

Volume 61
Published on November 2024Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biological Engineering and Medical Science
Since the 18th century, vaccines have played a crucial role in preventing infectious diseases, with the earliest example being Edward Jenner’s pioneering use of the cowpox vaccine to prevent smallpox in 1796. Vaccines work by inducing specific immune responses, effectively preventing the spread of various infectious diseases and protecting the health of individuals and communities. However, traditional vaccine technologies face certain limitations, such as reversion to virulence and long production cycles. In recent years, rapid advances in biotechnology have introduced new vaccine technologies, including mRNA, DNA, nanoparticle, and mosaic vaccines. These innovative technologies are expected to enhance the safety and efficacy of vaccines and accelerate development times. This review explores the latest trends and technological advancements in vaccine development, highlighting the potential applications of these new technologies. By addressing the challenges faced by traditional vaccines and emphasizing the benefits of emerging approaches, this paper aims to provide valuable insights for vaccine research and public health policy, ultimately enhancing global efforts in disease prevention and control.

 View pdf
View pdf


Autophagy is an intrinsic and universally present self-defense mechanism in eukaryotic cells, prevalent across a diverse array of cell types. Research has indicated that this process plays a significant role in the initiation and progression of kidney diseases, particularly through its involvement in endoplasmic reticulum stress, inflammatory responses, and mitochondrial dysfunction. LncRNAs, consist of over 200 nucleotides, primarily function as competing inhibit endogenous RNAs, and constituent complex with microRNAs, thereby influencing the expression of genes that are crucial to the autophagy process. Many studies have reported on the relationship between lncRNA and autophagy or between autophagy and kidney diseases, but few articles have summarized the interrelationships among lncRNA, autophagy, and kidney diseases. Therefore, this paper aims to elucidate the regulatory role of lncRNA in autophagy while exploring the interplay between autophagy and kidney diseases, thus establishing a close connection among the three. This exploration aims to deepen our understanding of the pathogenesis of kidney diseases and to pinpoint potential targets for therapeutic intervention.

 View pdf
View pdf


Equine infectious Anemia retrovirus causes equine infectious anemia and is mainly transmitted by insects from the group Hemiptera. This viral disease has an extremely high death rate due to the strength of the virus, and most importantly, there are still no EIAV vaccines that have been used out of China. Therefore, I will be researching about limited amount of EIAV vaccine designs that have been made for the past few years. The reason why researches of this vaccine have been chosen is because this disease has been a worldwide issue with others that study equine animals. Furthermore, the design of the vaccine will mainly focus on selecting the antigens of gp90 and gp45, which are the two that mostly come in contact with the host cell. The possible and most commonly used platform that will be chosen for this vaccine will be the live-attenuated vaccine, which has been commonly used against single-stranded viruses such as COVID-19.

 View pdf
View pdf


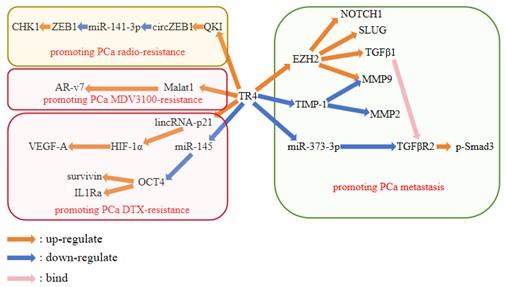
Due to the increasing prevalence of high-fat diets and obesity, the number of people diagnosed with prostate cancer is also rising annually. Men are experiencing serious health problems as a result of prostate cancer (PCa) nowadays. Three types of therapeutic methods to treat PCa have been developed: chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and molecular therapy. Although chemotherapy and radiotherapy have a relatively longer history, severe resistance problems still exist and urgently need to be solved. Not only does Testicular receptor 4 (TR4) belong to the nuclear receptor super family, but it is also an orphan receptor, meaning no endogenous ligands have been found for it as of yet. Studies have found that TR4 participates in PCa initiation, development, metastasis, and therapy resistance. This article will discuss the signaling pathways mediated by TR4 that influence PCa metastasis and therapy resistance, and will provide a brief overview of the small-molecule inhibitors that may have the potential to become effective treatments in chemotherapy.

 View pdf
View pdf


Research on animal vaccines is vital for protecting agricultural productivity, enhancing public health, and maintaining biodiversity. The impact of animal diseases on agriculture, the economy, and public health underscores the importance of vaccine research. Current achievements include developing new vaccines and advancing scientific understanding, though gaps remain in research and application. This article emphasizes the importance of vaccines in animal disease prevention and control, comparing the status and achievements of vaccines for three common animal diseases: rabies, foot-and-mouth disease, and swine fever. Vaccines play an essential role in preventing and controlling animal diseases, directly protecting animal health and improving production efficiency while indirectly ensuring human health and promoting international trade. The article discusses the epidemiology and clinical manifestations of these diseases, along with historical and recent progress in vaccine development. Despite challenges such as high costs and stability issues, new vaccines like mRNA, DNA, and viral vector vaccines are emerging, capable of rapidly responding to new pathogens.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper reviews the history and current status of HIV vaccine development, analyzes recent research progress and challenges, and explores potential breakthroughs and future directions. Since peaking in 1997, the global incidence of HIV has declined, yet the number of infections and mortality rates remain high. HIV has a significant impact on individuals and societies, and its high variability and immune evasion mechanisms present substantial challenges for vaccine development. Current HIV vaccines include viral vector vaccines, DNA vaccines, protein vaccines, and mRNA vaccines, each facing unique scientific and technological challenges. Recent clinical trials of HIV vaccines have shown significant progress, but their efficacy and safety require further validation. Public trust in vaccines and prioritization strategies for high-risk populations pose social and ethical challenges in vaccine deployment. Future research will focus on novel vaccine technologies, innovative immunization strategies, and global collaboration and resource integration. Through continuous scientific efforts and international cooperation, it is anticipated that a successful HIV vaccine will eventually be created to manage and eliminate this worldwide epidemic.

 View pdf
View pdf


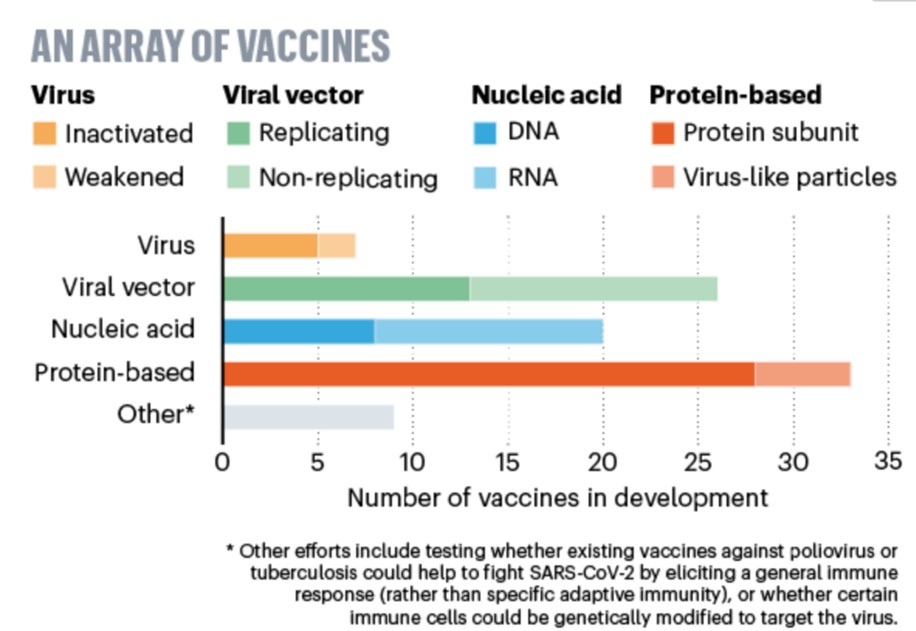
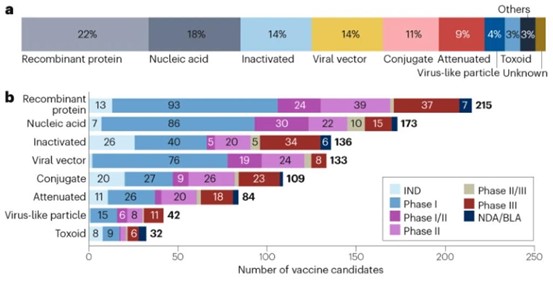
Vaccines have a significant impact on public health, with traditional inactivated or attenuated vaccines playing a major role. Advances in molecular biology have led to the development of other technological platforms, such as recombinant protein vaccines, nucleic acid vaccines, and viral vector vaccines, diversifying the vaccine development pipeline. Recombinant protein vaccines account for the largest proportion of candidate vaccines due to their well-known safety, stability, and ease of production. Due to the flexibility of the nucleic acid vaccine technology platform in developing candidate vaccines against pathogens with highly variable target antigens, many candidate vaccines are being developed for these pathogens, including COVID-19, influenza, and HIV. In recent years, viral vector vaccines have also garnered attention for their potential to induce strong and long-lasting immune responses. Various types of viral vectors (including adenoviruses, retroviruses, lentiviruses, and poxviruses) are currently being used in vaccine development technologies. Particularly, adenoviral vectors have been widely used in the development of vaccines for diseases such as Ebola, HIV, influenza, and COVID-19. Conjugate vaccines also hold a considerable proportion, typically targeting pathogens such as meningococci, pneumococci, and Haemophilus influenzae. These vaccines are based on the covalent linkage of immunogenic protein carriers (mainly tetanus toxoid, diphtheria toxoid, or outer membrane proteins of group B meningococci) with capsular polysaccharides or peptides to enhance immunogenicity and stability. This paper reviews the basic principles of vaccine development, types of vaccines, the vaccine development process, and prospects for new vaccine development.

 View pdf
View pdf


Despite significant advancements in cancer research, oral cancer remains a major global health challenge, particularly in high-risk regions such as India and Pakistan. This paper provides a comprehensive overview of various oral cancers, with a special focus on oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), its risk factors, and early diagnostic methods. Key risk factors for OSCC include cigarette and cigar smoking, alcohol consumption, betel nut chewing, chronic inflammation, and human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV-16) infection. The paper evaluates various early detection methods, including self-examinations, professional screenings, biopsies, toluidine blue staining, fluorescence screening, and liquid biopsies. Additionally, the study highlights preventive measures, such as lifestyle modifications, HPV vaccination, regular health check-ups, and the dissemination of public health information. The paper emphasizes that progress in early detection and prevention strategies holds promise for reducing the incidence and mortality of oral cancer. By promoting awareness and encouraging regular screenings, the fight against this devastating disease can advance significantly, ultimately improving survival rates and quality of life for affected individuals.

 View pdf
View pdf


The CRISPR/Cas9 system has revolutionized gene editing by offering a precise, efficient, and cost-effective method for targeting, modifying, and regulating genomic loci across diverse organisms. Initially discovered in bacteria, CRISPR/Cas9 has evolved into a powerful tool for cancer treatment, enabling both in vivo and ex vivo gene editing strategies. The system's ability to induce targeted DNA breaks and harness cellular repair mechanisms has facilitated significant advancements in genetic research and therapeutic applications. In cancer treatment, CRISPR/Cas9 shows promise in disrupting tumor survival genes and enhancing immune cell therapies. In vivo applications have demonstrated significant tumor inhibition and increased survival rates in preclinical studies, while ex vivo approaches, such as the modification of T cells for enhanced antitumor activity, have shown promising results in clinical trials. Despite its potential, CRISPR/Cas9 faces several technical and ethical challenges. Off-target effects, delivery system optimization, and ensuring the stability and safety of edited cells are critical technical hurdles. Future directions for CRISPR/Cas9 technology include developing new CRISPR systems with enhanced specificity, precise and efficient delivery methods, and multiplex gene editing capabilities. Integrating CRISPR with existing cancer treatments, such as immunotherapy and chemotherapy, can boost treatment efficacy and overcome drug resistance. In summary, CRISPR/Cas9 offers a promising future for cancer treatment through continuous development and refinement.

 View pdf
View pdf


The swift evolution of genetic modification techniques has ushered in transformative prospects and challenges for the therapeutic utilization of gene therapy in medical practice. Over the past few years, the Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR) system has swiftly ascended to prominence as the pivotal methodology in genetic engineering, attributed to its remarkable efficacy and accuracy. Innovations such as base editing and prime editing, which are offshoots of CRISPR technology, have significantly bolstered the refinement and productivity of genomic alterations. However, there are still many significant challenges in current research on gene editing, including the safety, off-target effects, and ethical issues. This paper introduces the basic principles of the CRISPR-Cas9 system and its applications, and the innovations and applications of base editing and prime editing by reviewing the latest research in related fields. Additionally, it discusses the current gene therapy applications of therapeutic strategies for hereditary diseases, as well as the challenges and prospects for their clinical application. This paper aims to provide an overview of the current state of gene editing technology and gene therapy development. The research in this paper will not only help to deepen the understanding of gene editing, but also provide novel insights and approaches for the clinical application of gene therapy.

 View pdf
View pdf




