

Volume 45
Published on July 2024Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Modern Medicine and Global Health
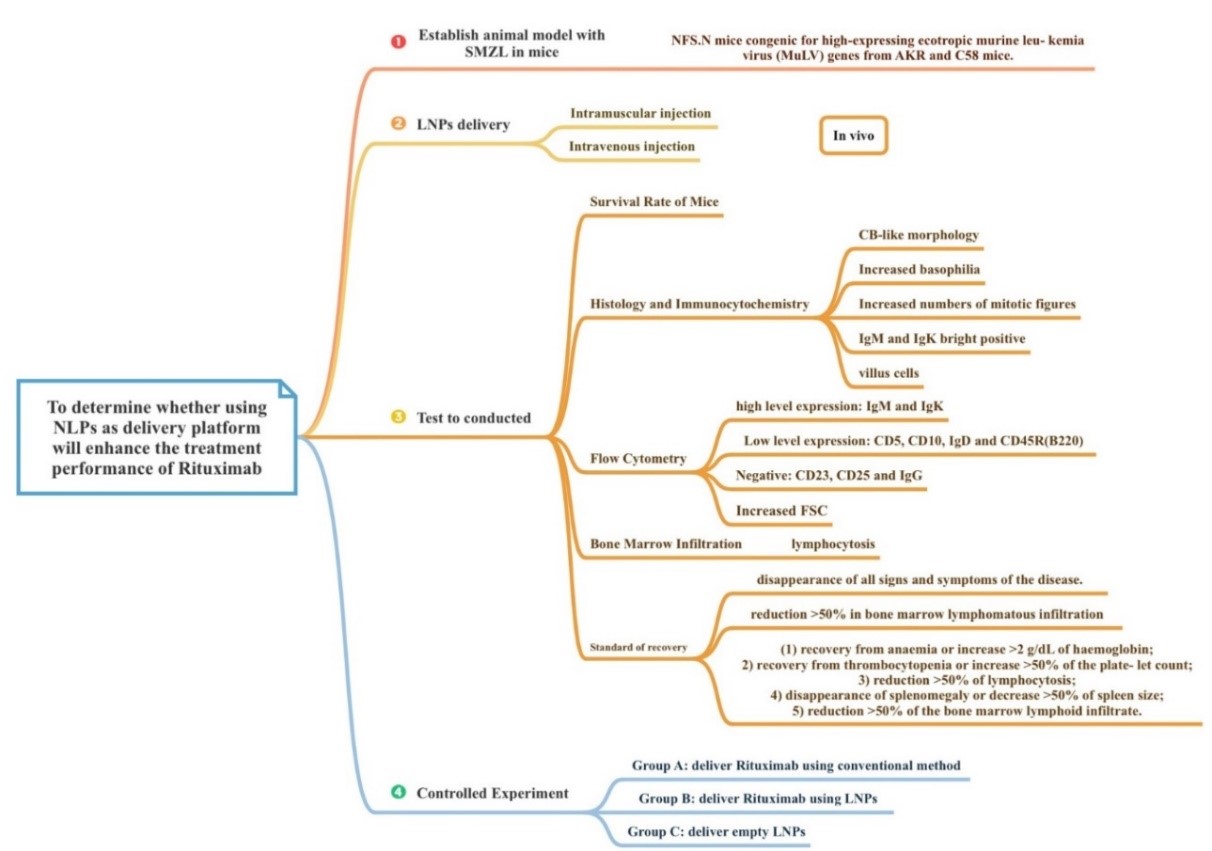
Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma (SMZL) is a low-grade B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma from which patients may suffer anemia, autoimmune disorder and splenomegaly respectively. Due to its chronic nature, it has been increasingly hard to identify and treat effectively. The study establishes an SMZL mouse model and explores the potential of enhancing Rituximab treatment using Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs). Designed experiment includes how to establish the NFS.N mice model, characterization of the disease on mice and recovery standard of mice. First, SMZL mice model is establish followed by histology and immunocytochemistry investigation which looks directly at the mice’’s lesion. Then flow cytology is carried out which looks at the expression level of IgM, IgK, CD23, CD45 etc., before bone marrow infiltration is carried out. A controlled experiment of three groups of mice is designed, including mice treated with conventional Rituximab, delivery with LNPs and delivering empty LNPs, respectively. The effect of LNPs on treating mice SMZL is investigated. And some expected results and analysis methods were also discussed alongside with recovery standard. This experiment aims to provide theoretical support to the development of more effective and targeted therapies for this specific type of lymphoma. However, this is only an design rigorous experimentation strengthens the scientific validity of these findings.

 View pdf
View pdf


Schizophrenia affects about 1% of the total population. It is a complex psychological disorder that may be caused by the interaction between genetic and environmental factors. Studies have identified some candidate genes that may contribute to the cause of the disorder. However, most genetics finding in schizophrenia have not been implicated in clinical use. Antipsychotics are drugs commonly used to treat psychosis, such as schizophrenia. First-generation antipsychotics, or typical antipsychotics (e.g. haloperidol), were the first type of medicine for psychosis that was developed. They mainly target dopamine D2 receptors in the basal ganglia and possibly the mesolimbic pathway as antagonists. Second-generation antipsychotics, or atypical antipsychotics, including clozapine, were developed after typical antipsychotics. They have multiple targets and cause less extrapyramidal side effects. Since atypical antipsychotics target multiple receptors, the complexity of these drugs is extremely high, and we now do not have a solid understanding of their mechanism of action.

 View pdf
View pdf


As a result of covid-19, children with autism have experienced a substantial increase in screen time at home. This study delves into a dataset from Italy, exploring the impact of the severity of a child's doctor's diagnosis of autism on the child's choice of online activities and on the improvement of social interaction and behavioral problems. Results showed that television viewing was most strongly associated with these core symptoms, and that most children with varying severity of symptoms showed some improvement in social interaction and behavioral problems through watching TV.

 View pdf
View pdf



Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a series of depressive symptoms mainly caused by abnormalities in the patient’s genetic system or dramatic changes in the acquired environment. Specific autobiographical memories can be difficult to retrieve due to a phenomena known as overgeneral memory (OGM).Parental depression increases the risk of cognitive vulnerability in offspring, a type of cognitive vulnerability associated with the intergenerational transmission of depression .Only the potential effects of motherly depression on the development of OGM in descendants are examined in the current study; however, we had little acquaintance about the prospective impressions of paternal depression on the development of OGM in offspring. We can conduct an assessment for children aged 8 to 14 who lived with their parents every 6 months in 2 years. A complete assessment of whether the fathers with MDD history should be conducted in the beginning, the study was grouped by this followed by comparing the results with the current social data to draw a conclusion. This paper only provides theoretical experiment design and possible results about how paternal MDD history and depressive symptoms affect offspring OGM, which needs further research in the specific social samples. We try to find how paternal MDD history and depressive symptoms affect offspring OGM, and find ways to prevent adolescent depression.

 View pdf
View pdf


Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a superbug that is resistant to multiple antibiotics commonly used in medication and has caused severe infections in humans for hundreds of years. This review examines the MRSA drug resistance mechanism and compares the efficacies between two antibiotics, daptomycin and vancomycin, in treating MRSA infections. The resistance mechanism of MRSA alters the structure of inactivating the antibiotics. Therefore, the MRSA resistance to daptomycin and vancomycin is analyzed to show how MRSA reacts to different antibiotics preferred in therapy. Moreover, the efficacies of two antimicrobial drugs were analyzed by the research and data from journals and magazines. Combined with rifampin, two antibiotics show more potent efficacies with fewer doses, and could be an alternative therapy to conventional individual antibiotics only.

 View pdf
View pdf


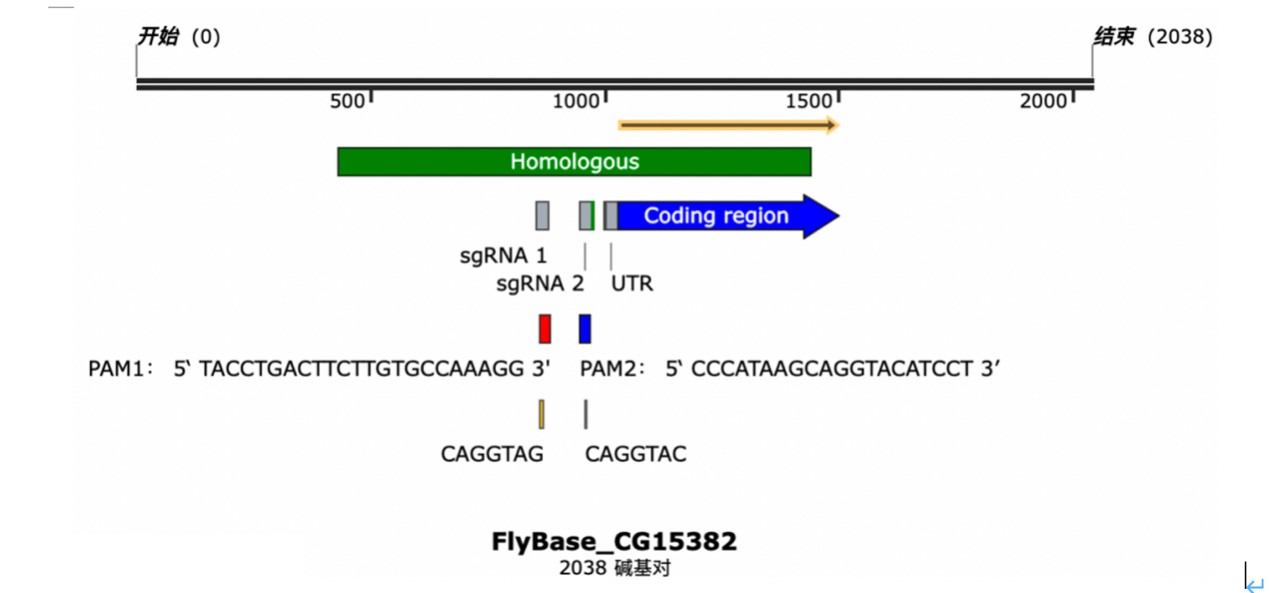
Zelda protein (Zld) is a transcription factor in drosophila. It binds on specific sequence to activate the expression of genes involved in the early development of drosophila, which hinted a method to study the function of these genes. Since the expression of genes can be regulated by Zld, mutation of Zld binding site can be used to silence target genes. Three base pairs were substituted by using CRISPR-Cas9 editing. The function of target genes in the development process can be studied by comparing wild type drosophila and the Zld absent mutant (Zld-). This paper will focus on CG15382 and discuss the design of the mutant drosophila.

 View pdf
View pdf


Bioelectronics is an interdisciplinary field that merges principles from biology, electronics, and materials science to develop innovative devices and technologies that interface with living tissues and organisms. It focuses on creating electronic devices that interact with biological systems. A cardiac pacemaker is a distinct implantable device that can be helpful to cure heart diseases. However, traditional materials used in cardiac pacemakers are mostly alloy which causes foreign body reaction (FBR) at a high level. Hydrogels are a class of soft substances that show outstanding biomimetic properties in biological tissues. Their elevated water content, mechanical properties, and porosity similar to extracellular matrix pave the way to support cell growth and proliferation. Here in this article, we introduce the advantages of using hydrogels in bioelectronics and review the state-of-the-art and modern methods utilized to alter the properties of hydrogels to improve their properties aiming to be conductive, non-swelling, and self-healing.

 View pdf
View pdf


Nowadays, food packaging is the most essential part in the food industry, as it is the key part to stop food from contamination. In the 20th century, most of the food package used plastic products. However, it turns out that it contains lots of problems, especially for the natural environment, as it can hardly finish degradation. As a solution of this, many scientific researchers state the proposal of biomaterials due to lots of advantages, such as recyclability, degradability and sustainability. Actually, there are various types of biopolymers for food packaging, like polysaccharides and proteins. To be more specific, biopolymers like tannic acids, chitosan and nano-chitin get the most potential.

 View pdf
View pdf


Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurological disorder that causes the buildup of amyloid-beta plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in the brain. One key mechanism designed to mitigate the buildup of these misfolded proteins is the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS). In healthy individuals, the UPS marks these amyloid-beta plaques and neurofibrillary tangles with ubiquitin markers, facilitating their subsequent degradation by the proteasome complex. The UPS is critical for the degradation of the proteins, and its dysfunction has been observed in AD. In this paper, a potential treatment for diminishing dysfunction of the ubiquitin-proteasome system is composed for Alzheimer’s disease individuals. This research paper explores the correlation between impaired UPS and AD, focusing on its role in degrading damaged proteins. The paper also collects evidence suggesting that enhancing the ubiquitin-proteasome system can have a positive impact on clearing amyloid-beta plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. Additionally, potential UPS-based treatments for AD, such as PA28 activators and natural compounds, are investigated.

 View pdf
View pdf


Down syndrome is a disease that has relations with Alzheimer’s disease. In this work, it mainly focus on the mechanism of additional 21st chromosome in Down syndrome patients causes the rise of Aβ protein (a protein would cause Alzheimer’s disease). Two diseases that would reduce the life expectancy and loss of memory. This paper also discuss the exist therapy for curing Alzheimer’s disease in Down syndrome by choline supply during pregnancy, using acetylcholinesterase for inhibiting and secondary prevention in experiment on Ts65Dn mice. Results show that though the samples size is small, some side effects are caused and there is no specific results show that those therapies is also useful in clinic trials, the great success is achieved in animal lines (near 50% to 60% of success). These therapies can play a significant role in the future and it can reduce the impact of Down syndrome and Alzheimer’s disease in patients.

 View pdf
View pdf




