

Volume 6
Published on August 2023Volume title: Proceedings of the International Conference on Modern Medicine and Global Health (ICMMGH 2023)
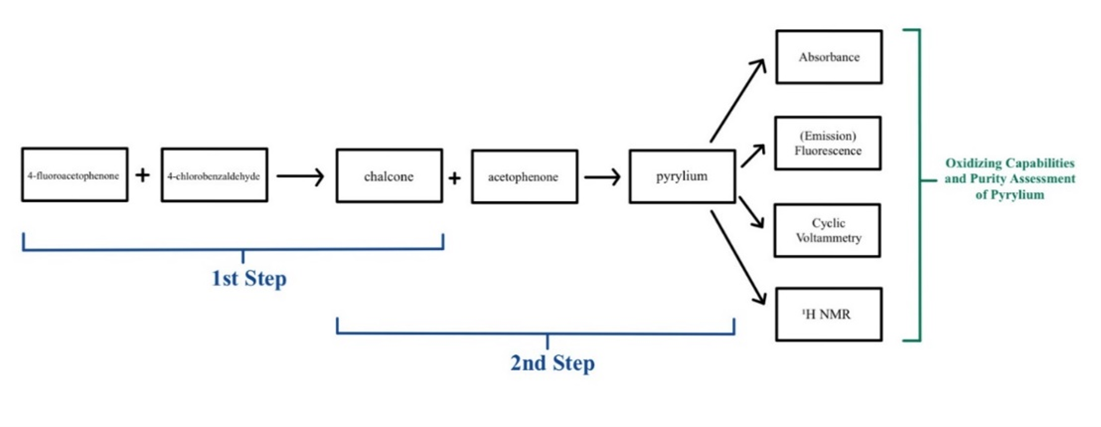
Photoredox catalysis is a relatively new concept, and it involves the absorption of light for more productive use of lower energy radiation and to catalyze selective reactions. Traditionally, catalysts used for oxidation or reduction reactions were metal catalysts, such as iridium. However, these metal catalysts are not environmentally friendly and are expensive, prompting the use of organic catalysts. Pyrylium salt, an organic catalyst, can be used as a catalyst. However, the oxidizing ability of basic pyrylium is not that good and can still be improved. In this project, a pyrylium salt with substituents that include fluorine and chlorine (halogens) was synthesized to boost its oxidizing ability in an alcohol oxidation reaction due to its electron-withdrawing groups. Despite unsuccessful oxidation, there is still much research to prove that it can substitute for metal catalysts.

 View pdf
View pdf


Obesity is a prevalent disease found among adolescents in the United States. The rising incidence in recent years has raised concerns among the public, for obesity is known as the risk factor for several chronic and severe diseases. Programs aimed at treating and preventing childhood obesity are therefore in high demand. Since the enrollment of American youth–who are between 5 and 17 years old–in schools is higher than in any other institution in the United States, schools can implant effective obesity-targeted programs by providing cheap, convenient, and accessible settings for treating and preventing obesity for the student population. This article will review and analyze the success of primary preventive initiatives implemented in schools by comparing the effectiveness of four out of eight components of am integrated comprehensive model for school-based prevention of obesity: physical education courses, food service and nutrition environment, school-site health promotion, and health service. At the end of this article, a future research plan will be introduced. A sample of 154 residential students from a local high school located in Fryeburg, Maine will be observed and surveyed to test the effectiveness of the school-based primary prevention model for obesity.

 View pdf
View pdf


Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is one of the most common, frequent, age-related diseases, and it is also an important cause of chronic renal failure and end-stage renal diseases. It has always been one of the research hotspots. The high cost of treatment will bring a great burden to society and families. Therefore, it is very important to study the pathogenesis and treatment methods of DN. At present, many methods have been put forward for clinical diagnosis and treatment like Thiazolidinediones, renin inhibitor drug -aliskiren, tregs cells. These methods have their own advantages and disadvantages. However, the etiology of diabetic nephropathy is complicated and the course of the disease is long, and current treatments cannot achieve the expected target. Scholars also have studied many symptomatic treatment methods for different pathogenesis. However, the specific pathogenesis of DN has not yet been fully elucidated, and there is no special medicine for DN yet. This article briefly reviews the pathogenesis and treatments of DN based on the existing kinds of literature and new advances to provide some references for its clinical diagnosis and treatment.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the biological lab of Zhejiang University, we justified and tested a type of bacillus to improve the anti-bacteria ability of commonly affecting diseases of fruits, such as pear and grape, which would lead to a large amount of economic loss and unpredictable negative influence if they were rotten before being sold. Using techniques such as gram staining and bacteriostasis test, this paper explores and confirms the results that bacillus sp. 22T has a strong ability to inhibit the growth of penicillium expansum on pear and grape. After 96 hours of exposure to fermentation broth containing bacillus sp. 22T to suppress the growth of penicillium expansum, 33.33 percent of pear and 16.66 percent of grape were not impacted by the bacterium.

 View pdf
View pdf


This article will summarize the results of recent years of exploration into deeper causes of Alzheimer’s disease with possible therapeutic strategies. The most popular pathological hypothesis for the causation of Alzheimer’s is the Aβ cascade hypothesis. Aβ has a dominant role in the pathophysiology of Alzheimer’s disease, according to genetic and pathological data. Another significant histological characteristic of Alzheimer’s disease brains is the presence of neurofibrillary tangles made of the protein tau, which is related with microtubules. In the brain, neuronal loss, neuroinflammation, and oxidative stress can result from the cascade consequences of tau toxicity. But as research has progressed, it has been found the Aβ. The accumulation of protein and neurofibrillary tangles composed of phosphorylated tau are only manifestations of AD, not the result. This is also the reason why many drugs fail the phase III clinic. So people began to look for a way out of the problem, starting in the direction of the gene. How to diagnose AD early in the MCI stage, how to find markers for early diagnosis and how to inhibit the progression from the MCI stage to the dementia stage are all questions that need to be investigated in the future.

 View pdf
View pdf



Since the beginning of 2020, COVID-19 has swept the world and continues to threaten human society. Forecasting the future trend of the epidemics is very important for the prevention of COVID-19. The SIR model is an important mathematical model to forecast future epidemic in epidemiology. In a press conference from London on July 5th, British Prime Minister Boris Johnson said the British government will end nearly all of the coronavirus restrictions starting July 19. This paper aims to use the SIR model to predict epidemics after deregulation of social distance. The results show that as of July 8, 2021, the number of people infected will continue to increase after deregulation, reaching approximately 30000 per day. The British government should reconsider completely liberalizing epidemic control.

 View pdf
View pdf


Fluorescent probe technology was discovered in the 19th century and imaging techniques were applied to microscopy around 1670. Fluorescence microscopic imaging is a classical method for observing the structure of organisms in the life sciences. In this regard, single-molecule fluorescence imaging uses fluorescent probes to label, detect, and analyze individual molecules, helping scientists to clearly observe the activities of individual molecules without disrupting the normal physiological state of the organism. In this paper, the principles and applications of fluorescent probe imaging techniques are described and analyzed. The common detection methods of fluorescent probes are spectrophotometry, electrochemistry, atomic absorption spectroscopy, high performance liquid chromatography, and fluorescence spectroscopy. Rapid detection results can be obtained depending on the specific method.

 View pdf
View pdf


Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a well-known mental illness and memory loss is its most common symptom. Until now, the reason of AD has been an unsolved mystery, with the two most prominent previous hypotheses being β-amyloid deposition and Tau protein phosphorylation. However, this year, a seminal paper studying the β-amyloid precipitation hypothesis was found to be falsified, therefore, a large number of scientists have questioned the research value of this hypothesis. This paper is a review of the β-amyloid precipitation hypothesis. The development of β-amyloid precipitation hypothesis is described and previous studies on Aβ*56, Aβ42, and Aβ40 are reviewed. It is concluded that β-amyloid precipitation should continue to be studied. The author also argues that the falsification does not mean that the "amyloid" hypothesis is wrong; the only protein suspected of falsification is Aβ*56. The Aβ hypothesis can still be pursued because there are many other Aβ oligomers that have been shown to be neurotoxic.

 View pdf
View pdf


Asthma is one of the common chronic diseases in children, and so far there is no cure for asthma. Asthma sufferers are estimated to be more than 300 million people worldwide, and the number of asthma treatments is growing every year. In recent years, thanks to advances in therapeutic medicines, asthma symptoms can now be successfully controlled with inhaled corticosteroids and, if necessary, in combination with bronchodilators. However, even with maximum use of these drugs, the effect may be insufficient, and there are still some patients with refractory asthma that are not adequately controlled with general treatment. Drugs called biologics may become a drug that works well for previously poorly treated asthma and is recently available in children with severe asthma. Three biologics are currently available for use in children: omalizumab, mepolizumab (6 years and older), and dupilumab (12 years and older). However, there is still a lack of clinical research evidence for the specific clinical improvement rate. Therefore, in this study, this paper conducted a literature review on the latest clinical trials of biological agents at home and abroad, summarized the clinical trials of common biological agents, and introduced the latest treatment methods. The differences and deficiencies between each other achieve the effect of enhancing the prevention and cognition of asthma.

 View pdf
View pdf



Generally, a new targeted medicine takes a long time, usually 5 to 15 years, from the discovery and validation of its target to its actual use in treating a disease. There is no doubt that steps such as target validation and target evaluation are essential in preclinical development of new drugs to ensure safety, bioavailability, and efficacy of the drug, and in the target validation phase, RNA interference (RNAi) is a very important method. RNAi drug has double-stranded RNA function, so the targeted mRNA of a specific gene sequence is degraded, its transcription process is abnormal, which leads to gene silencing, and related protein synthesis failure. RNAi technology could specifically shut off specific genes, and, it is a targeted drug with great potential. Therefore, RNAi technology can be used to treat some rare diseases, such as acute hepatic porphyria (AHP) in adults, by using drugs as carriers. In 1998, Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello first defined the RNAi phenomenon and was honored with the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2006 for their discovery of RNAi and their outstanding contributions to the field of gene silencing. Since then, RNAi drugs have been studied by pharmaceutical scientists around the world, but many of the previous drugs have been stopped at the evaluation stage due to their chemical instability. Until October 2018, the world’s first RNAi drug (patisiran) was successfully marketed so that the RNAi drug development became popular again because of remarkable pesticide effect.

 View pdf
View pdf




