

Volume 8
Published on November 2023Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Modern Medicine and Global Health
The rising dependency on video games is increasingly posing substantial social and therapeutic challenges and can be diagnosed as a disease. Extensive research in the past has explored the relationship between game addiction and various mental problems, but there is limited research in this area in China’s cultural environment. This study explored the impact of depression, aggression, and perceived stress on Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD) among young adults in China with Spearman analysis and multiple linear regression. This paper hopes to contribute to solving the increasingly common IGD (Internet gaming addiction). Findings revealed a positive correlation between depression, aggression, and IGD, with both depression and aggression serving as significant predictors. Yet, there wasn’t a significant correlation between perceived stress and IGD. The model elucidates 20.5% of the variance in gaming dependency, underscoring the multifaceted nature of IGD and hinting at the presence of a myriad of other contributing determinants. These results underscore the importance of considering mental health in identifying and addressing IGD, while also highlighting the need for further research, particularly regarding cultural differences in stress coping mechanisms and deciding the causal relationship between mental issues and IGD.

 View pdf
View pdf


Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a highly lethal type of lung cancer and the current therapeutic challenges remain daunting. Alkaloids have become a compelling area of research due to their diverse structures and wide range of biological activities and are considered as potential antitumor agents. In this paper, we review the research progress of different classes of representative alkaloidal actives in recent years in terms of their anti NSCLC effects, with a view to provide a reference for alkaloidal actives in anti NSCLC research.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the development of the times, the high intensity of work and pressure in the workplace has led to more and more people in the workplace experiencing major and minor health problems. Although work is important, but not at the expense of health. Only with a healthy body and good mental state, people can do better outstanding work. This paper focuses on the impact of different working conditions on the health of the population, focusing on the impact of overwork, lack of daily exercise, high-pressure working environment, irregular work patterns and other working conditions on the population. It finds that all of the above will lead to the emergence of various types of physiological or psychological illnesses, which affect the daily life of the population as well as the expected life expectancy, and at the same time, these undesirable factors will lead to burnout and even affect the social development of the population. At the same time, these adverse factors also lead to burnout and even affect the social development of the population. In response to these problems, this paper has looked for programs and interventions that may be able to address this situation. It is hoped that more people will pay attention to the health problems caused by poor working conditions.

 View pdf
View pdf


Since the discovery of antibiotics, antibiotics have been developed and used in large quantities, and the misuse of antibiotics has caused the problem of bacterial resistance to become more and more prominent, with an increasing number of drug-resistant bacterial species, a weakening of the unit effect of antibiotics, and a constant increase in the dose of antibiotics, which has greatly endangered human health and production and life. Most of the natural antibiotics come from natural components of plants and animals, which have been vigorously developed and applied in recent years due to their various antibacterial mechanisms, good antibacterial effect, not easy to produce drug resistance, and little harm to human body. In this paper, it will summarize some of the antibacterial mechanisms of natural antibiotics, such as antimicrobial peptides, alkaloids and flavonoids, and the mechanism of the above natural antibiotics to reduce drug resistance. Additionally, based on the research on the application of natural antibiotics in recent years, it will put forward new ideas on the intervention of natural antibiotics in the treatment of common infections.

 View pdf
View pdf


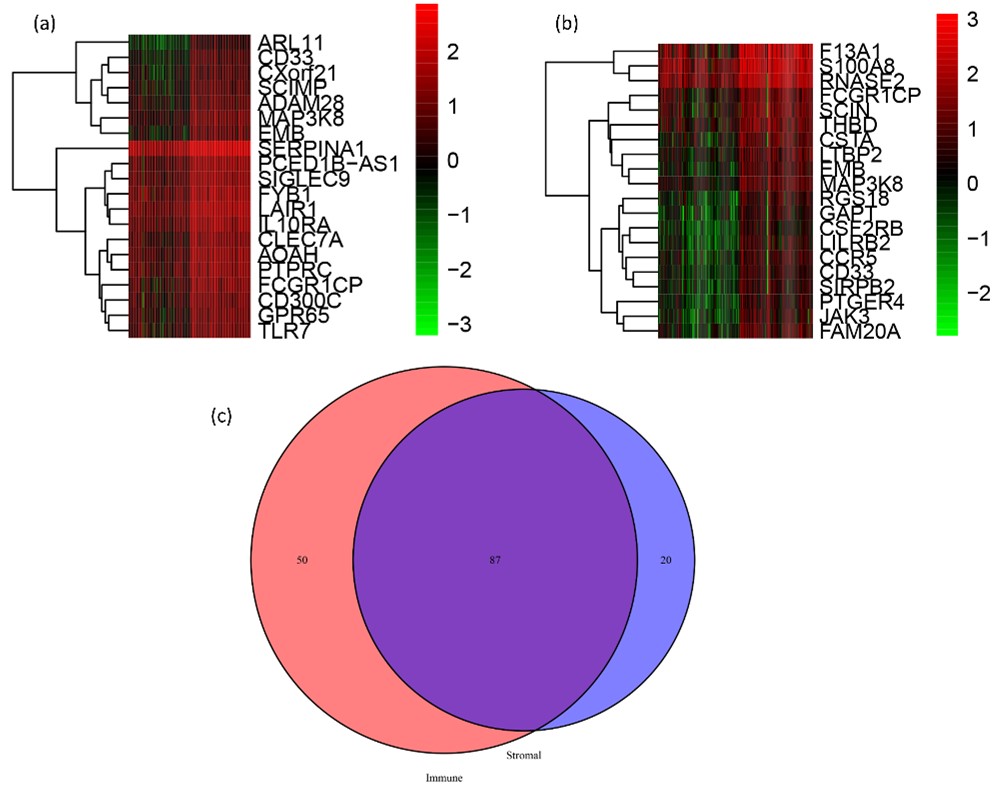
Glioblastoma(GBM), as a common kind of brain cancer, has a poor prognosis and a recurrence rate of nearly 100 percent. Tumor immune microenvironment is a crucial factor for glioblastoma progression. Some prognostically relevant genes in the immunologic microenvironment of glioblastoma remain to be further explored. This article aims to ascertain genes involved in the immune microenvironment of glioblastoma, and this topic has not been identified before. R version 4.2.1 and the appropriate packages were used for all analyses in this paper. Relevant transcriptomic data for GBMs as well as clinical data were extracted from immune score data in the TCGA database, and stromal score data were acquired from this URL (http://www.cbioportal.org/). Differentially expressed genes were obtained from immune score data and Stromal score data. After intersections of all these genes, the PPI interaction network was applied. According to functional analysis, these genes are intensively distributed in immune-related pathways. Eventually LncRNAs co-expressing with immune-related genes were positively identified. We characterized genes related to the GBM tumor microenvironment not previously identified in similar studies, as well as some lncRNAs that co-expressed with these immune genes

 View pdf
View pdf


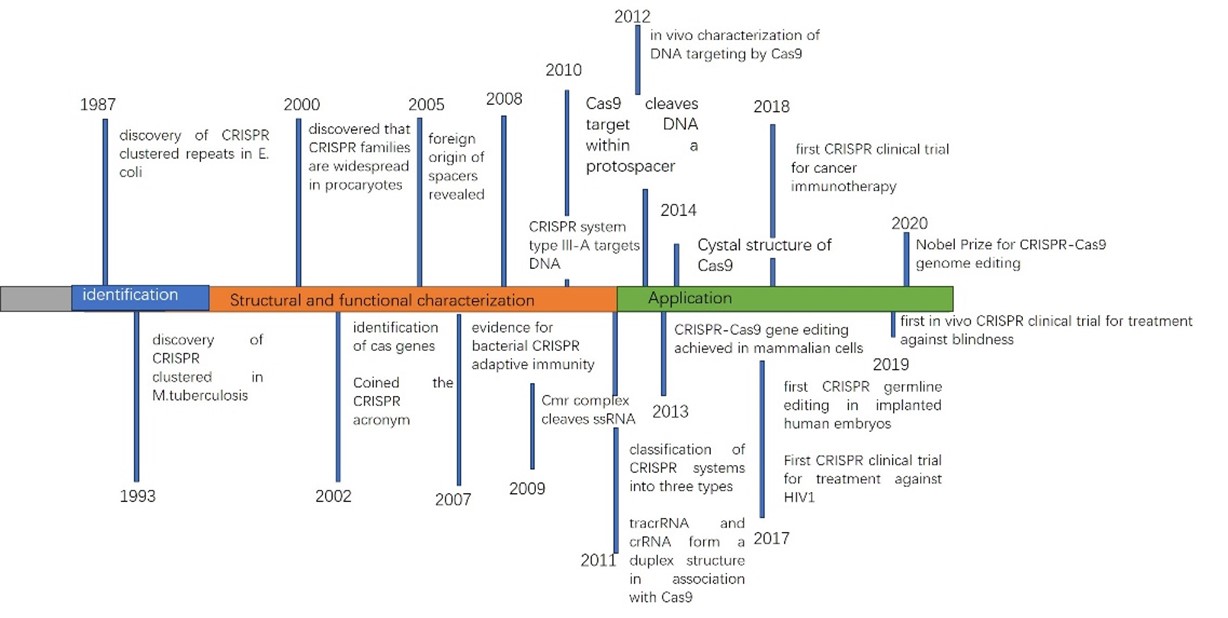
Mosquito-borne diseases are a threat to about half of the world’s population, the harm caused by it has remained serious in recent years. However, traditional methods of insecticide and environmental control have not completely solved the mosquito problem, and many times they come with certain side effects on environment. At the biological and genetic level, it may be possible to find safe and sustainable ways to alleviate the burden of mosquito-borne pathogens. This study focuses on gene editing technology, introducing CRISPR technology and its development, reviewing recent advancements and their applications on kinds of illness like Dengue fever and COVID-19, discussing the future development of mosquito-borne disease control. Moreover, there are several limitations of CRISPR, to solve them, this review presents ideas that the CRISPR system can combine with Digital twin and achieve a better result in experiment. Against the backdrop of rapid developments in artificial intelligence, many cutting-edge technologies are expected to be applied to gene editing in the future.

 View pdf
View pdf


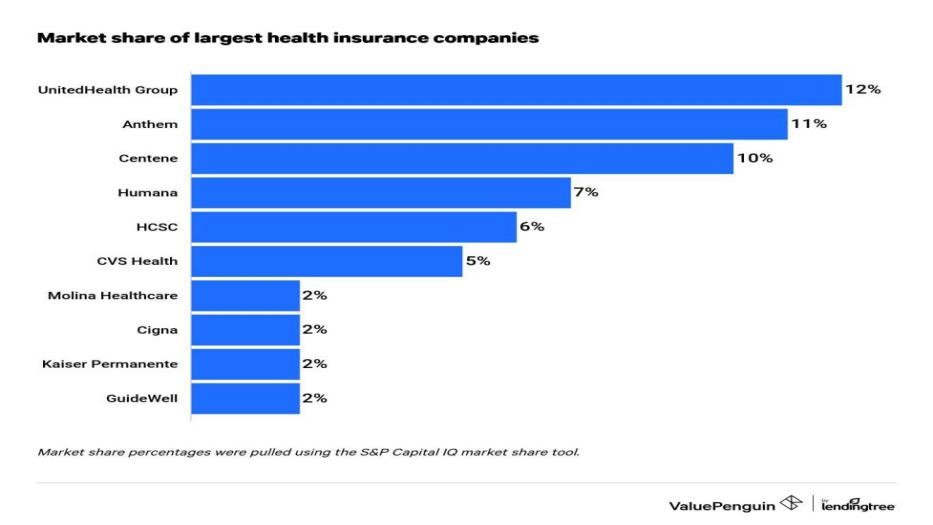
The United States is one of the most developed countries in the world, but unlike most other developed countries, it does not have a universal healthcare system that provides easy and equal access for all people and communities regardless of ethnic and socioeconomic status. The private healthcare system in the United States not only drives higher costs of illness but also provides a lower quality of services than those of the universal healthcare systems. This paper compares the private healthcare system in the United States to the universal healthcare system from three perspectives: hospitalization, health insurance, and administration cost. And it finds that since the healthcare industry has higher entry barriers than most other industries, industrial monopolization appears as new businesses could not enter the industry easily, which leads to a high cost of illness. Also, the quality of services in the private healthcare system may not be guaranteed due to the lack of government direct control of fund distribution, service quality, and horizontal integrations. Furthermore, the new healthcare technology may also benefit from the universal healthcare system as a result of better resource allocation. This study indicates that the universal healthcare system may benefit care access and population health.

 View pdf
View pdf


Dexibuprofen is an over-the-counter drug often used to relieve pain and reduce fever. However, dexibuprofen is less soluble in the gastrointestinal tract, resulting in a slower rate of absorption. In order to enhance the bioavailability, researchers have devised inclusion complexes including dexibuprofen and cyclodextrin. β-cyclodextrin is a cyclic molecule characterized by its annular configuration and possesses a distinctive void structure that enables the entrapment of other molecules via an enveloping mechanism, ultimately leading to the formation of a robust inclusion complex. The incorporation of dexibuprofen into an inclusion complex resulted in enhanced stability, higher aqueous solubility, and improved oral bioavailability. Furthermore, the incorporation of the inclusion complex can potentially mitigate the gastric mucosa irritation caused by dexibuprofen and minimize the gastrointestinal tract's unfavorable effects via the inclusion combination. The inclusion complex of dexibuprofen and β-cyclodextrin is a form of drug with improved solubility and bioavailability that has broad application prospects to provide more effective pain relief and fever treatment. This study focuses on the investigation of the preparation and identification of dexibuprofen clathrate through a comprehensive analysis of existing literature. The primary objective is to determine the most effective inclusion technique for dexibuprofen based on considerations of yield and clathrate rate. Additionally, the research article examined the methodology for the formulation of clathrate into dispersible tablets, along with an initial investigation into the pharmacokinetics of these tablets in rat models.

 View pdf
View pdf


Bipolar Disorder and Unipolar Depressive Disorder are both mental disorders that contain depressive episodes, and the patterns of depression are similar between the two diseases. People are likely to meet their clinicians for the first time when they experience depression while there is no significant evidence of the existence of mania episodes—the other episode of bipolar disorder. Therefore, it is likely that the clinicians misdiagnose the disorder, thus prescribing the wrong medication or applying therapies harmful to patients. For example, some antidepressants will stimulate the mania episode of bipolar patients, increasing the frequency of switch between extreme depression and mania, thus developing the results of bipolar disorder in the patients. At the same time, some mood stabilizers are not that effective to cure major depression compared to medication specialized in treating depression. This article aims at providing several diagnostic methods that can differentiate bipolar and unipolar disorders, and introducing some plausible therapies that work for the two disorders at the same time without severe harm or exacerbation.

 View pdf
View pdf


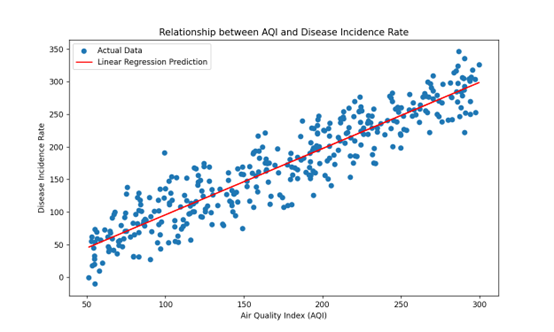
Air pollution is a global problem and a serious threat to public health. According to the World Health Organization, 99 percent of the world's population lives in places where air quality guideline standards are exceeded, resulting in 4.2 million premature deaths each year. Air pollution not only leads to respiratory diseases such as respiratory infections, asthma, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), but is also associated with chronic non-communicable diseases such as lung cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes. This study analysed the relationship between the air quality index (AQI) and the incidence of respiratory diseases and found a positive correlation, i.e., the worse the air quality, the more respiratory diseases. This result is consistent with other studies and with the mechanism of the adverse effects of air pollution on the respiratory system. Therefore, this study is important for raising public awareness of the hazards of air pollution and promoting air quality improvement and respiratory health protection. This study also provides valuable information for environmental policy makers to help them consider the impacts of air quality on public health more comprehensively. This study used randomly generated data, so the results may not fully reflect what happens in the real world. Future studies need to use real environmental and health data to validate and extend our findings and provide a more sophisticated model for scenario simulation and analysis.

 View pdf
View pdf




