

Volume 96
Published on November 2024Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Machine Learning and Automation
In recent years, with the rapid development of technology, the concept of “Smart Home” has gradually emerged into people's view., Because of its remarkable convenience, it has won the favor of many consumers in the present era. However, as the utilization of smart home devices becomes more widespread, several challenges have emerged that need to be addressed for future development. One such challenge is the compatibility problem, which has now transformed into a significant barrier hindering the development of Smart Home. Therefore, in order to bring back a truly intelligent smart home environment, it is of utmost urgency to address the compatibility problem. In this paper, the author mainly focuses on this issue. By leveraging the knowledge of IoT and transport protocols, and using Python as the research and test platform, the researcher strives to either work out or alleviate the compatibility problem within the Smart Home domain.

 View pdf
View pdf


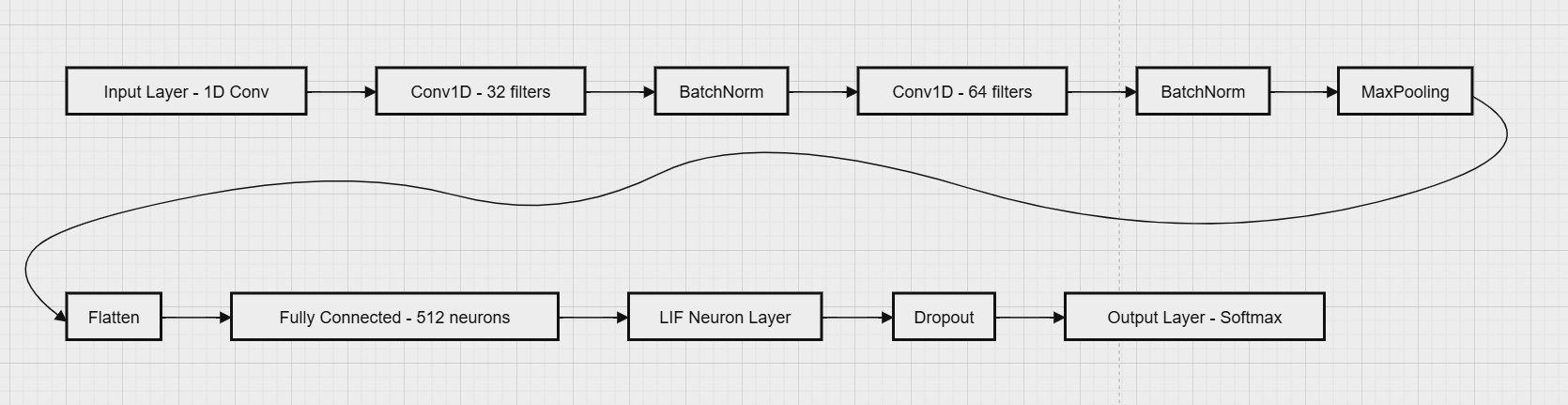
Electrocardiogram (ECG) diagnosis is pivotal in clinical practice, providing an essential means for early heart disease detection. However, traditional automated diagnostic approaches often face challenges such as limited accuracy, noise sensitivity, and inadequate real-time performance. This paper proposes a novel solution utilizing Spiking Neural Networks (SNN) to address these challenges. This method combines Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) with Leaky Integrate-and-Fire (LIF) spiking neurons, offering advantages like low energy consumption, high computational efficiency, and enhanced robustness, particularly in dealing with noise in ECG signals. The MIT-BIH Arrhythmia Dataset, a widely recognized resource for arrhythmia detection containing annotated ECG signals for various heart conditions, is utilized in this study. The results indicate that the proposed method achieves a 97.98% test accuracy, significantly surpassing traditional Long Short-Term Memory networks (LSTM)-based architectures. These findings underscore the effectiveness and potential of this approach in ECG signal analysis.

 View pdf
View pdf


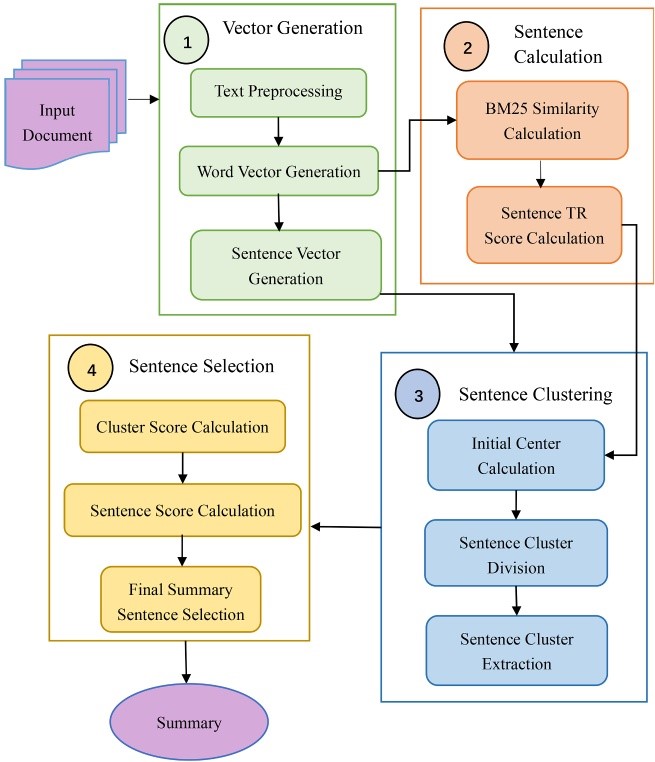
In the era of information explosion, the Internet produces a large number of text documents daily, providing rich information but also posing a challenge: how to swiftly extract key information. Traditional manual reading is time-consuming and inadequate for handling vast data. Thus, automatic text summarization technology emerges as a crucial solution. This paper reviews the application and deviation analysis of this technology across various fields, focusing on addressing shortcomings of traditional methods, such as initial cluster center selection and redundancy. An automatic text summarization method based on an improved TextRank algorithm and K-Means clustering is introduced. Existing methods often struggle with inaccurate initial clustering center selection and high summary redundancy, especially with long texts, resulting in summaries that fail to reflect core content accurately. Furthermore, the widespread use of pre-trained language models introduces potential biases that can propagate to downstream tasks, affecting summary accuracy and impartiality. To address these issues, this paper proposes an innovative automatic text summarization method that optimizes initial clustering center selection and clustering refinement strategies to enhance summary accuracy and readability. Additionally, it discusses name-nationality bias in pre-trained language models and its propagation in text summary tasks, offering a theoretical foundation and practical guidance for developing a more just and reliable Natural Language Processing (NLP) system.

 View pdf
View pdf


The rapid advancement of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) technology underscores the essential role of PID (proportional-integral-derivative) control in ensuring flight stability, particularly through precise motor speed adjustments. Thus, this paper systematically analyzes the fundamental principles and limitations of traditional PID control, further highlighting its insufficient adaptability to dynamic external conditions, which includes load fluctuations and wind disturbances. In response to these challenges, it explores adaptive control strategies such as self-tuning PID and fuzzy logic PID, points out how these advanced methods can effectively improve flight stability by dynamically adjusting control parameters, and demonstrates their superiority over traditional PID through comparative analysis. In addition, the paper anticipates future developments in UAV control systems, thereby emphasizing the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies into PID control. And this integration seeks to optimize control strategies and markedly enhance the autonomous decision-making capabilities and adaptability of UAVs. Meanwhile, the paper also predicts the development trend of hybrid control systems, that is, combining PID with other advanced control methods (such as linear quadratic control) to enhance the overall control capabilities of UAVs. In short, it underscores the necessity for continuous innovation and in-depth research in response to the dynamic flight environment and the diverse mission requirements.

 View pdf
View pdf


This study aims to compare the performance of regression and classification machine learning models in crop prediction by analyzing data from IoT-driven agriculture. Linear regression and random forest regression models were used to predict the percentage of root growth dry matter, while logistic regression and support vector machines were employed to classify crop production regions. To enhance model interpretability, the LIME tool was applied to analyze feature importance. The experimental results demonstrate that the models perform well in terms of prediction accuracy, and LIME provided clear feature explanations, helping identify the variables with the greatest impact on prediction outcomes. This research offers data-driven insights for optimizing resource management in smart agricultural systems.

 View pdf
View pdf


In today's digital era, where waves of digitization sweep across the globe, voice, as one of the fundamental forms of human communication, is being captured, transmitted, and stored in unprecedented ways. From everyday phone conversations to remote conferences, from voice commands in smart homes to the digital distribution of musical compositions, voice data has become an indispensable part of the digital landscape. However, as these applications proliferate, concerns over the security and privacy of voice data have become increasingly prominent. This article delves into the innovative applications of ArtificialIntelligence (AI) in the realm of voice encryption, aiming to construct an efficient and secure shield for the transmission and storage of voice data.

 View pdf
View pdf


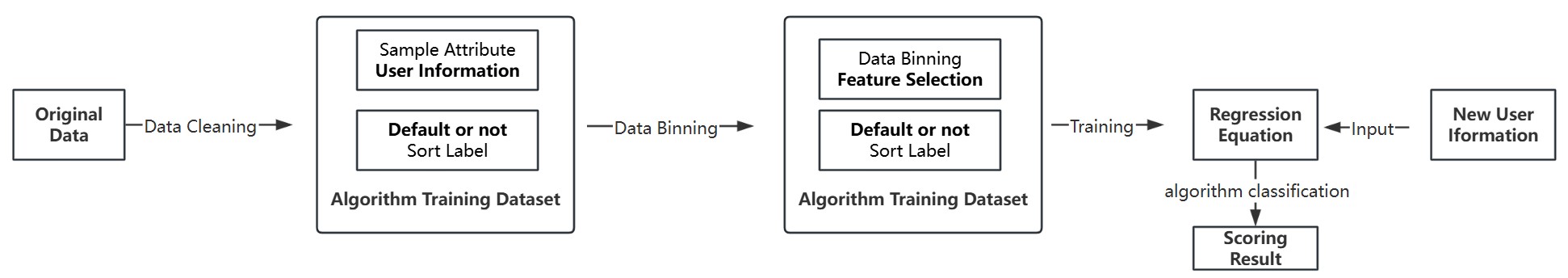
As credit transactions become more prevalent, financial institutions require effective methods to assess credit risk and reduce the likelihood of borrower default. In the U.S., the Fair Isaac Credit Organization (FICO) score is widely used by banks and insurers to evaluate personal creditworthiness. This paper aims to develop an automated credit scoring tool based on the FICO system to help financial institutions improve risk assessment. The paper leverages the random forest algorithm for data preprocessing and feature engineering to extract key variables, such as the borrower's financial status and credit history. To ensure data stability and interpretability, Information Value and Weight of Evidence techniques are applied to process these variables. Additionally, the Sigmoid function is used to map the model output to a range between 0 and 1, making it suitable for generating credit scores. This random forest algorithm helps handle non-linear relationships and missing data, while cross-validation enhances the model’s generalization ability. After training, the paper achieved an automated credit scoring system, closely aligned with the FICO scoring system. The model’s Area Under the Curve (AUC) value reached 0.84, indicating strong predictive accuracy and reliability. This tool enables financial institutions to more accurately assess credit risk, offering a robust, data-driven approach to improve decision-making and risk management.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper uses advanced techniques for data visualization in order to provide clear guidance for both consumers and manufacturers within the breakfast cereal industry. The research primarily focuses on analyzing key characteristics such as caloric content, fiber content, and sugar levels across various renowned brands of cereal including Larana Inc., General Mills, Kellogg's, and Nestlé. By combining the powers of Python as a programming language along with the Pandas, Matplotlib, and Seaborn libraries, this analysis delves into consumer trends, general industry patterns, and nutritional concerns. Through a meticulous examination of these factors, this study aims to provide valuable insights that can aid stakeholders in making informed decisions towards promoting healthier product development. The findings obtained from this research act as a testament to the critical function that data-driven insights play in the formation of consumer decisions toward more nutritious options. These results not only contributes important knowledge for stakeholders but also pave the way for potential innovations in data analytics within the cereal market. Overall, by employing cutting-edge tools and methodologies in data visualization combined with an objective approach to examining relevant characteristics of breakfast cereals from prominent brands, this paper strives to enhance understanding within the industry while facilitating advancements in data analytics practices.

 View pdf
View pdf


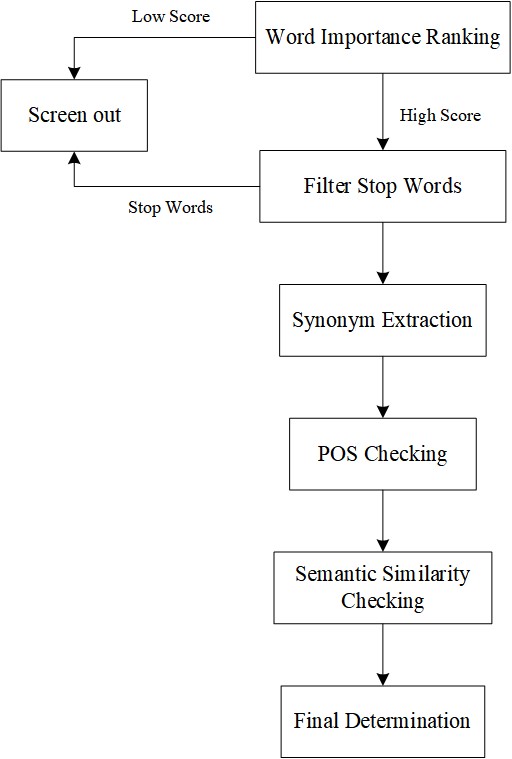
With the rise of neural networks, the need for accuracy, robustness, and security has increased. Research has shown that small, carefully crafted perturbations, known as adversarial examples, can deceive models and lead to incorrect predictions. Current research focuses on the image domain, while there is a notable lack of exploration in the text domain, due to its discrete nature. This paper reviews adversarial attack techniques and defense strategies in text-based neural network models, aiming to improve the security and resilience of these models in practical applications. Adversarial examples, which can deceive models with small perturbations, expose vulnerabilities in their robustness and security. Techniques such as TextFooler focus on synonym replacement for generating adversarial examples, while Text Random Smooth (Text-RS) enhances defense through adaptive noise strategies. The research of search space aims to explore the feature of that, proposing search space for Imperceptibility (SSIP) and Search Space for Effectiveness (SSET) to estimate the different attack methods. Furthermore, the Chinese Variation Graph Integration (CHANGE) method improves the resilience of Chinese language models by leveraging variation graphs. These advancements highlight the importance of developing effective generation and defense mechanisms for adversarial examples in text processing models. Future research should enhance adversarial example techniques, explore efficient defense strategies, and investigate transferability to improve the security and robustness of text processing models.

 View pdf
View pdf


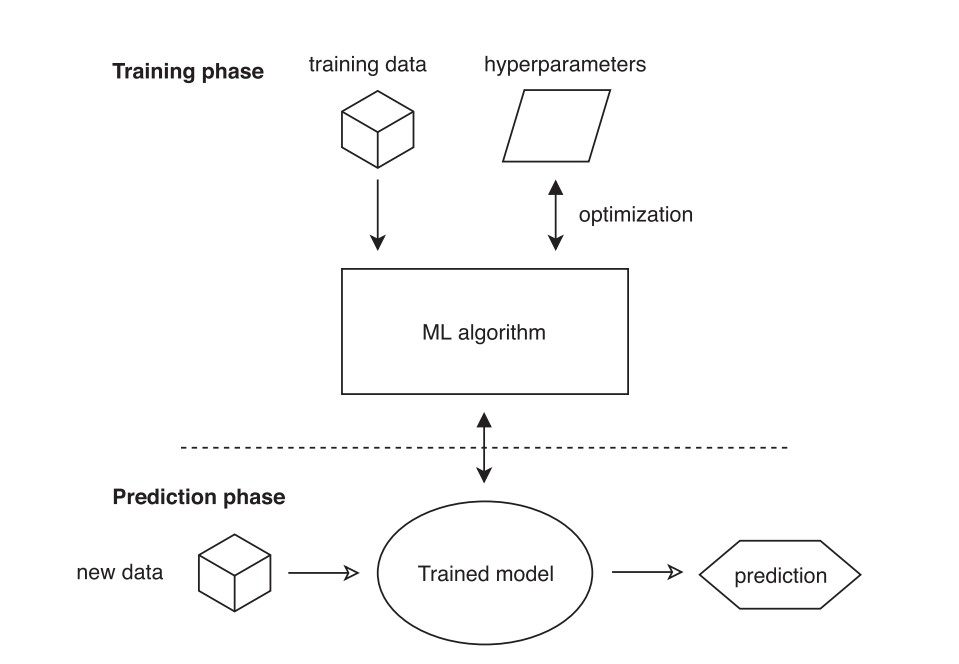
As machine learning is applied to more and more high-tech fields, optimizing tasks has become a key step in the pursuit of more efficient and accurate artificial intelligence. Thes study will present an overview for machine learning and address the implementation of distributed machine learning, including cleaning the collected datasets, selecting different models, and discussing the influence of loss function types (L-smooth and non-L-smooth) on error convergence under the premise of increasing the number of iterations. Experiments show that the two types of loss functions have opposite results. For the L-smooth loss function, larger iterations reduce the error convergence. Regarding to the non-L-Smooth loss function, larger iterations increase the error convergence. This research also adjusted other model parameters and analyzed them, which has more meaningful implications for the parameter selection of machine learning model training in the future, and one can optimize error convergence by changing the type of loss function, so that improve the efficiency of scientific research.

 View pdf
View pdf




