

Volume 210
Published on November 2025Volume title: Proceedings of CONF-MLA 2025 Symposium: Intelligent Systems and Automation: AI Models, IoT, and Robotic Algorithms
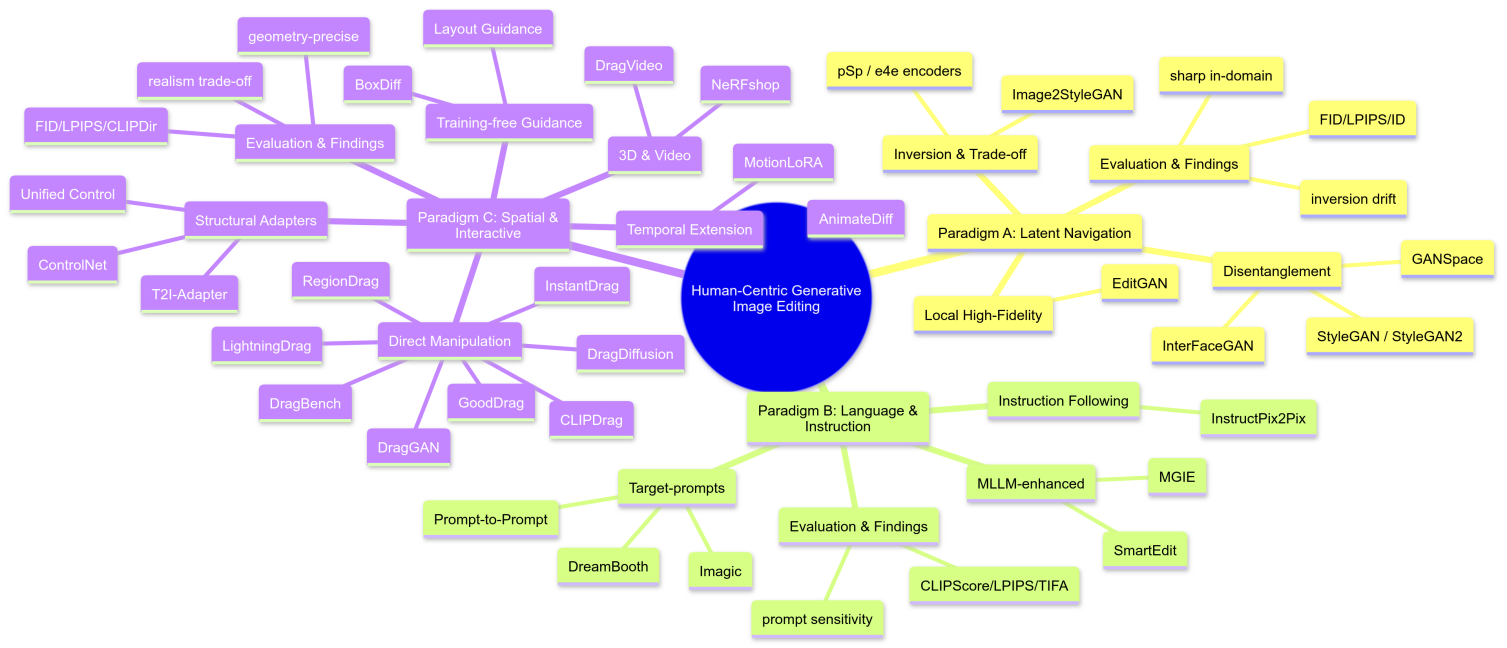
Over the past ten years, the image editing field has experienced a paradigm evolution driven by pixel-wise control, such as Adobe Photoshop, to generative models. With the rise of Generative Adversarial Networks(GANs) and diffusion models, it is now possible to control images through a higher-level semantic understanding. This core vision aims to bridge the gap between human intention and model performance. To address this challenge, the research has shifted from improving generative quality to editing methods, which puts "human-in-the-loop" at the core. The evolution of control reflects the changes in user communities: from code-based abstract latent space manipulation used by early researchers, to the later natural language-based text-to-image image editing (such as InstructPix2Pix), and finally developed to the direct drag-and-drop interaction represented by DragGAN for creators without background mechanisms. The alternative from technical mechanisms. "model-centered" to "user-centered" means the democratization of content creation tools, implying more focus on human-computer interaction principles in future research. To clearly outline the development of this field, this review categorizes existing methods into three paradigms based on the discrepancy in human control modalities: latent spatial navigation, language-guided manipulation, and direct spatial and structural control. This paper's unique contribution is that, systematically analyzes and reviews groundbreaking research that has been conducted since 2018, based on GANs and diffusion models, focusing on "human-control". This paper reveals the inner revolutionary logic of different types of methods, aiming to provide a unique perspective for understanding the future development trend of controllable generative technology.

 View pdf
View pdf


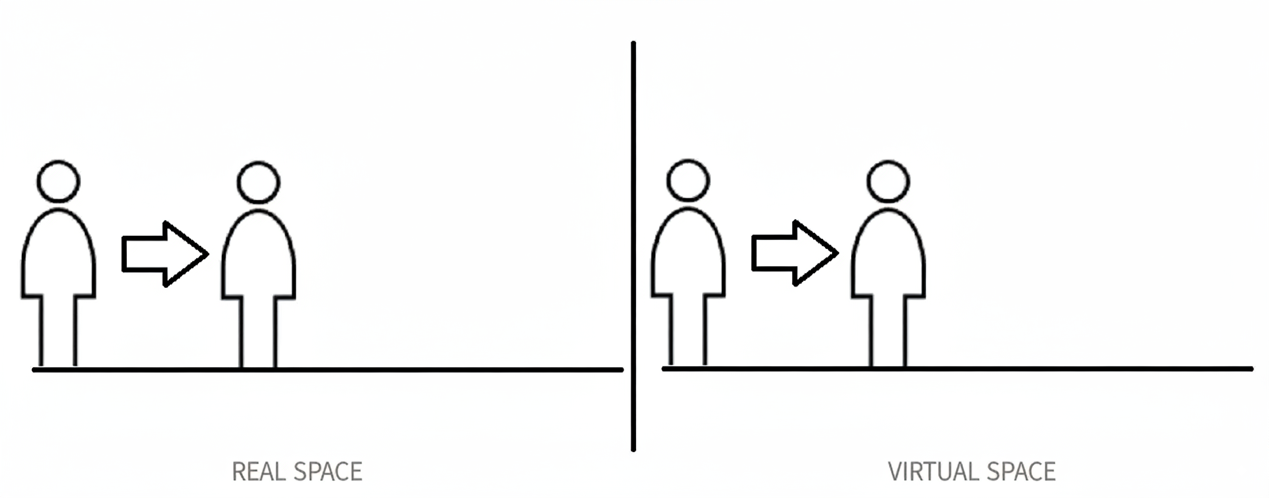
The movement methods in VR are essential in deciding users’ immersion, and it affects directly to the naturalness of interaction. Nowadays movement methods are divided into two major categories ('physical movement’ and 'man-made movement’),'physical movement’ chase for reality, while' man-made movement’ relies on device input. Through the analysis of six dimensions: immersion, comfort, space requirements, usability, applicability, and cost, the study reveals a core paradox: physical mobility provides an excellent immersion, but the limitation of space, device and physical strength makes it difficult to afford. Man-made movement are more comfortable and convenient, but often comes at the cost of sacrificing immersion, and the more one pursues immersion, the more likely it is to cause cybersickness. At present, there’s no any solution that could solve both problems, and the choice of movement methods are still based on specific application scenarios. Scientific research reveals that the movement methods in VR will tend to expand on the basis of 'physical movement’, breaking through current difficulties through innovative hardware and algorithms, and bringing users a lower threshold and highly immersive virtual world "walking" experience.

 View pdf
View pdf



The paper examines complex of Micro-expressions and Body Movement in XR social environments. It can help people find a balance between avatar precision and expression. Players, especially in Extended Reality (XR) games, may form more empathy connections but also face more conflicts due to their in-game actions. Those in -game actions often require intense social interaction. Therefore, this study will choose Star citizen and VRchat as the Example of the role play game. It focuses on facial and motion capture systems which can detect how players deal with emotional connection, and potential misunderstandings. This research addresses following key questions: In XR environment, whether lacking expressive cues weakens emotional bonds, if Player avatars with richer emotional detail in presence, whether there is a threshold for empathy, and if overly subtle expressions can cause confusion or conflict. With some role play game will Imitate the complex environment of real-world social interactions, this study will add uncertain interactions and multiple virtual identities. At the same time, trust-weighted algorithms and multi-modal expression mapping are very important method to capture realistic player feedback. The paper tells us that expressive avatars can improve empathy and immersion. However, there is a need to balance precision. Too many facial and motion details may cause players to feel confused. Therefore, in the XR environment, the technology designed to connect may also cause division and misunderstandings. The emotional connection depends not only on technology capturing micro expression and motion, but also on the balance between avatar precision and expression.

 View pdf
View pdf


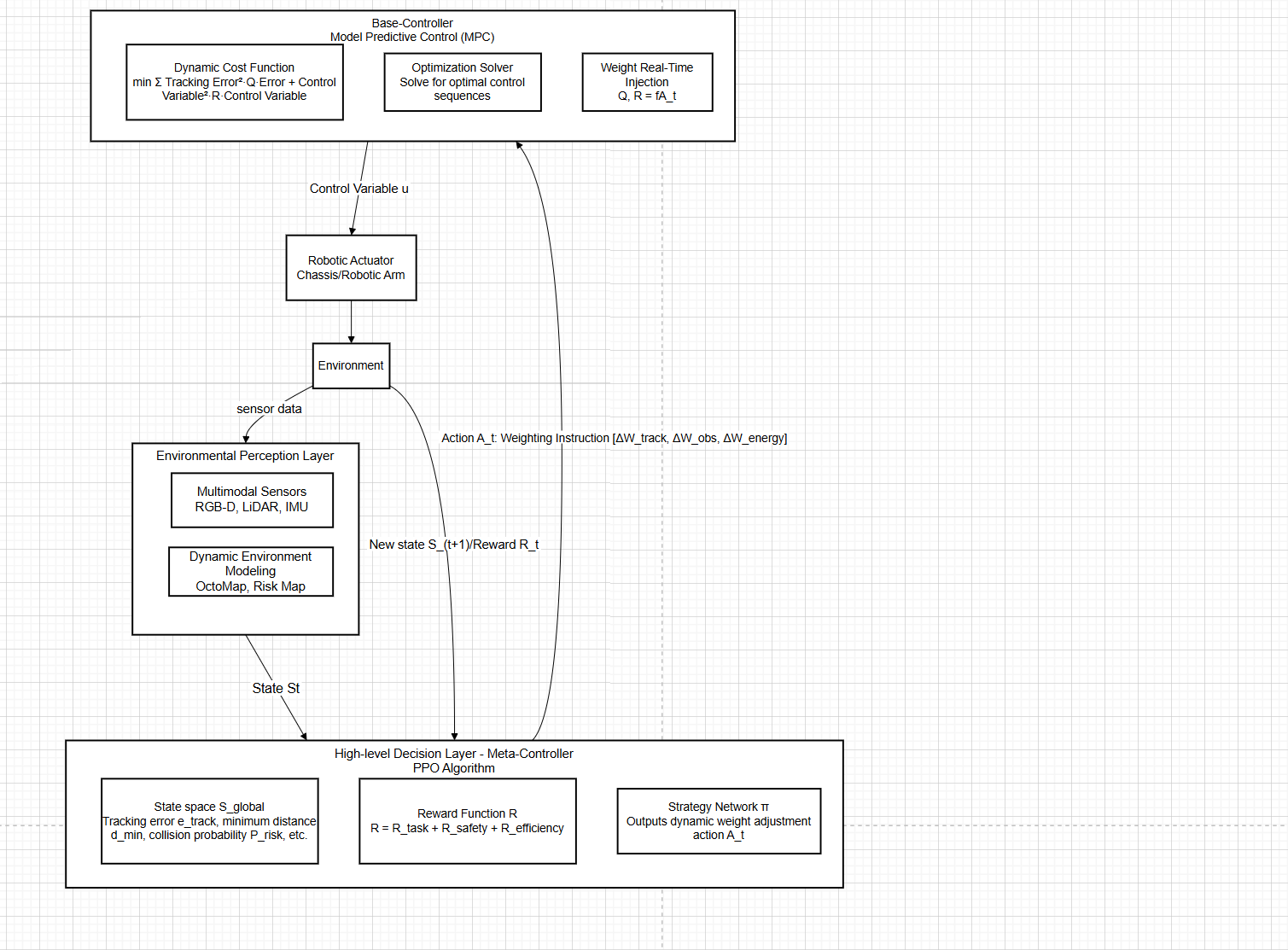
Trajectory tracking control for sorting robots in dynamic warehouse environments is challenging due to environmental uncertainty and frequent disturbances. The performance of traditional model predictive control (MPC) heavily relies on manually pre-tuned weight parameters in its cost function. This fixed configuration limits the ability to autonomously balance multiple objectives—such as trajectory tracking, obstacle avoidance, and energy consumption—in dynamic settings, thereby constraining adaptability and robustness.To address this, this paper introduces a hierarchical reinforcement learning framework for online autonomous adjustment of MPC weights. The framework consists of a high-level meta-controller and a low-level MPC executor. The high-level controller dynamically adjusts the MPC weight matrix based on the global environment state, enabling intelligent prioritization of control objectives. Comparative experiments in a high-fidelity Gazebo simulation demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms both fixed-weight MPC and PID controllers in tracking accuracy, task efficiency, safety, and energy consumption. The results validate the effectiveness of the approach and reveal an interpretable, learning-based decision-making mechanism, offering a reliable solution for high-performance robot control in dynamic environments.

 View pdf
View pdf


Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a health problem that can cause memory loss, trouble with thinking, and a decline in daily life. This health problem will bring a lot of stress to both patients and families. For a long time, diagnosis relied mainly on symptoms, but these symptoms appear late and overlap with other health problems. In recent years, a “biology first” approach has been developed, using biomarkers such as amyloid, tau, and neurodegeneration to give clearer and earlier answers. At the same time, Artificial intelligence (AI) becomes more important, for example, AI can analyze scans, speech, and clinical data. But there are still some problems, for example it is hard to make sure that everyone uses it fairly. This review brings together the current view of AD, the role of clinical and biological checks, and the growing support of AI. Its main goal is to help readers understand how diagnosis is moving from late symptom-based methods to earlier and more reliable systems.

 View pdf
View pdf


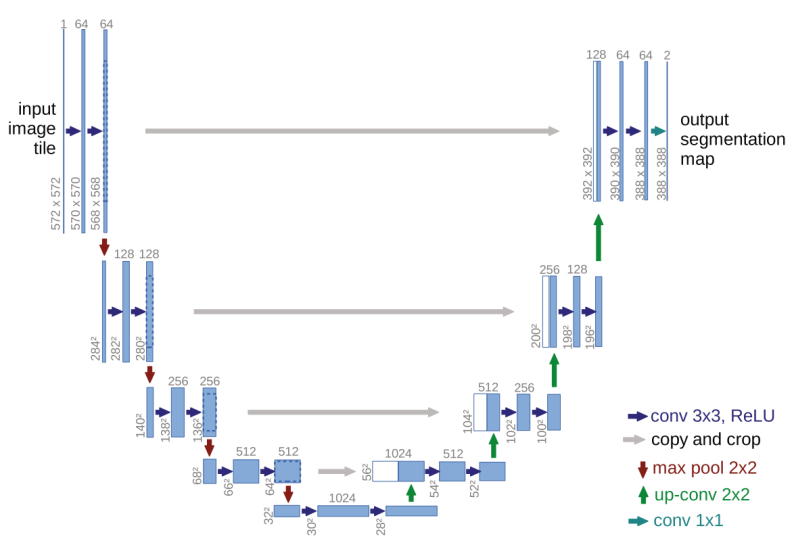
Semantic segmentation of high-resolution remote sensing imagery is pivotal for applications such as land-cover mapping, urban planning, and environmental monitoring. Since the introduction of U-Net, numerous variants have been proposed to address challenges unique to satellite data—namely, extreme class imbalance, small-object detection, and complex scene textures. This survey systematically reviews major U-Net extensions (including U-Net++, ResUNet-a, HCANet, CCT-Net, DIResUNet, CM-UNet, TransUNet, AER-UNet and U-KAN) and additional optimization techniques such as incremental learning. This study compares their architectural innovations—e.g., nested skip connections, residual or atrous blocks, multi-scale context modules, and attention mechanisms—and summarizes reported performance on standard benchmarks (ISPRS Vaihingen, Potsdam, GID, WHDLD, DeepGlobe, and GF-2). This work also identifies key factors that drive segmentation accuracy and discusses remaining challenges and promising directions for future research, including improved generalization, reduced annotation dependency, and better trade-offs between performance and computational efficiency.

 View pdf
View pdf


Deep learning (DL) is a key branch of artificial intelligence (AI). It has made remarkable progress in medical imaging, particularly in image classification and pattern recognition. In ophthalmology, the application of DLto fundus images for glaucoma assessment has become a rapidly developing research area. In recent years, this approach has represented promising results in terms of both analytical efficiency and accuracy, assisting in the differentiation of glaucoma patients from healthy eyes. This trend suggests that DL technology has the potential to improve existing diagnostic and treatment practices and optimize the clinical workflow for glaucoma diagnosis. However, challenges remain, such as a shortage of high-quality annotated data and limited model interpretability. This article reviews recent research progress on DL-based glaucoma assessment using fundus images, explores its potential clinical significance, and proposes future research directions. Through a systematic review of relevant literature, this study provides a comprehensive understanding of the application of DL in glaucoma diagnosis for both academia and clinical practice, and offers reference and guidance for future research.

 View pdf
View pdf


The rapid expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT) brings an abrupt breakthrough in intelligent homes, and allows people to live in a smarter and easier way. In this paper, some basic technologies of intelligent home based on IoT are explored, such as device communication protocols, data processing flow and smart control algorithms. Although these technologies have great potential applications in an intelligent home, there are some significant problems that need to be solved in real life. The different compatibility between devices is the biggest problem that exists now. Meanwhile, data security and protection for users’ privacy remain an important problem as well. The system energy consumption and reliability are another barrier that should be improved to satisfy the diversified interests at home. The conclusion can be made that in the future, the research topics should include standardizing techniques and specifications, improving the system security and developing machine learn ability of intelligent devices which can be matched to the intelligent home requirements. It is believed these improvements are necessary for the efficient development and wider application of smart home systems.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the context of the rapid development of electrification and intelligentization in the global automotive industry, vehicle structure design is undergoing a paradigm shift. Modern automotive structures face the increasing pressure of safety requirements and the dual pressures of improving energy efficiency and reducing emissions while extending driving range. This paper systematically analyzes the main characteristics of modern automotive structures and focuses on the technical route and key challenges of lightweighting and safety integrated optimization. The evolution of methodologies and the essential value of vehicle structural optimization are presented. Current optimization strategies mainly involve topology optimization, dimensional and shape optimization, and material selection optimization. The relevant technologies for optimization include lightweight design, crashworthiness enhancement, and manufacturing constraint consideration optimization. Main challenges include high computational cost and efficiency, multi-objective trade-offs, few experimental verifications, and difficulties in standardization and industrialization. This paper emphasizes the interdisciplinary collaboration between different disciplines.

 View pdf
View pdf


Recent developments in recommender systems have increasingly employed deep learning methodologies to confront long-standing challenges, including the modeling of intricate user–item interactions, the incorporation of temporal dynamics, and the mitigation of exposure bias. This study reviews and extends insights from four representative approaches. First, the Convolutional Transformer Neural Collaborative Filtering (CTNCF) model combines convolutional neural networks with Transformer architectures to capture both localized and long-range dependencies within user–item representations, thereby surpassing the performance of conventional Neural Collaborative Filtering (NCF). Second, the Neural Tensor Factorization (NTF) framework advances classical tensor factorization by embedding recurrent and multilayer neural components, enabling the representation of time-varying preferences and nonlinear interactions among latent factors. Third, the Deep Interest Network (DIN) introduces a local activation mechanism that adaptively models user interests in click-through rate prediction, effectively overcoming the limitations of fixed-length embeddings in capturing heterogeneous behavioral patterns; notably, this model has been deployed at scale in industrial advertising contexts. Finally, recent work addressing de-exposure bias in NCF incorporates reward signals derived from the LinUCB algorithm into the neural recommendation process, thereby enhancing both fairness and predictive accuracy by increasing the visibility of underexposed items. Taken together, these contributions illustrate the progression of neural recommender systems from static factorization paradigms toward dynamic, adaptive, and fairness-oriented frameworks, offering both theoretical contributions and practical value for the design of large-scale recommendation platforms.

 View pdf
View pdf




