

Volume 62
Published on November 2024Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biological Engineering and Medical Science
Animal vaccines play a significant role in preventing and controlling animal infectious diseases, ensuring public health, and promoting the economic development of the livestock industry. This paper reviews the historical development of animal vaccines and explores their role in public health, the livestock economy, and the prevention and control of zoonotic diseases. It details several common types of animal vaccines, including inactivated vaccines, live attenuated vaccines, subunit vaccines, and mRNA vaccines, describing their preparation methods, immune mechanisms, and advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, the paper outlines the current application status of vaccines for three major animal infectious diseases: swine fever, bovine tuberculosis, and avian influenza. It also analyzes the development trends of new vaccine technologies, such as genetic engineering vaccines, nanoparticle vaccines, and oral and spray vaccines. Despite significant advances in vaccine technology, challenges remain, such as pathogen variation, technical and economic barriers, and issues related to regulation and quality control. This paper aims to provide direction for future research, emphasizing the importance of continuous technological innovation and a globally unified regulatory system. The goal is to develop new vaccines with stronger immunogenicity, fewer side effects, and better adaptability to pathogen variations, thereby enhancing the application effectiveness of animal vaccines in public health and the livestock industry.

 View pdf
View pdf



Thyroid cancer, which has a high prevalence of BRAF V600E mutations, is the ninth most frequent cancer worldwide, especially in the aggressive anaplastic thyroid cancer (ATC). The mutation causes continual activation of the MAPK pathway, resulting in unrestricted cell multiplication that leads to the development of tumors. The therapeutic potential of a selective BRAF V600E inhibitor, dabrafenib, has been approved in the treatment of thyroid cancer, especially ATC. The efficacy of dabrafenib was investigated by analyzing various in vivo and in vitro studies and clinical trials. The therapeutic role of dabrafenib on thyroid cancer has been approved in studies involving tumor growth, cell viability, apoptosis, and effects on cancer stem cells (CSCs). Notably, the combination of dabrafenib and MEK inhibitors such as trametinib. significantly inhibited tumor growth and induced apoptosis in thyroid cancer cells. Studies have shown that this combination therapy can reduce tumor volume and target CSCs, which are key to tumor recurrence and drug resistance. Clinical trials have reported improvements in patient status. Dabrafenib, especially in combination with other drugs, offers a better treatment strategy for aggressive thyroid cancer. It enhances the therapeutic effect by effectively targeting the MAPK pathway and CSCs. Future studies may focus on optimizing these combination therapies and exploring their effects and safety to further improve patient outcomes in thyroid cancer treatment.

 View pdf
View pdf


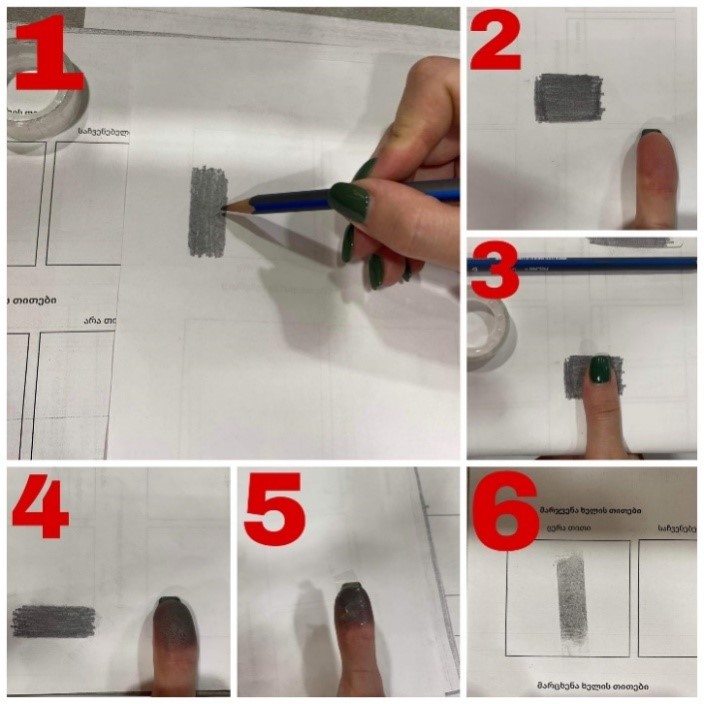
The current research presents that the fingerprinting method might be used for gender identification. The study involved 270 individuals allocated into two age groups, 12-24 years and 40-70 years old. Fingerprint relief of the research participants has been studied through the so-called pencil method. One of the factors that indicated a decline in participation in the survey was the damaged relief of the finger, signifying that not everyone had equal access to fingerprinting. Fingerprints were taken from the left and right thumbs of participants. White lines on the surface of the fingerprint were observed as an identification marker. The study revealed that the above-mentioned white lines were dominant in the fingerprints of female individuals with 71.17% of the total studied participants, while in males this indicator amounted to 29.81%. The obtained results of conducted research, allow us to assume the fingerprint white line ratio as an additional gender identification method.

 View pdf
View pdf


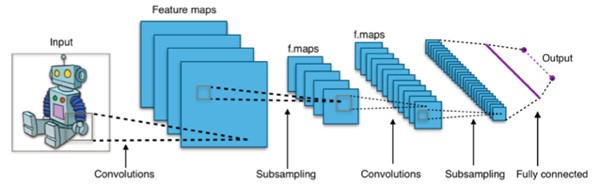
This paper reviews the application of deep learning methods in cardiovascular disease (CVD) prediction, comparing their performance with traditional statistical and machine learning models. We focus on the use of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs) in processing medical images and ECG signals, respectively. The reviewed studies demonstrate the superior performance of deep learning in capturing complex patterns and making accurate predictions. However, challenges related to data quantity, diversity, generalizability, and model interpretability still remain. Future research should focus on enhancing data representation, model comparison, and explainable AI to improve the efficiency and applicability of deep learning in clinical practice.

 View pdf
View pdf


Limited studies investigated the differences between the causes of coronary heart disease in men and women. While some focused on one gender or the other, minimal studies indeed examined the differences in the significance of each of the common risk factors present in both genders. Thus, this study intends to do just that. This study uses data from the Framingham Heart Study, a long-term cardiovascular cohort study of the residents of Framingham, Massachusetts. A variety of factors were considered in examining the risk of coronary heart disease, including gender, age, and previous medical history. Exploratory data analysis and regression analysis were used to reveal the differences between men and women in determining the risk of coronary heart disease. Through regression analysis, apparent differences between males and females arose. Significant factors for men included age, systolic blood pressure, total cholesterol, and glucose levels, and significant factors for women additionally included the number of cigarettes smoked per day as well as a previous history of hypertension. The Framingham Heart Study has demonstrated the distinctions between men and women when it comes to the risks of coronary heart disease, allowing physicians to gain a deeper understanding of the disease. However, it fails to be inclusive of all races and ethnicities as participants in the first cohort and many later cohorts of the study were all Caucasian. This study also calls for future studies to build off the Framingham Heart Study’s shortcomings and provide data and standards suitable for everyone.

 View pdf
View pdf


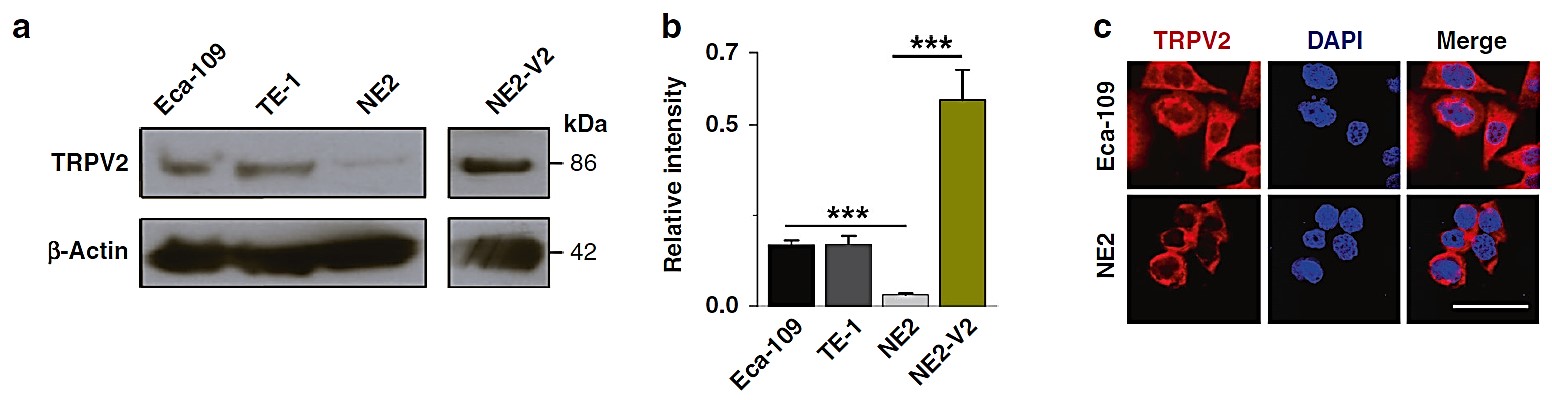
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is a common gastrointestinal tumour, and approximately 300,000 people worldwide suffer and lose their lives to esophageal cancer every year. This research will investigate the pathogenesis of ESCC caused by heat stress, and investigate the current state of research and future development of targeted and immunotherapeutic strategies based on the signaling pathways and key proteins associated with ESCC. In heat stress-induced ESCC, TRPV2, a temperature-sensitive gene, has been analysed as an important pathogenetic mechanism leading to ESCC by promoting the heterogeneous proliferation of esophageal epithelial cells as well as their metastasis and development. As for targeted therapy and immunotherapy, the advantages of targeting EGFR and PD-1/PD-L1 (ligands of PD-1) for ESCC over surgery and chemotherapy were analysed respectively. The above analyses will provide an important research direction for future research on the pathogenesis of ESCC and the development of related therapeutic strategies in this field.

 View pdf
View pdf


Breast cancer (BC) has become one of the major malignant tumors affecting women's health in recent years, and the expression of human epidermal growth factor HER2 elevates the proliferation and migration of BC tumors. The HER2-targeted drug trastuzumab is initially effective, but resistance can develop after a period of time. There is currently no particularly effective approach to drug resistance in HER2-positive BC. In this paper, we have compiled and summarized several major drug resistance mechanisms of HER2-positive BC cells and proposed several coping strategies, suggesting the possibility of immunotherapy, as well as providing theoretical references for future immunotherapy for the remaining tumors. However, the safety of immunotherapy has not yet been demonstrated, and future studies could focus on ensuring the safety and prognosis of patient treatment.

 View pdf
View pdf


Chemotherapy is one of the commonly used means of tumour treatment, but the occurrence of tumour multidrug resistance (MDR) has added great difficulties to tumour treatment and caused serious physical and psychological harm to patients. Modern pharmacological studies have shown that Zhebeimu (Fritillaria thunbergii Miq, ZBM) has the effect of reversing the drug resistance of tumour cells, and it is commonly used in the study of various malignant tumours, such as leukaemia, breast cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma. By analysing and summarizing the chemical constituents of ZBM and their related studies on reversal of tumour cell resistance in recent years, the article concludes that the chemical constituents in ZBM can achieve their reversal of drug resistance in a variety of tumour cells by inhibiting the expression of P-glycoprotein (P-gp), decreasing the exocytosis of drugs, increasing the concentration of intracellular drugs, modulating the ROS, and other mechanisms. At present, there is a relative lack of research and treatment of tumour MDR in clinical practice, and the search for reversal agents and reversal strategies for tumour MDR has become an urgent problem, and this paper provides an in-depth study of ZBM, which provides a reliable basis for subsequent application in clinical practice.

 View pdf
View pdf


Stroke is one of the leading causes of disability and death worldwide. Acupuncture, as a traditional Chinese medicine, has received considerable attention recently for its use in stroke-related nervous system treatments. Acupuncture exerts therapeutic effects through multiple mechanisms, including stimulating and regulating related factors and signaling pathways to play anti-inflammatory, neuronal repair and protective effects; controlling glial cell polarization to promote self-repair after brain injury, etc. Acupuncture has been shown to markedly decrease the inflammatory response following a stroke, facilitate nerve regeneration and cell proliferation within the central nervous system, enhance cerebral blood flow in ischemic regions, diminish neuron apoptosis, and ultimately lead to improvements in neurological function and quality of life for stroke patients. Nevertheless, the precise neural mechanisms underlying acupuncture's effects on stroke remain incompletely elucidated, warranting further comprehensive investigation. This article reviews the research progress on the neural mechanisms of acupuncture in the treatment of stroke in recent years, with a view to providing scientific basis and reference for its clinical application.

 View pdf
View pdf


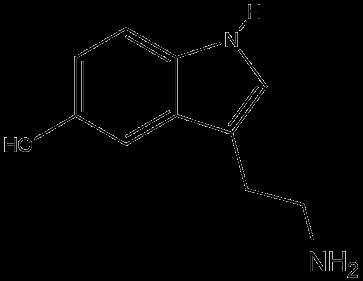
Neurotransmitters play a crucial role in the production and treatment of psychiatric disorders. A neurotransmitter is a chemical that transmits signals and is very closely associated with a variety of neural activities such as mood, memory, growth and development, and drug addiction. In recent years, significant progress has been made in the research on psychiatric diseases caused by uneven neurotransmitter secretion and drug treatment for psychiatric disorders. By studying the way drugs act on different neurotransmitters and their receptors, regulate the functional activities of the brain or body, so as to effectively improve the symptoms of patients, and analyze the mechanism of action of each drug to obtain the most effective drugs with minimal side effects to further treat psychiatric diseases. However, the current scientific and technological conditions are limited, and the specific mechanism of action of some drugs has not yet been determined. This article analyzes various neurotransmitters, such as serotonin (5-HT), norepinephrine, dopamine, psychiatric diseases caused by unbalanced secretion, and the mechanism of action of their representative therapeutic drugs, which provides a theoretical basis for the clinical treatment of psychiatric diseases in the future. There are still a small number of drugs with unclear mechanisms of action and unsolved drug side effects, and future research can focus on the direction of drug application safety.

 View pdf
View pdf




