatment methods are developed, including targeted therapy using monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). However, there is insufficient data and research about the efficacy of specific ADC drugs, for example Kadcyla, as well as the detailed side effects of different drugs. More experiments may have to be carried out in order to obtain more data. This article mainly focuses on comparing different treatment approaches for HER2+ BC. The mechanisms of mAb and ADCs and effect of immunotherapy combined with drugs are analyzed. This article provides a reference for further research about the development and history of mAbs and ADCs. As for the future of treatment of HER2+ BC, more experiments have to be carried out in order to demonstrate the efficacy and safety of new ADC drugs.

 View pdf
View pdf


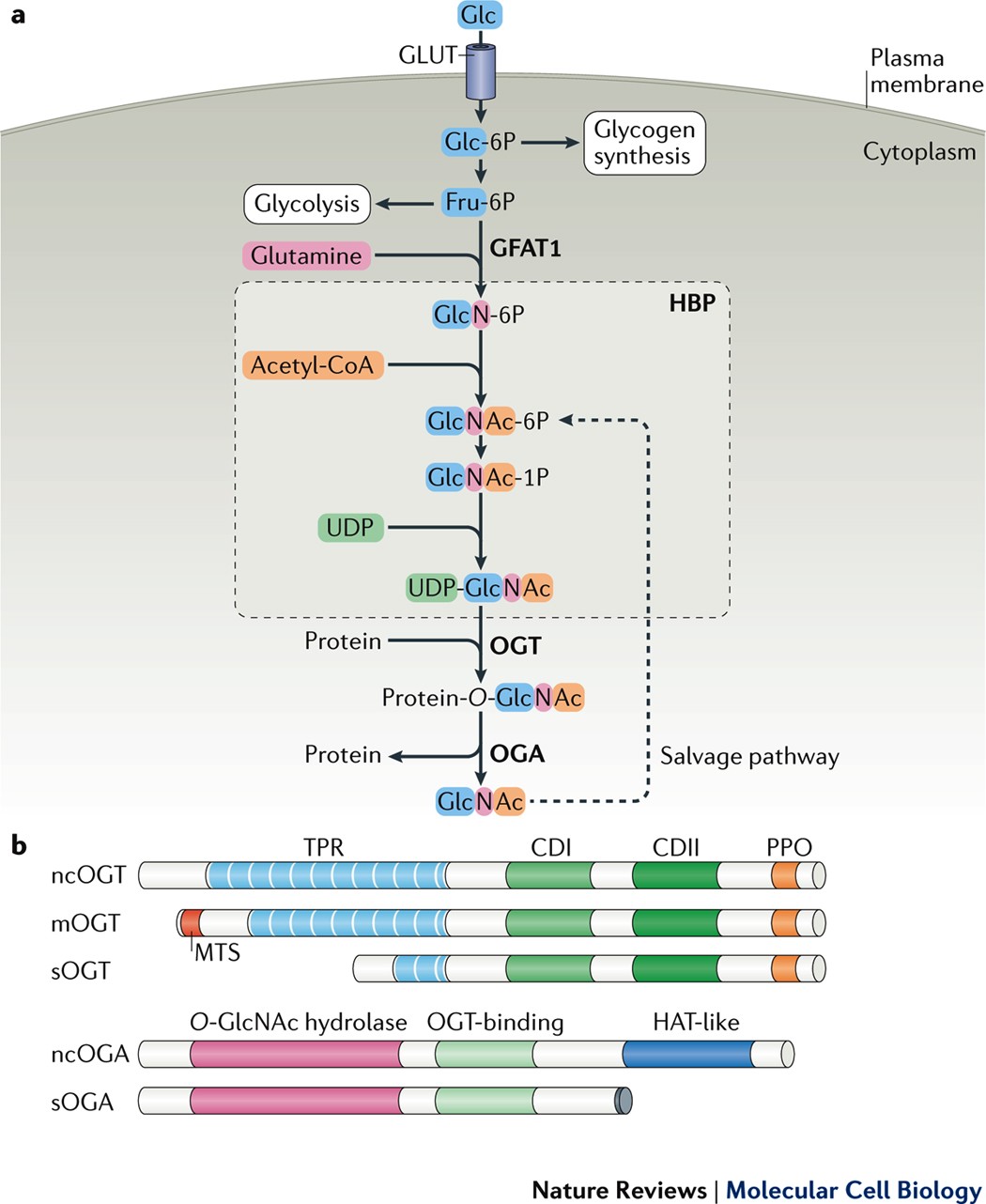
O-GlcNAcylation is a dynamic and reversible post-translational modification that modulates key cellular processes, including transcriptional regulation, signal transduction, and metabolic adaptation. This modification is catalyzed by a unique enzyme pair: O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT), which installs O-GlcNAc moieties on serine/threonine residues, and O-GlcNAcase (OGA), which removes them. Aberrant O-GlcNAcylation has been implicated in the initiation and progression of multiple cancers, promoting tumor growth, metastasis, metabolic reprogramming, immune evasion, and resistance to therapy. Mechanistically, O-GlcNAcylation alters the function, localization, and stability of oncogenic proteins such as MYC, NF-κB, and HIF-1α, and interfaces with other post-translational modifications including phosphorylation and acetylation. Elevated OGT expression is frequently observed in cancer tissues and correlates with poor clinical outcomes. Targeting O-GlcNAcylation pathways has shown therapeutic potential in preclinical models by impairing tumor cell survival and stemness. Despite growing interest, major challenges remain, including the lack of selective OGT inhibitors and incomplete characterization of the O-GlcNAc proteome. Advances in single-cell multi-omics, spatial metabolomics, and glycoproteomics may facilitate the construction of tumor-specific O-GlcNAc maps and enable precision targeting of glycosylation-dependent vulnerabilities.

 View pdf
View pdf


Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most prevalent types of cancer in the world and is extremely invasive, with few available treatments as today. Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR)/CRISPR-associated protein 9 (Cas9), short for CRISPR/Cas9, is a gene editing tool, derived from the natural defence system of bacteria against exogenous viruses, that has recently been widely under research. It involves a guide RNA and Cas9 protein from the Cas family, and cleaves double stranded DNA to inhibit genes. CRISPR/Cas9 technology could have groundbreaking impacts into curing hepatitis B virus (HBV), the virus that stands as the most common cause of HCC. This paper reviews the mechanism and function of the CRISPR/Cas9 system in detail, suggesting some methods by which CRISPR/Cas9 can be used to deactivate genes (targets) that cause cancer. This review discusses the challenges of the CRISPR/Cas9 technology at present and suggests further research direction as it is ultimately an innovative approach that holds great potential for cancer treatment.

 View pdf
View pdf


Lung cancer is currently the most deadly type of cancer, with non-small cell lung cancer dominating, thus making it the primary focus of clinical research and treatment. Despite advances in modern medicine, traditional treatment methods still have limitations in improving patient survival rates. This is especially true in advanced cases, where the survival rate is extremely low, below 20%. Immune checkpoint inhibitors represented by PD-1 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have made significant progress in NSCLC treatment, which restores T cell function by blocking the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway and prolongs the patient's survival, but there are problems such as drug resistance and adverse reaction management. Currently, there is insufficient systematic integration of PD-1 mAb in NSCLC, drug resistance mechanism and combination therapy strategies. This paper analyzes the mechanism of action of PD-1 mAb, elaborates on the clinical application data of Pembrolizumab, Atezolizumab and Nivolumab in different stages of NSCLC, including efficacy, safety and adverse reaction management strategies, and discusses drug resistance mechanism and response plans. The findings demonstrate that their single-agent or combination treatment can increase patients' survival and objective response rate, but attention should be paid to immune-related adverse events (irAEs) and drug resistance issues. This study provides theoretical support for optimizing the individualized application of PD-1 mAb in NSCLC. In the future, biomarkers can be explored to accurately predict the efficacy, develop new combination treatment plans to overcome drug resistance, and promote the more efficient and safe development of NSCLC immunotherapy.

 View pdf
View pdf


Objective: Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a high-risk disease in elderly men, and its incidence continues to rise with aging. Traditional western medicine treatment has a bottleneck in efficacy and a risk of adverse reactions. This article systematically reviews the pathogenesis and clinical treatment of BPH, focusing on the combination of Chinese and Western medicine treatment strategies. Results: The pathogenesis is the imbalance of sex hormones and the abnormal activation of growth factors, which jointly drive the proliferation of prostate cells. In the treatment of western medicine, although α-receptor blockers can quickly improve symptoms, they can easily cause dizziness and hypotension. 5-α reductase inhibitors reduce prostate volume, but there are limitations such as insufficient short-term efficacy and increased nocturia. In terms of combined treatment of traditional Chinese and Western medicine, the clinical effective rate of Huang 'e capsule combined with tamsulosin/dutasteride increased to 68.13 %. Qianlie Shutong capsule combined with western medicine, can improve bladder function, which is better than single western medicine treatment. Conclusion: The combination of Chinese and Western medicine provides a new path for BPH to enhance efficacy and reduce toxicity. In the future, it is necessary to deeply analyze the targets of active components of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and establish a standardized joint program.

 View pdf
View pdf




