

Volume 159
Published on January 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Business and Policy Studies
The security and stability of the global food market are closely linked to the long-term healthy development of the global economy. This paper mainly examines the basic operational characteristics of the food market and the main development trends in food trade. The main research findings are as follows: (1) In terms of the global food supply structure, current supply fluctuations are increasing, demand is steadily growing, and food prices initially rise before declining; (2) The total volume of global food trade is continuously increasing, the concentration of exports may continue to rise, and the significance of major international grain merchants in global food trade is becoming increasingly prominent; (3) Geopolitical conflicts disrupt the stability of food supply, trade protectionism impacts the stability of food market trade, and fluctuations in global monetary policy affect the price stability of the food market. To address the various challenges and difficulties facing global food security, it is recommended that governments enhance macro-control of the food market, improve financial support for food trade, cultivate internationally competitive large-scale grain merchants, and strengthen international coordination of national food regulatory policies.

 View pdf
View pdf


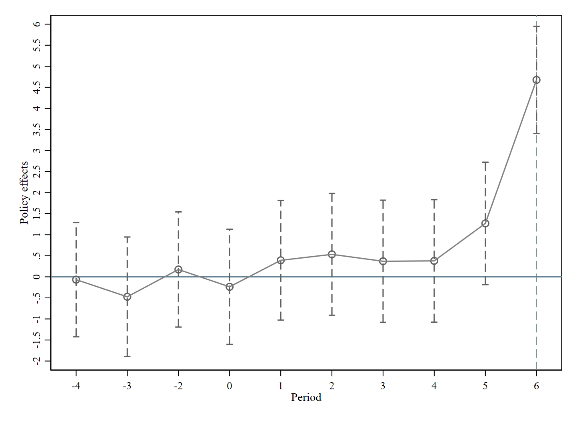
This study analyzes the influence of smart city development on cross-border venture capital investments. The author employs panel data from 280 prefecture-level and higher cities in China, spanning 2009 to 2021, utilizing the difference-in-differences (DID) model and the propensity score matching difference (PSM-DID) method. The results indicate that the construction of smart cities significantly promotes the inflow of cross-border VC, specifically reflected in the increase in both the quantities and values of cross-border VC inflows, and this effect is characterized by long-term persistence and a certain degree of lag. Upon evaluating spatial spillover effects, the development of smart cities continues to exert a substantial positive influence on local cross-border venture capital inflows, while simultaneously creating a siphon effect on adjacent cities. In megacities and megalopolises, the development of smart cities markedly increases the influx of cross-border venture capital, but this impact is less pronounced in big and medium-sized cities. In cities with elevated levels of research and education, the development of smart cities significantly influences cross-border venture capital inflows.

 View pdf
View pdf


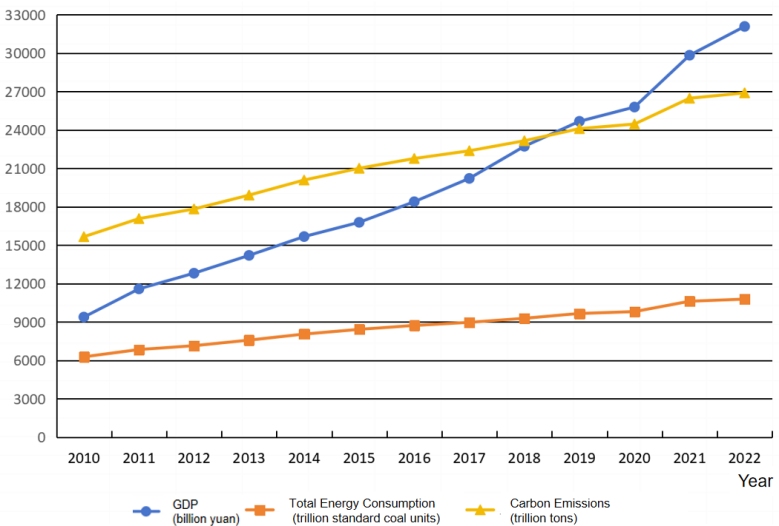
As global climate change intensifies, carbon emissions have become a paramount concern for policymakers and researchers. These emissions undermine ecosystem integrity and pose considerable obstacles to economic development and long-term sustainability. As the world’s largest carbon emitter, China faces substantial pressure to mitigate its emissions. Jiangxi Province, a critical region in the country, has experienced rapid economic growth, driving significant research into the relationship between energy consumption and carbon emissions. This paper examines data from 2010 to 2022, including Jiangxi’s GDP and total energy consumption, to estimate carbon emissions. In addition, through rigorous correlation and regression analyses, a significant positive association between carbon emissions and economic growth is identified, culminating in the development of a univariate regression model to quantitatively assess this relationship. Employing the Tapio decoupling elasticity method, the study evaluates the dynamic decoupling relationship between carbon emissions and economic growth, revealing a state of weak decoupling. The results indicate that despite a reduction in carbon intensity relative to economic growth, Jiangxi’s total carbon emissions continue to rise. To achieve absolute decoupling, the province will need to implement more effective and comprehensive policy measures.

 View pdf
View pdf


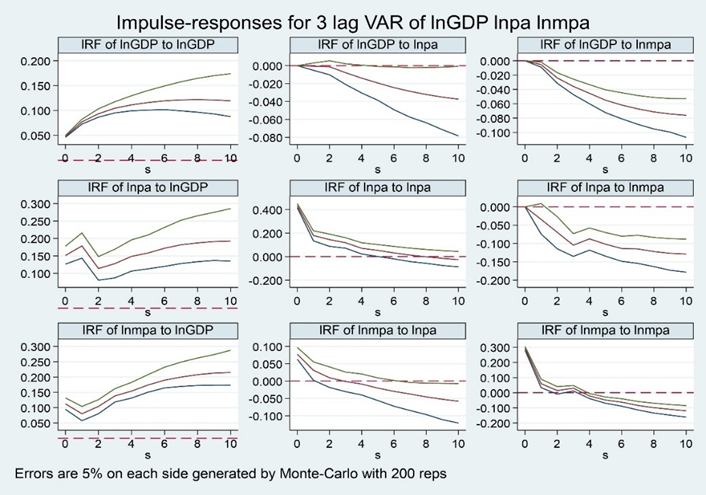
Using data from 1992 to 2021, this paper examines the dynamic relationship between economic growth and green innovation in China by applying a panel Vector Autoregression (VAR) model along with the system-Generalized Method of Moments (GMM) procedure. We break down green innovation into two main components: the number of green invention patents and the number of green utility model patents, allowing for a more detailed analysis of each type’s impact. The findings reveal a significant dynamic interaction between economic growth and green innovation. Specifically, economic development demonstrates a strong, positive effect on green innovation, suggesting that as the economy grows, there is increased support for eco-friendly innovations. However, the results also indicate that green innovation exerts a negative effect on economic development, potentially due to the initial costs and shifts in resources required for sustainable initiatives. This complex interplay sheds light on the challenges and opportunities for sustainable growth in China.

 View pdf
View pdf



Using 2007-2017 panel data from 31 provinces,this paper analyzes the impact of high-standard farmland construction policies on agricultural carbon emissions in China. A continuous differential model reveals: (1) These policies consistently reduce agricultural carbon emissions, with significant effects confirmed by robustness checks. (2) Reducing agricultural chemical usage intensity is a key factor in carbon reduction. (3) The policy's effectiveness differs by region, being less pronounced in major grain-producing areas and more evident in non-major areas, and more significant in regions with strong land circulation. Therefore, local governments should adopt differentiated strategies, maintain policy independence, and focus on reducing chemical usage to promote low-carbon and green agricultural development.

 View pdf
View pdf


China's aging population society has entered a high-speed deepening stage, promoting energy saving and emission reduction, realizing low carbon development history is an important strategic task in our country. On the Basis of panel data since 2011 to 2021, using an intermediate effect model, this paper studies the relations among the population aging, industry structure upgrading as well as rationalization and the emission of carbon dioxide. The results indicate that aging exerts a significant positive impact on carbon emissions. The influence of population aging on carbon emissions is inverted U shape. When aging reaches a certain level, the influence on carbon emissions has a nonlinear feature of decreasing marginal effect. The aging can exert a prominent influence on carbon emissions in the regions through upgrading and rationalization of the industrial structure. That influence about population aging on carbon emissions is remarkable in the region. Therefore, promoting the optimization process of industry structure forced by population aging contributes to realizing "reduction effect of carbon emissions" under the background of population aging.

 View pdf
View pdf


Technology-driven economy is leading the way in the global technological and industrial revolution, emerging as a significant catalyst for the growth of new productive forces. The Central Economic Work Conference emphasized the need to actively foster new industrialization, advance technology-driven economy, and accelerate the development of artificial intelligence. Additionally, technology-driven economy considerably alters the green transformation and upgrading of high-pollution industries. In this context, quality-driven audits offer essential oversight and management throughout this transition. The research focuses on listed firms in high-emission industries over the period 2012 to 2022, analyzing how digital transition contributes to the advancement of enterprise quality. The findings demonstrate that digital transition significantly fosters quality-driven growth, with audit quality serving as a positive moderating factor between digital transition and corporate development. These results not only provide valuable insights into improving total factor productivity and leveraging digitalization's multiplicative and additive effects on economic progress but also offer important guidance for traditional enterprises aiming to balance economic growth with environmental sustainability during their digital transition journeys.

 View pdf
View pdf


This study examines the effects of digitalization on exports of green products and addresses the mechanisms of action and regional heterogeneity using provincial panel data from China from 2012 to 2016. The findings of the study indicate that the growth of the digital economy significantly boosts exports of green products. At the same time, this promoting effect exhibits regional heterogeneity, specifically significant in the eastern regions but not significant in the central and western regions. On this basis, this paper continues to use a mediation effect model for analysis. Further research has found that digitalization can expand green product exports by promoting green technological progress and reducing trade costs. The research in this paper has certain practical significance for deeply understanding the economic and environmental effects brought by digitalization and exploring new forms of synergistic development between digitalization and greening. It also provides a possible basis and inspiration for further promoting the construction of the digital economy and optimizing China's foreign trade structure.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the rapid development of Internet technology and the widespread popularity of social media platforms, the purchasing behaviour patterns of Chinese consumers have changed significantly. Consumers can easily obtain rich product information and shopping channels through social media platforms, while paying more attention to the personalisation, emotionality and value resonance of products. Based on this, this paper aims to explore the changes in Chinese consumers' purchasing behaviour patterns and their impact on fashion brands' marketing strategies in the context of the development of Internet technology and social media platforms through literature review and case study analysis, so as to provide fashion brands with effective marketing strategy suggestions. It was found that KOLs significantly influence consumers' purchasing decisions, and the interactive experience on social media platforms closely shapes consumer brand loyalty. Through a case study, this paper further reveals how a fashion brand successfully increased brand exposure and consumer engagement by cooperating with KOLs through social media platforms. Fashion brands should make full use of the influence of social media platforms and KOLs to innovate their marketing strategies in order to meet consumers' personalised needs and enhance brand competitiveness and market share.

 View pdf
View pdf


In agricultural production, agricultural non-point source pollution threatens the safety of water supply and food safety, restricts the sustainable development of the agricultural economy and rural ecological environment, and is the bottleneck of agricultural development in China. To explore the impact of this situation on the real income of rural households, the paper is based on the data from China Family Panel Studies (CFPS) from 2014 to 2018. With the pollution status in agricultural production as the explanatory variable and the total value of household agricultural and sideline products as an explanatory variable, a fixed effect model was established to estimate the influence of fertilizer and pesticide application on labor income level. The results show that the income brought by pesticide and fertilizer input is low efficiency, and some farmers have achieved high yields with low input. In addition, the education level of the agricultural population and the size of the family had no significant effect on this. Considering the output problem, the application of pesticides and fertilizers is necessary, but the cognition that pesticides and fertilizers can increase crop yield and income makes the application of pesticides continue to increase, which is not conducive to the increase of agricultural output value. It is necessary to attach importance to new methods of increasing agricultural production based on the application of small amounts of fertilizers and pesticides and use technological reform and professional agricultural education to promote the rational use of pesticides and fertilizers and achieve rapid development of agriculture.

 View pdf
View pdf




