

Volume 143
Published on June 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Functional Materials and Civil Engineering
Low-altitude economy has prompted low-altitude transportation, a new public transportation mode, to bring new changes to citizens' daily travel. Low-altitude transportation has broad prospects. In low-altitude airspace, aircraft are used as vehicles to cover low-altitude flight activities such as manned and cargo. It has the advantages of alleviating ground traffic congestion and improving travel efficiency. The development of low-altitude transportation faces many challenges, such as inaccurate airspace resource management and lack of coordination in the life cycle of the entire industrial chain. Therefore, it is crucial to promote the reform of the management system of the entire civil aviation industry, accelerate the implementation of airspace classification management, improve service guarantee quality, and improve the service system for low-altitude flight activities. And with the help of big data analysis and artificial intelligence technology, optimize flight paths, improve flight efficiency, and reduce operating costs. Although facing many challenges, with policy support, technological innovation, and management optimization, low-altitude transportation is expected to be widely used and developed, injecting new vitality into the public transportation system. This article mainly discusses the integrated development of low-altitude transportation in the public transportation system, analyzes its definition, characteristics, application status and proposes optimization strategies for airspace management, technical bottlenecks, laws and regulations, and other restrictive factors. This article provides theoretical basis and practical reference for the future development of low-altitude transportation, promotes the healthy and sustainable development of low-altitude transportation, and brings changes to urban transportation.

 View pdf
View pdf


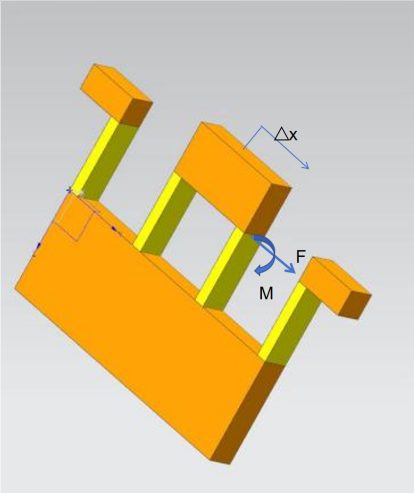
In recent years, precision motion systems have played an increasingly important role in scientific research and engineering applications. Among them, compliant mechanisms are typical enabling components for precise motion. Establishing models for compliant mechanisms is crucial for their design and analysis. In this paper, stiffness modeling is conducted for four typical compliant mechanisms: single parallelogram compliant mechanisms, mirrored single parallelogram compliant mechanisms, double parallelogram compliant mechanisms, and mirrored double parallelogram compliant mechanisms. To validate the accuracy of the proposed models, three-dimensional models of the compliant mechanisms were constructed using UG software, and finite element analysis (FEA) was performed using ANSYS software. The results demonstrate that the deviation between the theoretical stiffness and simulated stiffness of the four compliant mechanisms is less than or equal to 3.5%. The stiffness models developed for the compliant mechanisms lay a foundation for the design of complex compliant motion systems.

 View pdf
View pdf


At present, the new scientific and technological reform in the world is having a tremendous impact on the transportation industry, and the future development direction of the transportation field is the focus of the current research. In this context, Australia's transportation system is also in an important period of transformation in the direction of on-demand, low-carbon, network connection and automation. This paper studies and discovers Australia's existing achievements and problems in the field of transportation from three aspects: transport services, transport management and transport policy. Facing the development direction of Australian future transportation, the paper studies the strategic deployment, advantages and disadvantages, and upcoming challenges of Australian future transportation from the two main aspects of self-driving cars and intelligent transportation systems. In the aspect of building a powerful transportation country, learning and accepting the strategies of other countries with an open mind and continuously studying the ideas and progress of other countries in solving traffic problems can contribute to the construction and development of transportation in our country.

 View pdf
View pdf


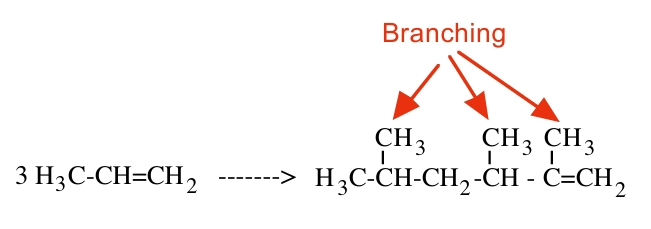
Fabric softeners play a pivotal role in maintaining clothing's comfort and softness. In modern formulations, cationic surfactants are commonly employed. However, both the manufacturing process and the final products of this industry have raised significant concerns leaving ample room for enhancement. The disposal of surfactants can cause damage to the environment and affect the health of organisms. Furthermore, the current fabric softeners also have side effects on the comfort of the apparel, such as causing skin irritation and making the clothes less thermally comfortable. This paper is dedicated to summarizing the mechanism of surfactants, analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of current products, and exploring the feasibility of using esterquats as an alternative. Through a concise literature review, this paper uncovers an area of uncertainty in the theories regarding how surfactants function. It also reveals the benefits of esterquats, such as biodegradability and flexibility, along with some lingering doubts. This paper concludes that there needs to be further research regarding the properties of esterquats to fill up the current literature gap as well as the potentialities of using other types of surfactants to substitute cationic surfactants in the production of fabric softeners.

 View pdf
View pdf


Tungsten and its compound, tungsten carbide, play significant roles in aerospace, aviation and friction welding fields. Through a systematic review and analysis of the literature, this paper summarizes the friction and wear characteristics of pure tungsten coatings from room temperature to high temperatures, the evolution of their microstructure, and the changes in tribological properties because of the formation of oxide films caused by alterations in the surrounding chemical environment at high temperatures. For tungsten carbide coatings, this paper summarizes their friction and wear processes, the formation of mechanically mixed layers, and their friction response in different environments (dry and lubricated)This research investigates the variation in the friction coefficient of pure tungsten across a temperature range from ambient conditions to over 1000℃, highlighting inconsistent trends between room temperature and 600℃. Additionally, the study addresses ongoing debates and outlines potential avenues for future research on pure tungsten and its composite coatings.

 View pdf
View pdf


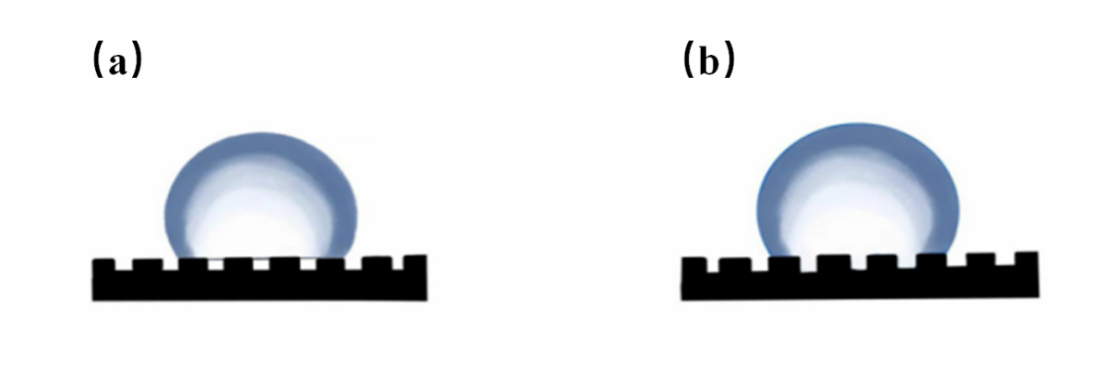
Superhydrophobic materials can realize the effective slippage of liquid on the surface, a with excellent properties such as self-cleaning and anti-pollution, they can be widely used in liquid transportation, anti-pollution coatings, microfluidic transport and other fields. In nature, organisms have evolved many special structures that adapt to their living environment, such as lotus leaves, water striders and other organisms with unique micro and nano structures, showing amazing water-repellent and self-cleaning properties. By studying and mimicking the microstructure of these biological surfaces, scientists have successfully prepared surfaces with excellent superhydrophobic microstructures. The paper will discuss the mechanism of superhydrophobic phenomena and introduce the applications of superhydrophobic materials in anti-icing, anti-oil, anti-fogging and self-cleaning. Finally, by reading the relevant literature, this paper discusses the future development of superhydrophobic materials, the preparation process of superhydrophobic surfaces is still relatively complex, and how to maintain the stability and hydrophobicity of the surface while simplifying the hydrophobic preparation steps is a key challenge for researchers.

 View pdf
View pdf


Proteinogenic amino acids – the primary monomers to form proteins on Earth – have been found successively in extraterrestrial areas over decades. It was reported that the detection of amino acids can be both ex situ and in situ. The discovery of proteinogenic amino acids from space may date back to the history of the solar system and is suggestive of alternative mechanisms of synthesizing amino acids. This article uses the literature review method and systematically summarizes the findings from meteorites, asteroids, comets, and the interstellar medium. The article concludes that complex organic molecules are widely spread across the universe and supports the hypothesis that the basic building block of life may be delivered to Earth via celestial bodies, increasing the likelihood of searching for living organisms outside Earth.

 View pdf
View pdf


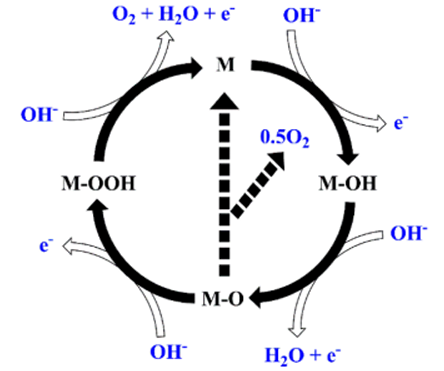
With the surge of energy demand and the aggravation of fossil fuel shortage, the development of efficient and clean energy technologies has become a research hotspot. Hydrogen production from electrolyzed water has attracted much attention due to its advantages of high purity and environmental protection, but its core catalyst still relies on the precious metal platinum (Pt), which has bottlenecks such as high cost and poor stability. This paper systematically reviews the research progress of electrocatalysts in hydrogen production from electrolytic water, focusing on the optimization strategies of noble metal-based catalysts and the breakthrough results of non-precious metal-based catalysts. It is shown that the diatomic catalysts can significantly enhance the catalytic activity through synergistic effects, while the transition metal-based materials exhibit hydrogen precipitation performance close to Pt in alkaline media. In addition, transition metal-nitrogen-carbon (M-NC) composites have become an important direction for replacing precious metal catalysts due to their high stability and low cost. However, the issues of catalytic activity site modulation, scale-up preparation and acidic environment adaptability still need to be further explored. This paper provides a theoretical reference for the design and optimization of electrocatalysts to help the practical development of electrolytic water to hydrogen technology.

 View pdf
View pdf


Heat pump systems, recognized for their energy efficiency and low-carbon footprint, are pivotal in advancing the global shift toward sustainable energy. This research focuses on a thorough comparative analysis of three primary heat pump systems: air-source heat pumps (ASHP), ground-source heat pumps (GSHP), and water-source heat pumps (WSHP).The research begins with the fundamental theory of heat pump technology, then delves into the core technical characteristics, suitable application environments, and actual performance of each type of heat pump, highlighting their unique strengths and potential drawbacks. Air-source heat pumps are flexible to install and cost-effective but experience reduced efficiency in low-temperature environments; ground-source heat pumps provide excellent energy efficiency and consistent performance, though they involve greater upfront costs and are influenced by geological factors; water-source heat pumps have the highest efficiency but are constrained by hydrological conditions and may impact the ecological environment. Through these analyses, this study aims to contribute to the sustainable development and widespread application of heat pump technology, providing researchers and engineers in the field with a comprehensive and detailed evaluation report.

 View pdf
View pdf


Graphene-based antifreeze and deicing materials have demonstrated significant potential in antifreeze and deicing applications due to their exceptional electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, high specific surface area, and outstanding mechanical properties. These characteristics enhance thermal conversion efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and improve environmental adaptability. Current research primarily focuses on developing graphene-based composites by integrating polymers, metals, ceramics, and other materials to enhance their mechanical and thermal properties. Additionally, the exploration of environmentally friendly and cost-effective fabrication methods has become a key research direction. Future advancements in this field will emphasize optimizing the stability, durability, and cost-efficiency of these materials while expanding their applications in renewable energy sectors, such as the prevention of ice formation on solar panels.

 View pdf
View pdf




