

Volume 142
Published on April 2025Volume title: Proceedings of MSS 2025 Symposium: Automation and Smart Technologies in Petroleum Engineering
This paper proposes an enhanced TransFormer-based algorithm for key-frame action recognition in basketball shooting. The research addresses the challenges of accurate temporal localization and feature extraction in complex basketball environments through architectural innovations in deep learning models. The proposed approach integrates a multi-scale feature fusion mechanism with an improved spatio-temporal attention structure, enabling robust recognition of basketball shooting actions across varying conditions. A novel position encoding scheme is introduced to better capture temporal relationships in shooting sequences, while the enhanced attention mechanism facilitates more precise key-frame identification. Experimental evaluations on basketball shooting datasets demonstrate that the proposed model achieves 92.8% accuracy in action recognition tasks, outperforming existing approaches by 4.3% in mean average precision. The architecture maintains computational efficiency while improving recognition accuracy, processing video sequences in real-time at 30 frames per second. Ablation studies confirm the effectiveness of individual components, with the spatio-temporal attention mechanism contributing the most significant performance gains. The system demonstrates robust performance across different shooting styles and environmental conditions, making it suitable for practical applications in basketball training and analysis.

 View pdf
View pdf


Concrete is the world's most widely used building material, its main advantage is excellent compressive strength, but there is also brittleness, low tensile strength, poor cracking resistance, and other shortcomings. To solve these problems, researchers have put forward a variety of methods for the modification of concrete materials, among which increasing the toughness and crack resistance of concrete by adding plant fiber has become an important research direction. As a natural, renewable, and environmentally friendly material, plant fiber has a high specific strength, specific stiffness, and good cohesion, which can greatly improve the mechanical properties and durability of concrete.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the continuous expansion of the power system scale and the increasing growth of electricity demand, accurate load forecasting is of great significance for the safe, stable operation and economic dispatch of the power system. Traditional load forecasting methods have certain limitations in handling complex load data and are difficult to meet actual needs. This paper proposes a load forecasting method based on the Quantum Particle Swarm Optimization(QPSO) algorithm and the Long Short-Term Memory(LSTM) network. Firstly, the load data is pre-processed, including normalization and dataset division. Then, the LSTM model is used to learn the time-series characteristics of the load data. At the same time, the QPSO algorithm is adopted to optimize the hyperparameters of the LSTM model to improve the prediction performance of the model. Through practical example analysis, it is shown that this method can effectively improve the accuracy and stability of load forecasting. Compared with traditional methods, it performs better in handling complex load data and can provide a more reliable decision-making basis for the planning and operation of the power system.

 View pdf
View pdf


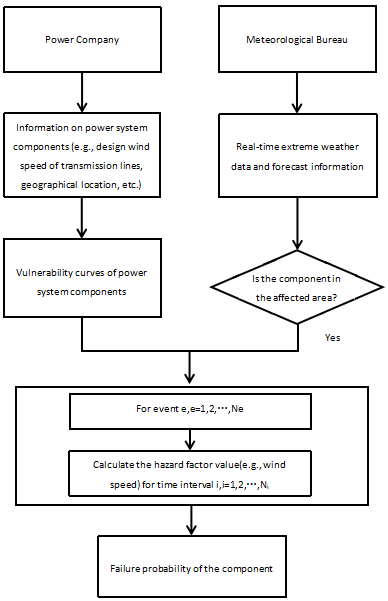
The increasing frequency of extreme weather events caused by climate change, such as typhoons, tornadoes, and ice storms, not only affects the stability of power loads but can also cause severe damage to power infrastructure, leading to frequent large-scale power outages. To enhance the risk resilience of power systems, effective reserve capacity configuration and dispatch strategies are necessary. Therefore, studying the optimization of reserve capacity under extreme weather conditions is of great significance. This paper uses a literature review research method to analyze the impact of extreme weather events on power system components, assess the failure probability of system components during extreme weather, and optimize the reserve capacity accordingly. Research on the optimization configuration and dispatch of reserve capacity under extreme weather conditions can enable rapid response during extreme weather events, reduce losses caused by weather, and support the sustainable development of power systems.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the popularization of the Intelligent driving, new energy vehicles have gradually replaced the traditional fuel cars. The environmental perception of light detection and ranging (LiDAR) in intelligent driving is the vital safeguard of drivers and vehicles themselves. Nowadays, LiDAR has been widely applied in the field of unmanned driving, which receives the information of surroundings through reflected Laser beam sent by its emitters. This article analyses the meanings and uses of LiDAR through the point cloud detection technology, combining with the application cases of LiDAR in electric vehicles. This paper finds that the effects of LiDAR are measuring the distance of the obstacles from the vehicles and reminding the drivers to pay attention to their driving safety. This technology has critical effects of vehicle security and driving safety. This study promotes the production and utilization of electric vehicles, helping to address the energy and environment issues and making contribution to the LiDAR technology.

 View pdf
View pdf


The Naive Bayes algorithm uses the theorem of Bayes to filter spam emails, achieving good filtering results. The improved Bayes algorithm addresses the assumption of "feature independence given the class" in Naive Bayes algorithm, allowing for a broader application range. This paper reviews the main content and representative achievements of both the Naive Bayes algorithm and the improved Bayes algorithm, and analyzes the advantages and disadvantages of each method. This study finds that the Naive Bayes algorithm has a limited application range due to the assumption of "feature independence given the class" while the improved Bayes algorithm effectively solves this problem and it has better applicability. This paper aims to help researchers engaged in spam filtering better understand and leverage the potential of the theorem of Bayes in spam filtering, providing a summary reference to promote technological innovation in related fields and better problem-solving, as well as facilitating the understanding of other readers and the application of Bayes filtering methods.

 View pdf
View pdf


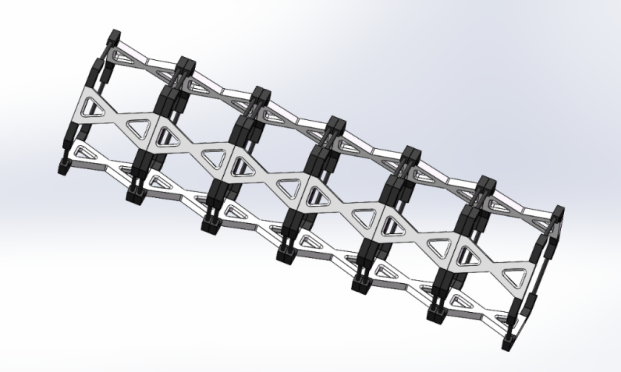
Bioinspired robots have been proposed and developed for years with their practicality in solving various issues, such as dangerous experiments, extremely narrow exploration sites, and delicate surgeries. Many existed natural mechanisms like elephant trunk, pangolin squama, and inchworm have been analyzed and imitated as machinery constructed by workpieces. The article demonstrates a device that improves the performance of the common bioinspired robot arm. This device was inspired by both common bioinspired robot arms and soft-legged pneumatic robots. The design combined the advantages of two types of robotic machinery under the condition that the two types of machinery both contain their own insufficiencies. This study utilized SolidWorks to construct the idea as a 3D model, which was also convenient to operate detailed adjustments. Ansys was used to analyze and compare the mechanical data of the common robot arms and the improved robot arms, which helped to get the conclusions. The study also analyzed various articles that summarized or explored bioinspired robots, and their experimental processes. The possible scenes robot arms might encounter were inspired by the experimented conditions and drawn by Adobe Illustrator. The design was demonstrated to be successful in that the improved arm’s data on longitudinal deformation and normal strain were smaller than the common arm’s under the same force.

 View pdf
View pdf


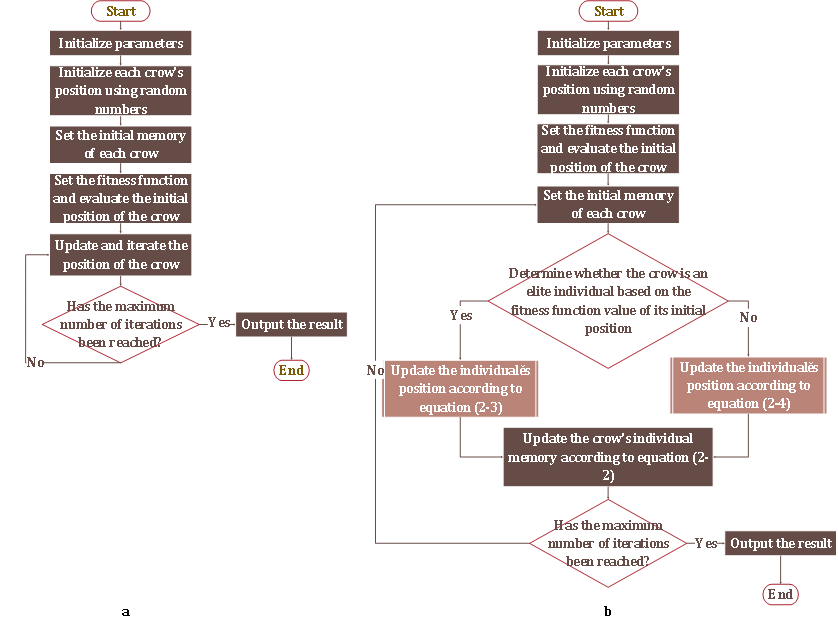
Under the condition of partial shading, the Power-Voltage curve of photovoltaic array presents a characteristic of multi-peak, when conventional maximum power point tracking (MPPT) algorithms, like Perturb and Observe method (PO), fail to track efficiently. Crow search algorithm (CSA) has outstanding global search capability, because of which it is used to track maximum power point under the condition of partial shading. But it also has the problems in local optimum and oscillating amplitude. To solve those problems, both of an auto judgment of power output and an optimization-orientation guided by elite individuals are introduced. The results presented in MATLAB/Simulink that the application of improved CSA in MPPT can track efficiently with lower level of oscillating amplitude.

 View pdf
View pdf



In the field of computer vision, low-light image enhancement is crucial for tasks such as target tracking, detection and entity segmentation. In recent years, although supervised learning-based low-light image enhancement methods have achieved promising results, they still have problems such as relying on a large amount of paired data and high computational cost. To solve these problems, unsupervised methods such as Zero-DCE have emerged, however, through practical observation, the model has bias for color processing. Therefore, in this paper, the color loss function of Zero-DCE model is improved, and experiments are carried out on LOL and VE-LOL-L datasets to compare the performance of the model before and after the improvement, as well as ablation experiments and hyperparameter selection experiments. The results show that the improved model significantly improves the image reconstruction quality and structural similarity, effectively improves the low-light image enhancement effect, and provides a new direction for subsequent related research.

 View pdf
View pdf


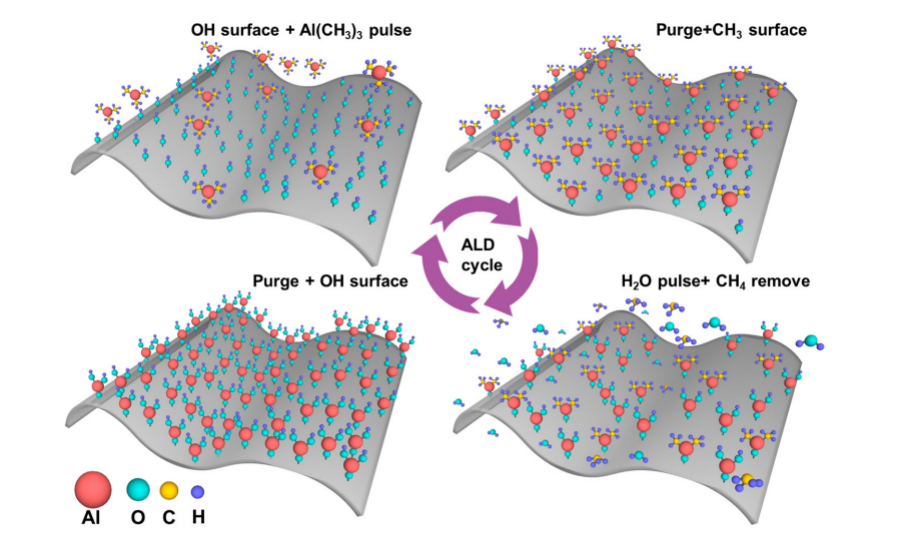
Field Effect Transistors (FETs) are at the core of modern semiconductor technology, and the miniaturization of their size has posed challenges such as short-channel effects for traditional manufacturing processes. This paper reviews the principles of three novel semiconductor fabrication techniques: Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD), Metal-Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition (MOCVD), and Pulsed Laser Deposition (PLD). It analyzes their role in optimizing FET characteristics and provides directions for overcoming the bottlenecks of traditional processes, which will aid in advancing semiconductor technology.

 View pdf
View pdf




