

Volume 8
Published on August 2023Volume title: Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Software Engineering and Machine Learning
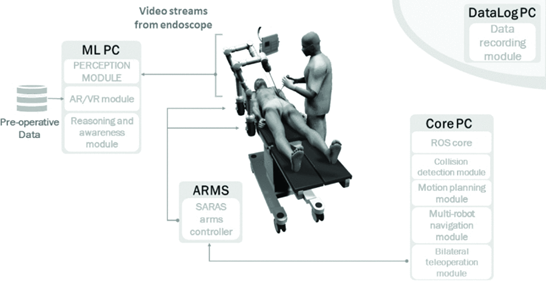
The emergence of artificial intelligence (AI) technology has once again promoted the development of robots by making them more efficient, independent, and intelligent. With the progress of the times, the two promote each other and develop together in many fields, especially in the field of medical and health. This paper describes the strengths and limitations of surgical robots and intelligent medical robots as well as their possible development trend in the future from both hardware and software aspects. Conclusions can be drawn that, on the one hand, surgical robots can improve the safety and reliability of the surgery and intelligent medical robots can help achieve drug research and development, intelligent diagnosis and treatment, intelligent image recognition, etc. These can help doctors make diagnoses and treatments more accurately; on the other hand, it is difficult to install an electronic sensor on the mechanical arm at present, the current positioning technology is not perfect, and the rotation angle of the mechanical arm is limited. These limitations improve the difficulty for doctors to use surgical robots. However, with the continuous progress of robot and AI technology, the limitations of many surgical robots can be improved and more targeted AI technology can be developed and applied in specific fields.

 View pdf
View pdf


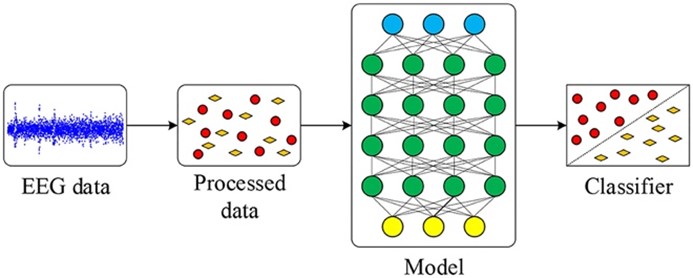
There are several different algorithms to train models in machine learning and for purpose of enhancing the accuracy of the models for emotion recognition systems by using EEG datasets, we can compare different algorithms and methods. To experience more intuitively the different impacts caused by different algorithms and methods, ‘Emotion classification by applying ‘Convolutional Neural Networks, Sparse Auto-encoder, Deep Neural Network’, and ‘ZTW-based epoch selection algorithm’, these three models of emotion recognition will be mentioned and compared in this essay to find out a way to improve the accuracy of the emotion recognition models based on EEG datasets, which also include the process and final results of these models.

 View pdf
View pdf


Brain tumor is a serious disease for human beings. MRI is the most widely used method for its innocuousness since people do not need to be exposure to radioactivity. The segmentation on MRI images is a vital step in tumor detection. To improve efficiency and accuracy of the segmentation, scientists apply different algorithms in this process. This paper focuses on three particular algorithms including Connected component label algorithm (CCLA), Watershed algorithm (WSA) and Fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm (FCCA). The principles and applied procedures of these three algorithms are introduced. Basing on this background information, algorithms are compared from three aspects. Fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm is considered as more efficient and accurate among these three algorithms. All algorithms have good research prospects, and the segmentation result can be improved through the improvement on algorithms.

 View pdf
View pdf


In real life, there is far more unprocessed data than labeled data, which brings a large amount of data that cannot be directly used for machine learning training. Based on the tweet dataset processed by Natural Language Processing (NLP), this paper uses a variety of machine learning models for training and comparison. Moreover, different performances are analyzed and discussed. Since labeled datasets are difficult to obtain, the use of supervised learning will be limited. However, the number of unlabeled datasets is very large, which can provide a continuous training set for machine learning. This paper conducted a comparative experiment on the effect of semi-supervised learning and obtained better results than supervised learning and unsupervised learning. The experiments in this paper prove that semi-supervised learning can effectively use unlabeled data and train machine learning models.

 View pdf
View pdf


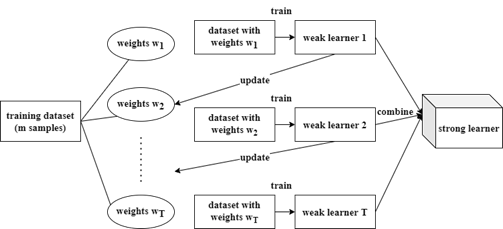
Recently, machine learning(ML) has become a hot issue, and most brain-computer interface(BCI) systems contains machine learning structured classifiers. The classifiers are designed to process the selected feature and send the most possible signal user generates to the reception device. However, it’s not easy to realize without some advanced ML methods. This survey mainly focuses on some effective ML means to classify features, including state-of-the- art invention: MDM classifier. Moreover, we propose some promising directions to further research this topic.

 View pdf
View pdf


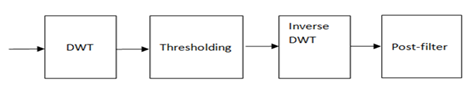
Medical images are commonly used today by medical practitioners for the purposes of diagnosis. For the purposes of diagnosis, diagnostic images are widely used today by medical professionals. In general, MRI works on soft tissues, and CT works on hard tissues. Due to device and hardware limitations, mathematical calculations, transition mechanisms in computers, there are chances of creating noise in medical images.In yhis paper, a critical review on CT image denoising has been performed in wavelet domain. In the transform domain, the process of removing noise from an image starts with the image or data being divided up into a representation in scale space. It has methods for setting thresholds, rules for shrinking, and a way to clean up noise based on wavelets, among other things.

 View pdf
View pdf


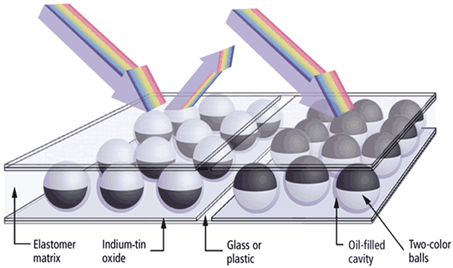
This paper deals with reviews of the various publishing methods available. Due to emerging published technologies like electronic paper, newspaper publishers must now produce, print, and disseminate their information in new ways (e-paper). In addition to creating technical challenges for publishers, e-paper will change how people consume news. We address the impacts of this new channel in this article from the outside-in by assuming a starting point in prospective new consumption. We examine the impacts that the e-paper publication channel will have on distribution, media house systems including editorial, advertisement, and subscription, and procedures based on three empirically validated future consuming scenarios.

 View pdf
View pdf


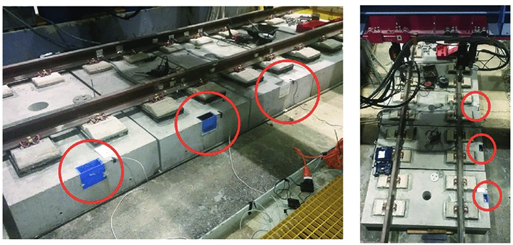
The paper introduces a monitoring system for the health structure of rail-tracks. The slab track system is highly demanded due to its quality for safety measures and highly sustainable quality for high-speed railway infrastructure, particularly in India for the Bullet-train project. Previously, the system used to monitor the health of slab-tracks was costly and not done regularly, but the evolution of digitalization and wireless sensor networks is doing tremendous work for monitoring the health of infrastructure and other activities. In rail-track systems, wireless sensors can provide us with information, detection, and prediction of the health-infrastructure of rail-tracks. An efficient design for communication systems is needed for such safety-critical railway tracks. The paper proposes an accurate and efficient design for communication.

 View pdf
View pdf


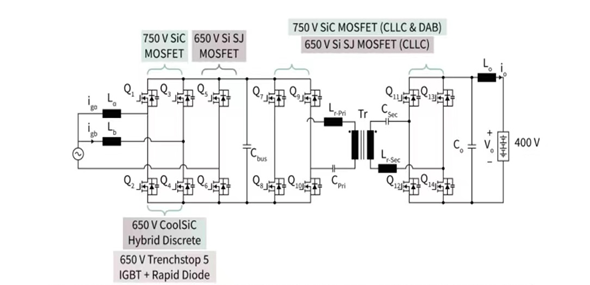
With the large-scale use of EV around the world, it has become a popular research direction to integrate EV into the power grid to achieve the purpose of peaking and valley filling for the power grid. With V2G technology as the core, this paper firstly analyzes the V2G grid-connected control technology, namely active power and reactive power control and clustering control at the theoretical level. From the perspective of cooperative game, it elaborates the commercial operation mode of V2G after grid-connected. Finally it puts forward relevant assumptions on the future development trend of V2G based on the current development status of V2G technology.

 View pdf
View pdf


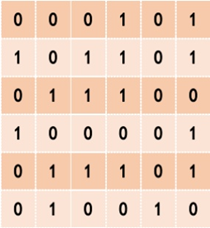
This research propose a user-centered combinatorial data anonymization method. whereas a data matrix is said to be k-anonymous if each row occurs at least k times. Therefore, the authors propose PATTERN-GUIDED k-ANONYMITY, an improved k-anonymization problem. It allows users to designate the combinations in which suppressions may occur, building on prior work and addressing relevant shortcomings. Users of anonymous data can indicate that the aspects of the data are valued differently. The so-called K-anonymity is usually realized by Generalization and Suppression techniques. Generalization refers to Generalization and abstraction of data so that specific values cannot be distinguished, for example, the age data group can be generalized into an age group.

 View pdf
View pdf




