

Volume 69
Published on January 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Modern Medicine and Global Health
Diabetes mellitus is a growing global health issue with an increasing incidence rate. Traditional methods for predicting diabetes, which rely heavily on clinical data and physical examinations, present challenges such as high costs, time-consuming processes, and difficulties in providing timely and personalized risk assessments. However, with the rise of machine learning (ML), new opportunities have emerged in diabetes prediction, utilizing large-scale data and advanced pattern recognition techniques. This study examines the application of ML in diabetes risk assessment by leveraging electronic health records (EHR) and big data, leading to significant improvements in accuracy and efficiency. The results demonstrate that ML methods can more effectively identify high-risk individuals, facilitating early intervention and contributing to the advancement of diabetes prediction.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the continuous development of rehabilitation medicine and robotics, rehabilitation robot (RT) is also adapting to the development of the times and ushering in a new era of development. It has become a kind of emerging technologies and one of the important searching topics currently. With the deepening of multidisciplinary cross-disciplinary cooperation such as medicine and engineering, RT will need strong support from rehabilitation medicine theory and clinical experimental data and need to meet social rehabilitation needs. Existing RT equipment is mainly used for functional disorders of different parts of the body in the late stage of stroke and can be roughly divided into upper limb rehabilitation robot, hand function rehabilitation robot and lower limb rehabilitation robot. However, there is still a long way to go in the development of RT. In the future, researchers should focus on researching other robot-assisted technologies suitable for different diseases, different populations and different occupational fields.

 View pdf
View pdf


The intricate relationship between the gut microbiome and neurodegenerative diseases has become an emergent topic in biomedical research. This study delves into the interplay between intestinal microbial communities and the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. Drawing on theoretical frameworks that suggest a bi-directional 'gut-brain axis', the hypothesis driving this investigation postulates that the gut microbiota may influence central nervous system dysfunction directly through microbial metabolites or indirectly by modulating immune responses. Employing a combination of metagenomic analysis and neurophysiological assessments, the research elucidates the compositional and functional alterations in the gut microbiota of individuals with neurodegenerative diseases. Findings highlight a significant correlation between specific microbial profiles and disease progression, laying the groundwork for potential therapeutic interventions targeting gut microflora. The novelty of this study lies in its comprehensive analysis of the microbiome's role in neurodegeneration, providing valuable insights for the advancement of microbiota-centered therapies in clinical practice.

 View pdf
View pdf


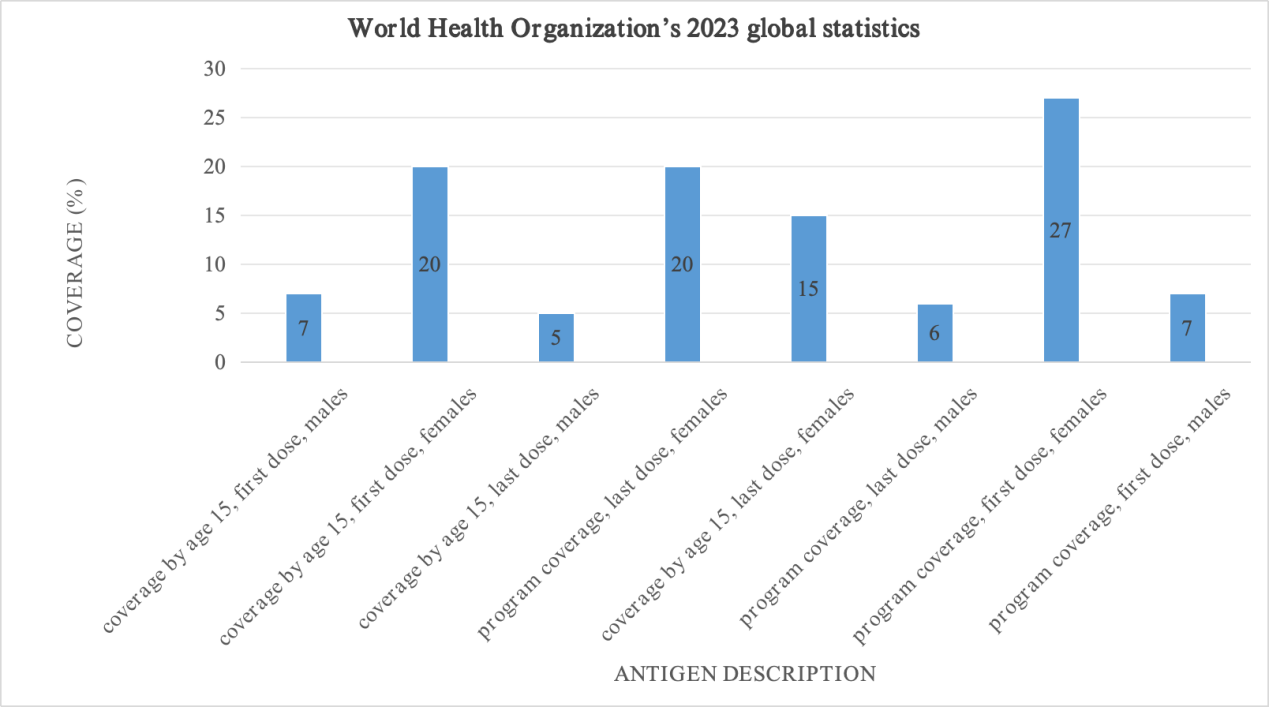
In order to better prevent HPV infection, HPV vaccine has been promoted worldwide. Most of the current research on HPV vaccine is related to a specific region or involves the comparison of two regions. It is still worth exploring whether the influencing factors of people's attitudes to HPV vaccine are the same in different regions. This review searched the public data of the World Health Organization and analyzed several studies on the attitude or vaccination behavior of HPV vaccine to complete the cross-cultural research. This article found that culture, publicity and education, economic level, religious belief, social psychological status and other factors can affect the public's attitude to HPV vaccine. Positive attitudes lead to positive vaccination behavior. This review provides a reference for future research in the cross-cultural field. However, this paper has not yet compared the importance of the influencing factors, so future research can make this comparison. It is also recommended that health professionals pay attention to the role of men in HPV transmission, disease prevention, and vaccination.

 View pdf
View pdf


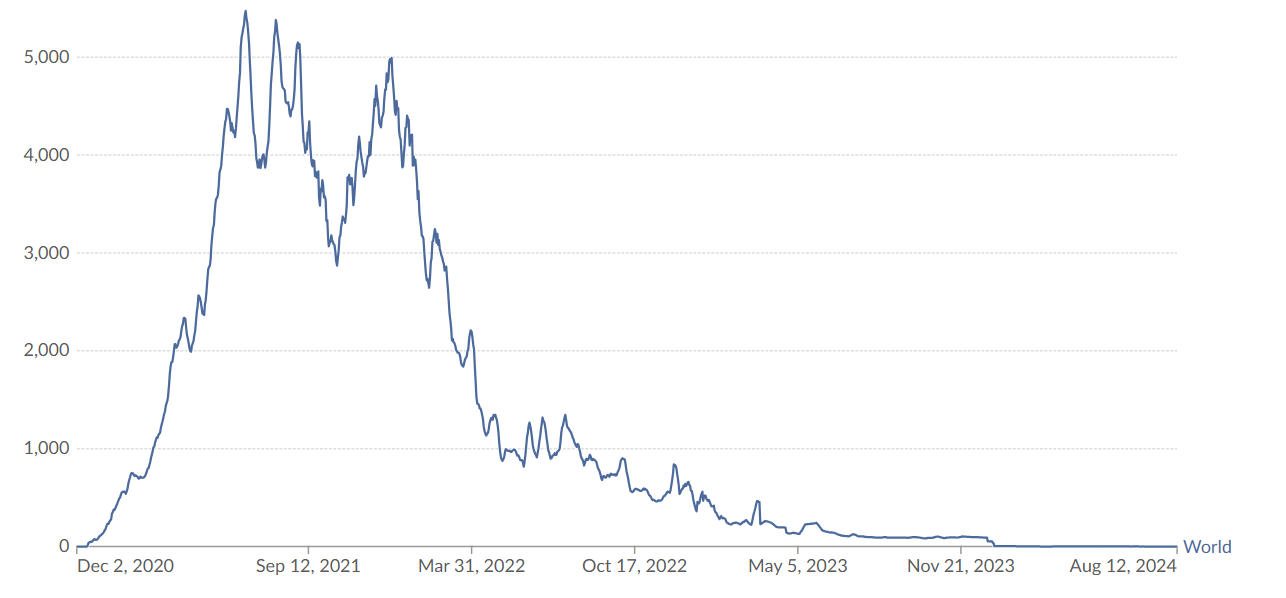
This essay describes the global response to the COVID-19 pandemic, focusing on its virus characteristic, public health strategies employed, and the role of vaccination and technology in the management of the crisis. Back in March 2020, the COVID-19 virus was declared a pandemic by the World Health Organization, which required the international community's collaboration to reduce the health impact of the virus. This essay exposes how SARS-CoV-2 spreads, the complications of asymptomatic transmission, and its mutations, which further complicate the efforts to contain it. The very basic early detection through testing, protection by social distancing and wearing masks, and wide vaccination were the fundamental strategies that had kept the pandemic in control. It was vaccination, with an emphasis on vaccines based on mRNA, that proved to be key in the fight against severe diseases and in lightening the load of health services. The essay identifies that the vaccines represent a big scientific milestone and show promise for the future treatments beyond infectious diseases. Besides, big data, tracking technology, international cooperation were all important technologies to help manage the crisis.

 View pdf
View pdf


Tumorigenesis and progression are complex process with multifarious molecules and related mechanisms, while most of them are still elusive. Most research into the mechanisms of cancer today are focusing on encoding RNAs. However, for the past few years as the emergence and development of epigenetics, a kind of new molecule: non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), RNAs without protein-coding function, have gained prominence in recent scientific discussions. Since the first ncRNA was discovered in 1990s, extensive research has shown that ncRNAs significantly influence processes such as cell growth, differentiation, metabolic regulation, and programmed cell death at both transcriptional and post-transcriptional stages. By means of acting as the tumor suppression and oncogenesis, research has identified several ncRNAs with abnormal expression patterns in cancer cells, marking them as primary oncogenic factors or valuable targets in cancer treatment. This review focus on three kinds of ncRNA, MicroRNAs (miRNAs), long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), and circular RNAs (circRNAs), the molecule structure, generative mechanism, characteristic function and regulatory mechanism in tumor progression. In addition, we will discuss the application value and future expiration of the therapeutic that are focusing on ncRNA, that will open up a new idea and methods for the treatment of cancer for future investigation.

 View pdf
View pdf


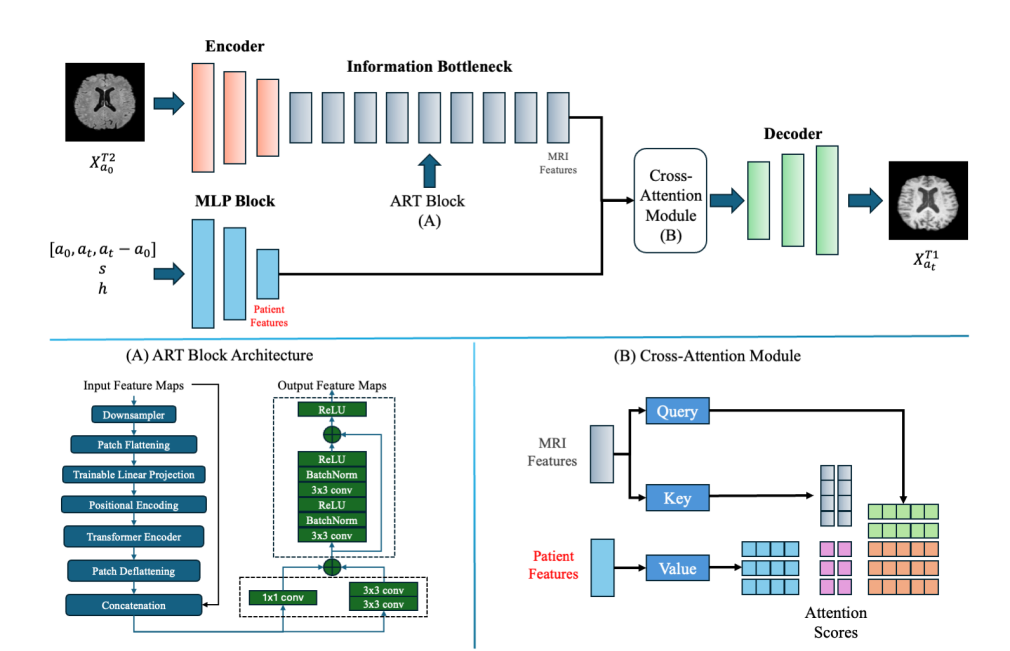
Multimodal medical image synthesis plays a crucial role in enhancing diagnostic accuracy and understanding disease progression, particularly in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). However, existing methods often focus on single-modality or single-time synthesis, overlooking the complexities of integrating multiple imaging modalities and longitudinal data. Furthermore, these models tend to ignore patient-specific factors like age, health conditions, and sex, limiting their practical applicability in clinical settings. To address these limitations, we propose CrossSim, a novel residual vision transformer-based framework for multimodal and longitudinal medical image synthesis. Our model integrates cross-attention-based feature fusion to handle personalized data such as age, health state, and sex. This allows for the generation of more clinically relevant synthetic images that better represent the complexities of real medical data. In contrast to existing methods, CrossSim excels in synthesizing images that accurately reflect changes over time and across modalities. We conduct extensive experiments on the ADNI dataset to evaluate the effectiveness of our approach. The results demonstrate significant improvements in key metrics such as PSNR, SSIM, and RMSE, confirming the superior performance of CrossSim in both qualitative and quantitative analyses. This study emphasizes the clinical significance of CrossSim, offering a valuable tool for enhancing diagnostic accuracy and advancing our understanding of Alzheimer’s disease progression.

 View pdf
View pdf


The global prevalence of diabetes is on the rise, with its pathogenesis closely related to the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) that includes the classical antagonistic pathway and the ACE2-Ang-(1-7)-Mas axis. Despite its well-documented role in cardiovascular health, the potential mechanisms by which RAS is associated with diabetes require further study. RAS interacts with metabolic regulatory factors such as obesity and autophagy. Excessive activation of the Ang II-AT1 receptor pathway can contribute to insulin resistance and diabetic complications. This review elucidates the mechanisms by which RAS contributes to diabetes development and discusses both clinical applications and future directions for RAS inhibitory drugs in managing diabetes. And it concludes that RAS inhibitors hold significant promise for treating diabetes and its associated complications, warranting deeper exploration into their future roles within this field. The results indicate the intricate relationship between RAS and diabetes, alongside the therapeutic potential offered by RAS inhibitors.

 View pdf
View pdf


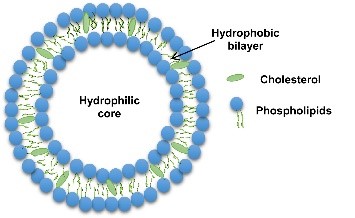
This study explores the mechanism of nanotechnology-based targeted drug delivery in cancer treatment, particularly focusing on the preparation and application of nanodrugs for specific types of cancer. The article first analyzes the physicochemical properties and drug delivery advantages of common carriers such as liposomes, gold nanoparticles, and polysaccharide nanoparticles. It then discusses the classification, preparation, and application of nanoparticle-based delivery systems and nanoemulsion-based delivery systems. Following this, the drug delivery mechanisms of nanodelivery systems are examined, particularly how pH, temperature, light, or magnetic field-responsive nanodelivery systems enable targeted release. Furthermore, this paper focuses on the compatibility of combined drugs, the stability of the mixture, and potential toxic side effects. Finally, while enhancing the therapeutic efficiency of drugs, nanotechnology-based targeted drug delivery systems offer new approaches for personalized cancer treatment and provide a theoretical foundation and reference for the future development of such systems.

 View pdf
View pdf


This review aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of the relationship between chili consumption and disease risk, as well as mortality, while exploring the underlying mechanisms involved. Methods: To gather relevant literature, we conducted a systematic search using keywords such as "capsaicin" and "spicy food consumption and mortality" in the CNKI and Wanfang databases, which primarily focus on Chinese-language publications. In addition to the direct search, we also identified key studies through references cited in the selected articles. Further materials were discovered by reviewing related content, contributing to the synthesis of this review. Results: A total of 28 studies were included in this review, consisting of 3 Chinese articles and 25 English-language studies. Among the English-language studies, 10 were conducted in China. The studies included both cohort and case-control designs, and they examined various aspects of chili consumption, from its impact on metabolic health to its role in reducing the incidence of diseases. Conclusion: The consumption of spicy foods, particularly those containing capsaicin, has been found to be associated with a reduced risk of developing a range of diseases, including malignant tumors, cardiovascular diseases, and parasitic infections. Additionally, spicy food consumption appears to be linked to a lower overall mortality risk, making it a potentially beneficial dietary habit in promoting health and longevity.

 View pdf
View pdf




