

Volume 131
Published on February 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Machine Learning and Automation
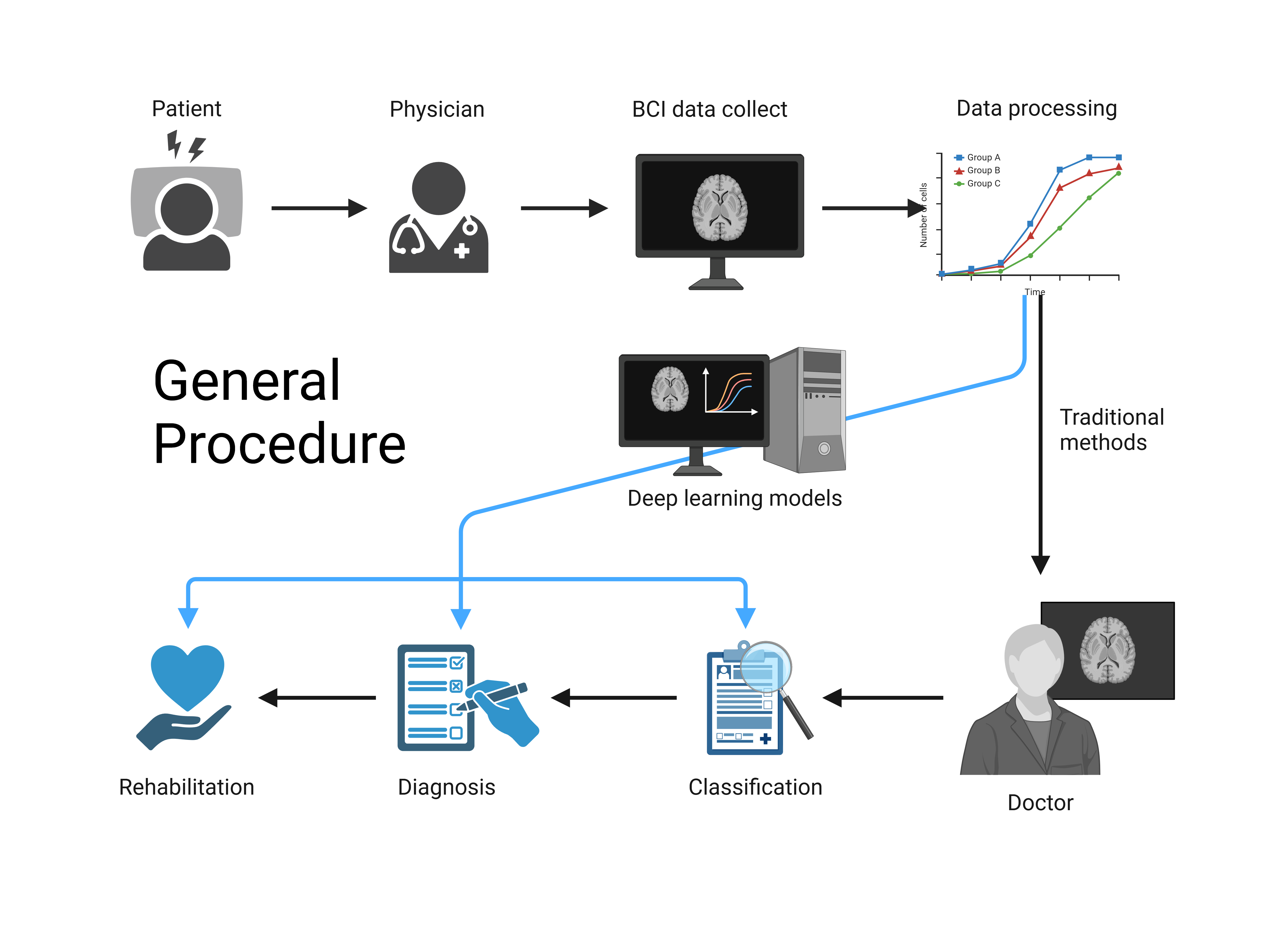
Stroke is considered a global disease that leads to death and certain neural disabilities. Deep learning techniques have revolutionized EEG-based Brain-Computer Interface(BCI), enhancing reliability and promising a transformative future for BCI applications in stroke rehabilitation. However, BCI's implementation in clinical practice has been restricted due to their low accuracy performance. The objective of this review is to summarize how the integration of deep learning and BCI technologies can contribute to the rehabilitation of stroke patients. This paper compiles studies that evaluated deep learning and BCI intersection for stroke subjects, analyses the methodological quality of these studies, and verifies the relationship between the effects of the interventions and performance achieved in rehabilitation. The deficiencies and the future development direction of stroke rehabilitation in BCI with deep learning are also discussed. The various deep learning techniques combined with BCI technology, will improve people's ability to cope with stroke and provide a way to recover from stroke.

 View pdf
View pdf


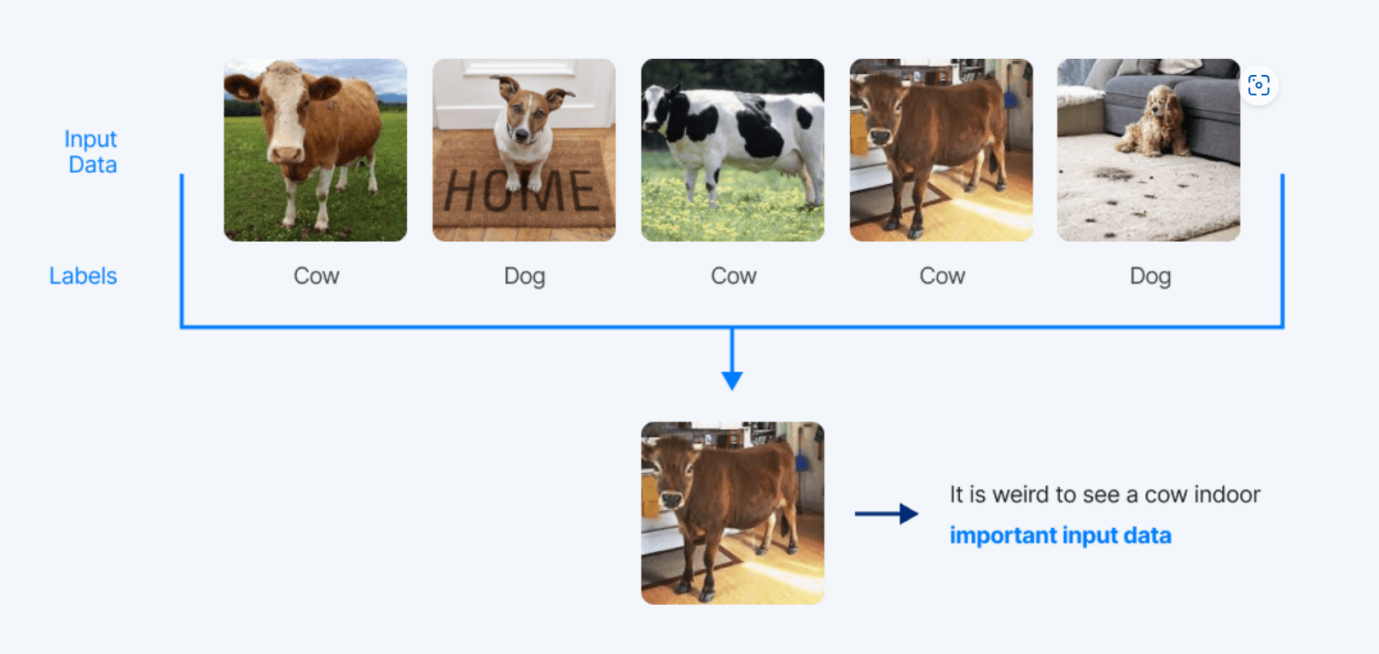
The paper we studied introduces concepts about machine learning and algorithms for corsets selection. A group of researchers from KAIST have developed an effective coresets selection algorithm to help Open-set self-supervised learning on image classification tasks. Experiments are being established using big open sets and making it more fine-grained, models will be trained using the fine-grained sets in order to classify and annotate different objects in the picture. In our studies, we have experimented using pictures of aircraft to train the model. An algorithm to select coreset named SimCore is being developed, and the group of researchers had found that by merging the coreset selected from the open set with the target dataset, had made the training process of the model more efficient.

 View pdf
View pdf


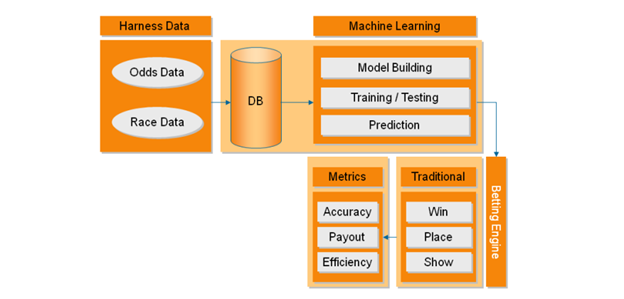
Horse racing is a globally viewed sport in which the performance of horses may be influenced by numerous factors, with the condition and moisture in the racing surface, known as the "going," being one of the most influential. Accurate reporting of the going is essential for ensuring fair competition. This study aims to measure the accuracy of reported track conditions by utilizing a dataset from three racecourses—Catterick, Chester, and Newmarket. We first identified discrepancies suspected to be caused by rounding in reported distances in the data and corrected them by reverting them to officially sanctioned distances. We started with linear regression models to predict winning times, using key variables such as race distance, class of the race, and the reported going. Then we applied log transformation to the data to solve heteroscedasticity. The final model will be used to generate prediction intervals for winning times under each going conditions, allowing us to figure out which goings might be reasonable for a specific race. The results indicate that approximately 6-7% of races were outside of the calculated bounds, which may lead to errors in strategic decisions by trainers and bettors. By calculating the posterior probabilities of each going condition using Bayesian inference, we created a list of reasonable goings for each new race, giving trainers and bettors more accurate information so that they can better prepare for future races in the day.

 View pdf
View pdf


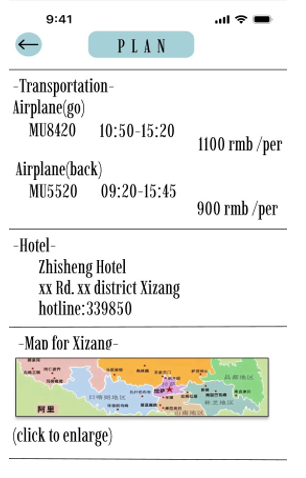
With the growth of population and economic development, tourism has become a popular activity. In this case, we have to know the importance of making a plan. However, making plans through various kinds of traveling applications and social media makes it difficult to identify information reliability and choose a suitable route for the journey. So we designed WonderTrip, an applet to be a plug-in program that appears in the form of a plan on the article browsing interface of social media platforms. Further, we used Figma, UI design software, to build our project. Through the combination of frames and text, we allocated pages in order to ensure the operation of the program. This applet is designed to have no advertisements or viruses, providing the simplest way of ordering tickets and checking out the recommended attractions. At the same time, providing schemes for people who don't want to take the time to make their own travel plans.

 View pdf
View pdf



This paper provides an exhaustive evaluation of different algorithms for the accurate detection and localization of dense clusters on complex image data with a resolution to maintain real centroids in obscure, overlapping, or densely packed situations. Our approach differs by its use of the local maximum algorithm to quickly identify potential cluster centers (by detecting local maxima in pixel intensity) as a first step. The algorithm starts by initializing cluster centers, which are then refined using the k-Means clustering method that iteratively relocates the positions of these clusters until an optimal configuration is reached. We tighten our approach by adding custom loss functions to Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) that encode the predicted number of clusters and their center positions. An early stopping mechanism is introduced to mitigate the issues of noise and overfitting, with performance measured against a test set. Furthermore, we examine the average pooling and center-of-gravity approaches for noise reduction to predict cluster centers without unnecessary outliers. This combination, along with the Hungarian algorithm, which is used to optimally match predicted and real centers, has shown better results in detecting the correct number of clusters across different datasets. These validation results show that our combined method effectively addresses challenges related to overlapping clusters, increasing robustness and accuracy in identification. The approach seems to have potential for applications in high-precision image segmentation and analysis.

 View pdf
View pdf


Landslides pose a serious threat to human life and can cause substantial economic losses. It also consumes a lot of time and energy to deal with landslides. In order to address the occurrence of landslides, it is important to predict the probability of land- slides and assess the risk level. Since the occurrence of landslides is based on many factors, it is impossible for people to make an accurate judgment. Therefore, it is the best choice to train machines to help people to make predictions and risk assessment. In this paper, we discuss how to predict the occurrence of land- slides through random forests and assess the risk level according to the water content of the soil. The results show that the accuracy of prediction by Random Forest is very high. We will also predict future changes in soil moisture content to update the risk level assessment for real-time monitoring.

 View pdf
View pdf


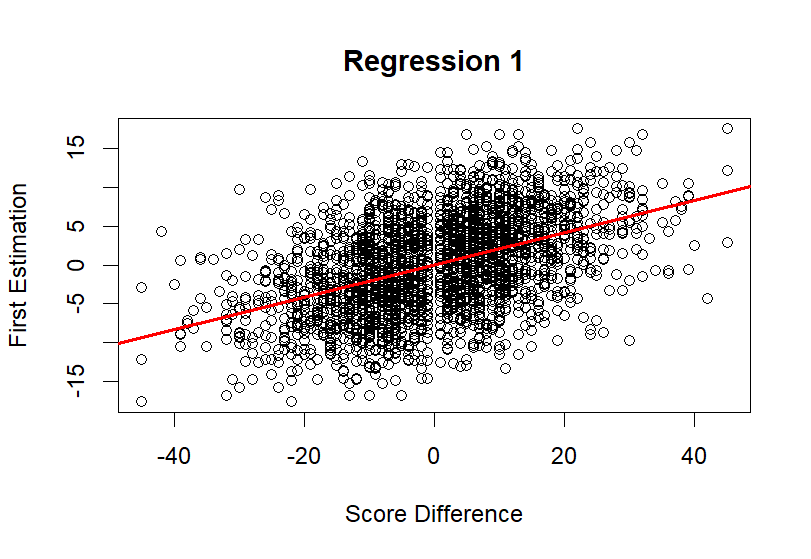
This research paper examines the diverse factors that affect score difference between teams in the NBA scene. With this intent, by utilizing data from the 2012-13 regular season, this research aims to develop a predictive model that can forecast the score difference between teams for the last 50 games of the season. Additionally, the same model can be expanded and used for many different seasons of NBA data. To accomplish this, the methodology implemented first involved a data collection process, where many years of injury data and NBA season data were gathered. Next, extensive cleaning was done so all the variable names matched, and only significant information remained. Then, by merging the injury data with data from the 2012-2013 NBA season, a larger, more comprehensive file was created. As last, through the use of regression modelling, a base model was created. In addition, factors impacting the score difference were considered and adjusted the model accordingly. To validate the final model’s prediction, actual score differences in the last 50 games will be compared to the differences given by the model, with statistical measurement methods to quantify the accuracy. By doing so, this research hopes to provide a more valuable system that produce insight towards basketball sports betting.

 View pdf
View pdf


In recent years, dialogue generation models have emerged as a prominent area of research, as a crucial role in the domain of natural language processing, garner significant attention from the academic community. Existing dialogue generation models predominantly emphasize human-computer interaction, however, various context-sensitive issues should not be overlooked inherent to the process. Consequently, this paper aims to summarize and categorize these context-sensitive processing issues. Firstly, based on extant literature, an overview of the current landscape of dialogue generation models is provided. Secondly, the definition of "sensitive" is clarified, and relevant scholarly works are briefly reviewed following the definition. Thirdly, previous methods addressing context-sensitive processing within dialogue generation models are directly categorized and their specific methodologies are briefly analyzed regarding this issue. Finally, pertinent research gaps and limitations are identified while future directions for research in dialogue generation models are proposed.

 View pdf
View pdf


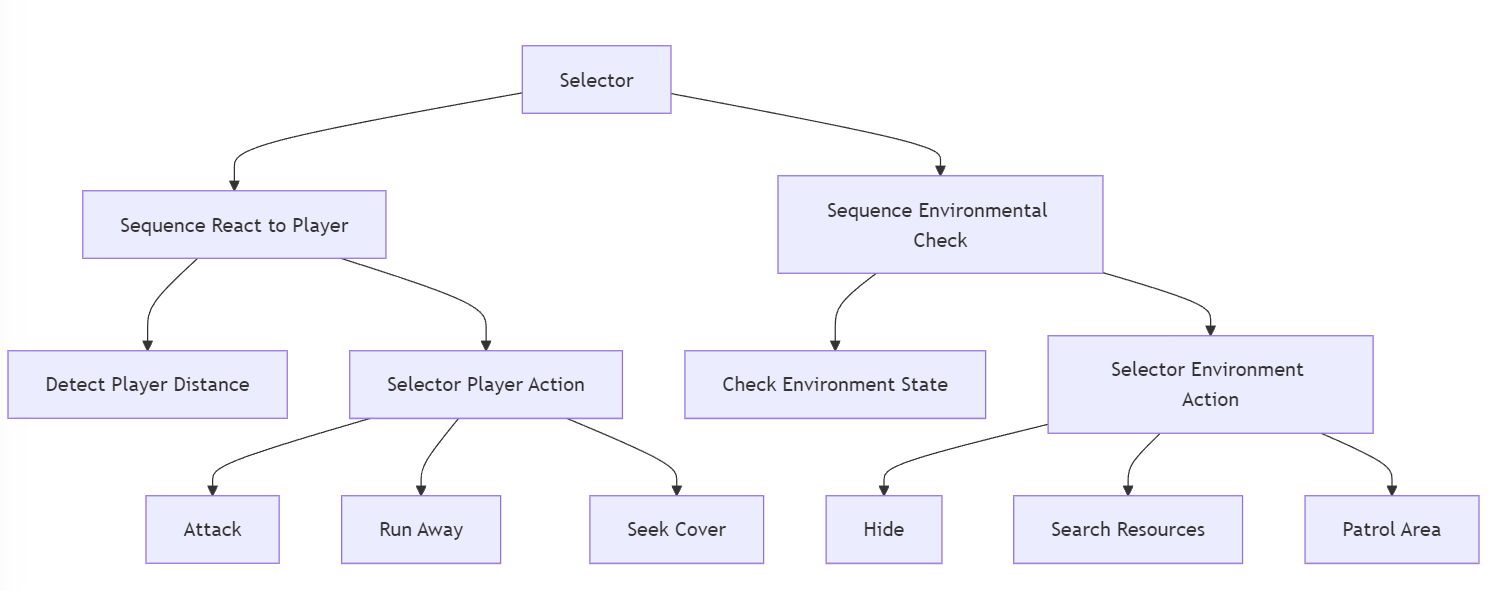
The purpose of this research is to improve the adaptability and intelligence of cooperative non-player characters (NPCs) in dynamic gaming situations. Although behavior trees (BTs) are commonly used to simulate non-player character (NPC) behaviors, their rigid hierarchical design restricts NPC adaptability in complex settings. This study employs a variety of optimization techniques, including evolutionary algorithms and hybrid strategies that combine Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) and Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS), to improve NPC adaptability. The findings reveal that these strategies enable flexible behavior transitions, with evolutionary algorithms strengthening BT's flexibility in decision-making scenarios and ANN and MCTS significantly increasing NPC intelligence and response capabilities. Furthermore, we highlight fundamental drawbacks in typical BTs, such as static node topologies, which may impede dynamic adaptation. These discoveries lay the groundwork for improving immersive gaming experiences, expanding the knowledge repository for NPC AI research, and providing vital insights into the development of more intelligent cooperative NPCs.

 View pdf
View pdf


Brain-computer interfaces have great potential in motor control and rehabilitation. In related research fields, how to effectively monitor users has always been a research focus. Many studies have found that the performance of brain-computer interfaces can be effectively improved by improving and integrating feedback methods. This article reviews the four main types of feedback currently available, including visual feedback, auditory feedback, vibration, and electrical stimulation in tactile feedback, and introduces their principles and applications. This article summarizes the improvements in experimental accuracy and efficiency brought about by these sensory feedbacks in research and finally proposes limitations and future development trends.

 View pdf
View pdf




