

Volume 109
Published on May 2025Volume title: Proceedings of CONF-MPCS 2025 Symposium: Leveraging EVs and Machine Learning for Sustainable Energy Demand Management
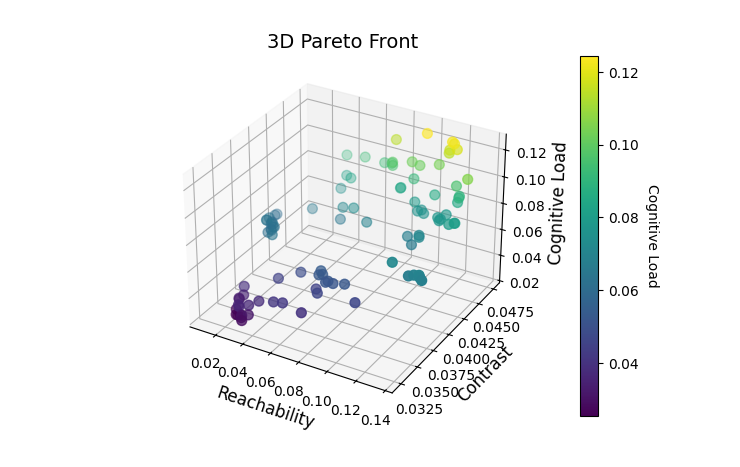
With the rise of the Single-Pilot Operation (SPO) mode, the human-machine interaction design of aircraft cockpits faces new challenges. This paper focuses on optimizing human-machine interaction in single-pilot aircraft cockpits by constructing a three-dimensional evaluation system based on the NSGA-II multi-objective optimization strategy. This system comprehensively analyzes the reachability of operating components (), the contrast of color information (), and the cognitive load of pilots (). Data are derived from assumptions and simulation analyses based on literature and theory, covering factors such as pilot characteristics, component layout, color contrast limits, and flight mission complexity. By generating Pareto front solutions, the paper reveals trade-offs among the three objectives, providing a new quantitative decision-making basis and research direction for cockpit design.

 View pdf
View pdf


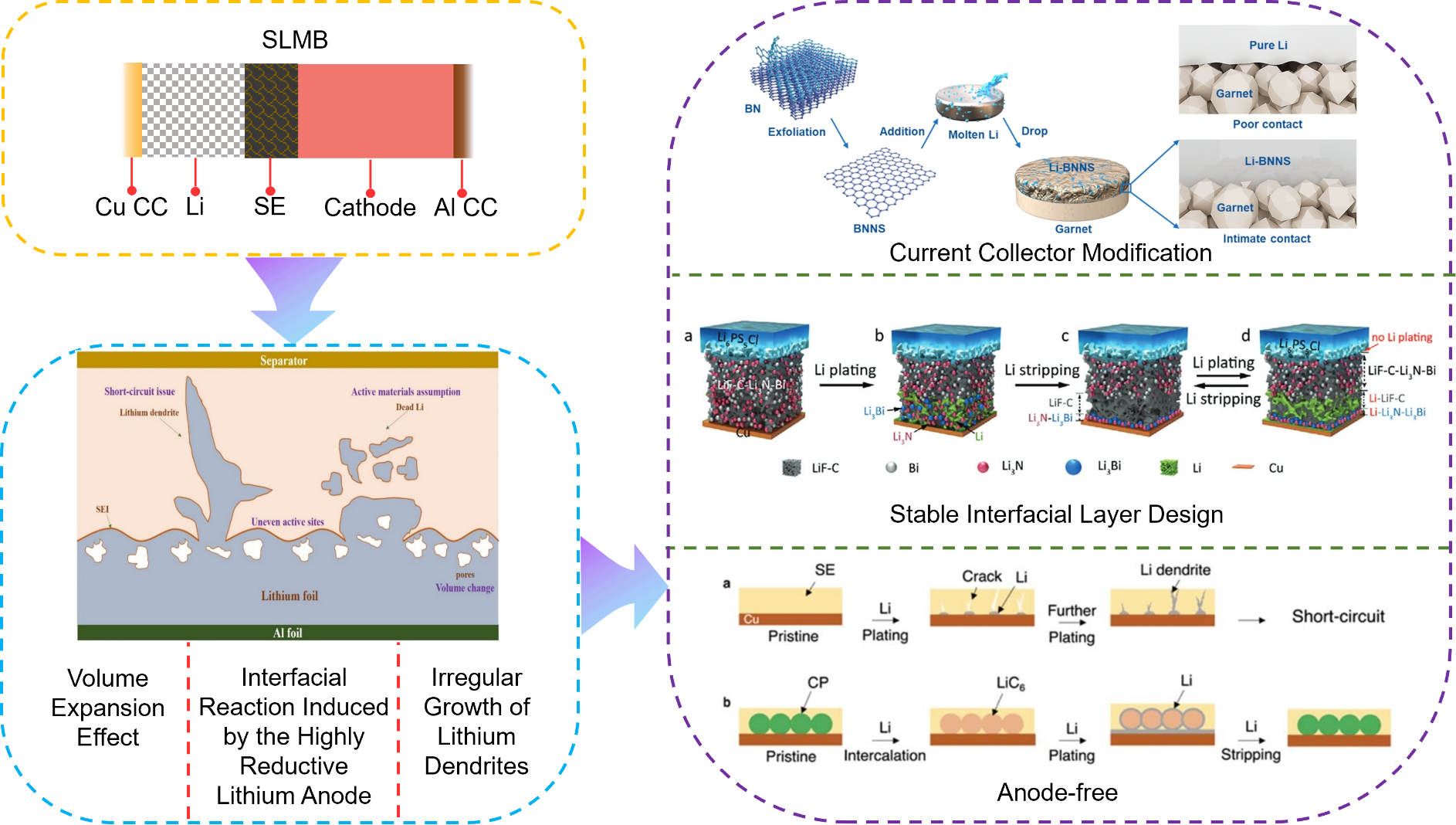
Solid-state lithium metal batteries (SLMBs), recognized as next-generation energy storage systems for their high energy density and intrinsic safety, face commercialization challenges stemming from interfacial instability, lithium dendrite proliferation, and rapid capacity degradation in anode-free configurations. This review analyzes the underlying mechanisms of performance deterioration in SLMBs: (1) the highly reactive lithium metal engages in chemical or electrochemical side reactions with the solid-state electrolyte (SE), leading to a continuous increase in interfacial impedance; (2) Volume fluctuations during lithium deposition/stripping trigger mechanical contact failure; (3) Irreversible lithium consumption in anode-free systems creates a self-amplifying degradation cycle. In order to solve these issues, we focuses on three major modification strategies: (1) Three-dimensional porous current collectors for homogeneous lithium-ion flux regulation and dendrite suppression; (2) Constructing a gradient artificial interfacial layer to inhibit electron leakage and promote ion transport; (3) Developing dynamic self-adaptive interfacial systems that utilize in situ alloying reactions to achieve interface self-healing. In addition, the core contradictions in anode-free systems are furtherly analyzed. Furthermore, we emphasize the critical role of synergistic optimization between current collectors and interfacial layers in enhancing lithium deposition reversibility. By elucidating the fundamental principles and interdependencies of existing modification approaches, this review provides theoretical guidance and innovative design principles for developing high-performance SLMBs with extended cycle life and commercial viability.

 View pdf
View pdf


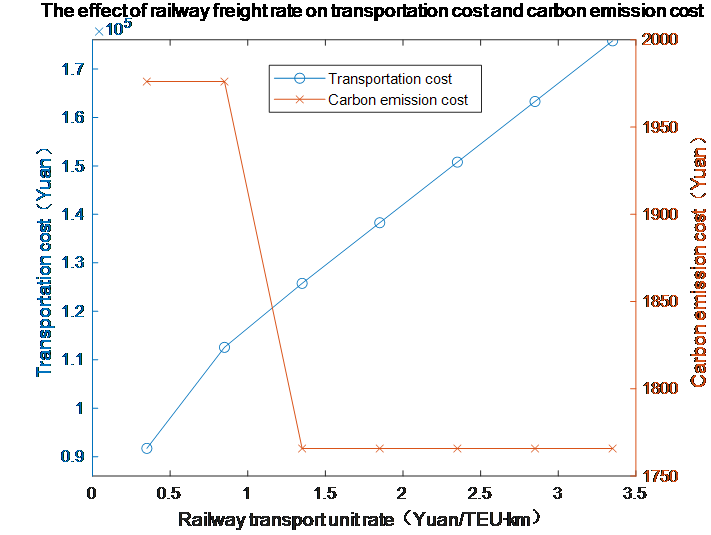
This study investigates the coal multimodal transportation route selection problem by integrating economic and environmental benefits, taking the current coal transportation landscape in China as its research context. Focusing on the transportation network from Shanxi region to Shanghai as a case study, we establish a multi-objective optimization model that comprehensively considers transportation costs, carbon emission costs, and transit time. The NSGA-II algorithm is employed to solve this optimization problem. The results demonstrate that rail-water intermodal transport emerges as an effective solution for optimizing transportation structures. Case analysis reveals that optimal route selections exhibit cost sensitivity, adapting to fluctuations in railway and waterway freight rates. Furthermore, sensitivity analysis indicates that carbon tax rate variations exert limited impact on total transportation costs, while conventional transportation costs maintain their dominant influence. This research provides decision support for sustainable transportation planning in coal logistics systems.

 View pdf
View pdf


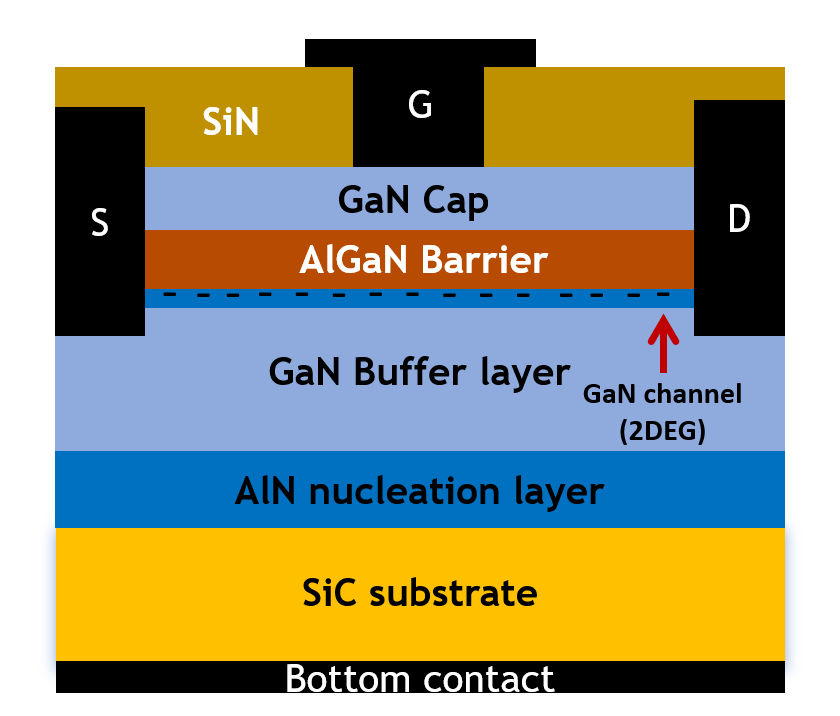
This paper investigates the DC and AC performance of T-gate Gallium Nitride (GaN) High Electron Mobility Transistors (HEMTs), with a particular emphasis on their high-frequency characteristics under various structure parameters and conditions. The study delves into the impact of different gate structures and the concentration of traps on the RF performance of the devices, including those at the AlGaN/GaN interface and within the GaN buffer layer. Moreover, the analysis includes the examination of short channel effects that can significantly influence the device behavior when the gate length is less than 100nm. Through comprehensive simulations, optimal structural parameters were identified, leading to notable advancements in device performance. Specifically, the devices achieved a remarkable cut-off frequency of 138 GHz and a maximum oscillation frequency of 192 GHz, accompanied by an extremely low gate leakage current, which is lower than 1E-8 mA/mm. These findings highlight the potential of T-gate GaN HEMTs in high-frequency applications.

 View pdf
View pdf




