

Volume 50
Published on November 2024Volume title: Proceedings of ICBioMed 2024 Workshop: Workshop on Intelligent Medical Data Analysis for Precision Medicine
The perinatal period can be a challenging and difficult time for many women, during which they experience a shift in their social roles and a gradual transition to motherhood. Perinatal depression (PND) is one of the most common perinatal mental health conditions that jeopardizes mental health. health. Electronic database searches were conducted to find suitable papers; these publications included risk factors for perinatal depression, interventions, limitations and perspectives of interventions, and finally the information was extracted for narrative synthesis. Personal psychiatric history and addictive behaviors, mother-infant and husband conflicts in the family, economic and employment in the society and teenage pregnancy were associated with the risk of developing the disease. Medication and psychotherapy, providing professional help and family-centered care, improving the health care system and psychological screening and education, and providing social support were effective solutions. Perinatal depression is an important global public health problem that deserves some attention from individuals, families, and societies.

 View pdf
View pdf


Hamstring injury (HSI) is one of the most common injuries in competitive sports, the recurrence of this injury is high, which has a huge impact on the athlete's return to the game. Muscle strength, flexibility, muscle fatigue and age may contribute to damage to the hamstring. Current studies have shown that some static stretching, proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF), warm-up and rest before and after the game, and the use of equipment such as foam shaft can effectively improve flexibility and prevent injuries, and hamstring strength training can also prevent injuries. The acute phase after injury can be managed by P.R.I.C.E principle to avoid aggravation of injury. This paper describes the dissolving structure, injury mechanism, risk factors, preventive measures and treatment of the hamstring muscle by citing literature and has a more comprehensive understanding of the prevention and treatment methods of hamstring muscle injury and provides some suggestions for athletes and rehabilitation therapists.

 View pdf
View pdf


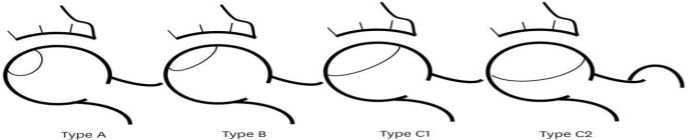
Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head (ONFH) is a kind of illness symbolized by the presence of a necrotic bone lesion in the femoral head. It usually caused by blood supply block in this area. Its pathogenesis usually is divided into traumatic pathologeny and non-traumatic pathogeny group, but this doesn’t have much influence on subsequent therapy. ONFH can last for several years, cause huge economic and mental stress for patients and their family, some useful treatments also can cost tens of thousands of dollars, while they also have some sequelas. The therapeutic schedule usually influenced by gender, age, physical condition, financial situation, and psychologic status. Because of some more and more common high-risk factors, like glucocorticoids, intemperance and immune diseases, the incidence of the population showed a trend of younger, that is why it has gained more attention than the last century. This article mainly focuses on high-risk factors, pathological diagnosis and stage, and common treatments. Combining with fast changing treatments, the doctors and patients choose a suitably personal therapeutic method together has become a prevalent tendency.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the popularity of national fitness campaigns, sports injuries, especially lower limb injuries such as anterior cruciate ligament tears and ankle sprains, are increasing year by year. There are limitations in traditional treatment such as muscle atrophy. In recent years, the blood flow restriction training method (BFRT) which simulates high-intensity exercise with low intensity and limits arterial and venous blood flow to promote muscle growth and strength enhancement, has drawn attention as a novel approach to rehabilitation. This article reviews the application of BFRT in the rehabilitation of lower limb injuries, discusses its effects on muscle function, pain management and quality of life, and evaluates its safety and prospects for clinical application. BFRT reduces mechanical stress, relieves pain, improves endurance and aerobic capacity, and improves cardiovascular function. However, there are discomfort and potential risks, such as muscle injury and thrombosis, which require individualised adjustments and standardised training. BFRT has shown positive result(reducing pain &oedema and improving function)s in rehabilitation of ACL reconstruction (ACLR) and chronic ankle instability (CAI). In addition, BFRT has been shown to aid in the functional recovery of the lower extremity in patients with Achilles tendon injuries and strokes. Despite the positive effects of BFRT, relevant studies have problems such as small sample sizes and non-uniform parameters. BFRT is considered a safe training modality, but contraindications should be examined before clinical application. Future research endeavours should investigate the impact of BFRT in many rehabilitation contexts and enhance tailored rehabilitation strategies. In order to maximize the therapeutic benefit, a rehabilitation training program should be developed and refined with a minimum effective dose based on the quantification of the in vivo physiological response to BFRT. The identification of the optimal prognostic approach will help to advance the standardisation of BFR treatment methods.

 View pdf
View pdf


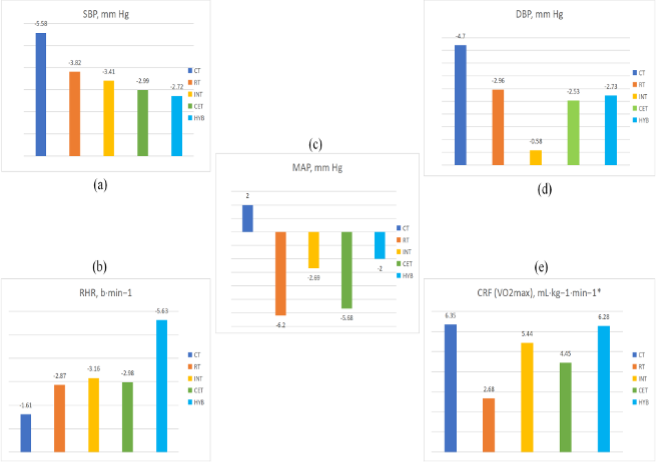
Since the 1960s, sedentary behavior has been on the rise globally. Modern culture is characterized by sedentary behavior (SB), which has become a distinct risk factor for non-communicable illnesses. Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are rapidly spreading around the world. A growing body of research has established the significance of SB as a risk factor for the onset of CVD. Additionally, blood lipoprotein (BL), blood pressure (BP), blood glucose (BG), and endothelial function (EF) are among the CVD risk variables that SB may significantly affect. Chinese scholars have not paid enough attention to the harm of SB to CVD, which needs urgent attention. Physical activity (PA) can improve the health of sedentary people. Increased PA may be able to counteract sedentary-induced CVD events, as analyzed by the study. In particular, a multi-component approach to exercise can significantly enhance cardio-metabolic health. Therefore, people may choose PA control as a means of reducing the incidence of CVD.

 View pdf
View pdf


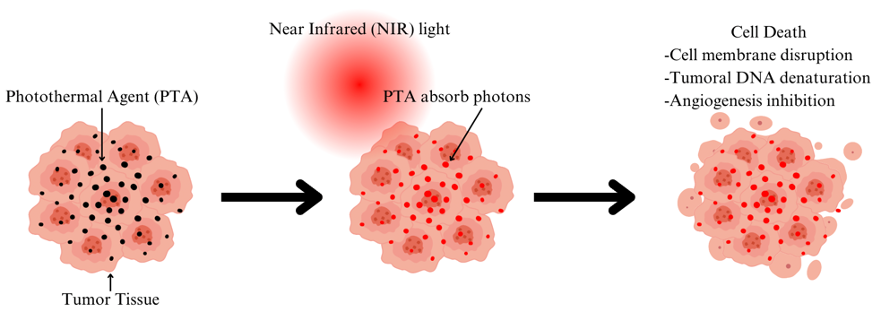
Breast cancer is the most often diagnosed cancer in women and the second largest cause of cancer mortality worldwide. Photothermal therapy (PTT) has emerged as a viable cancer treatment that uses near-infrared (NIR) light-absorbing chemicals to selectively heat and destroy tumor cells while sparing healthy tissue. PTT has advantages such as high specificity, little invasiveness, and efficient tumor ablation. Recent advances include developing imageable photothermal agents to aid in therapy planning. This review focuses on the function of carbon nanoparticles in PTT, investigating their processes and advantages and analysing in vitro and in vivo investigations. Carbon nanomaterials like carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and graphene have a large surface area, great electrical conductivity, and biocompatibility, making them ideal for PTT. Carbon nanomaterials absorb NIR light, enabling deep tissue penetration and targeted heating of tumor tissues, resulting in necrosis and apoptosis. Carbon nanomaterials also increase tumor vascular permeability, which promotes chemotherapeutic drug accumulation and improves treatment results. Repurposing carbon nanomaterials for increased PTT is a potential method because of its capacity to target various pathways, select cytotoxicity against cancer cells, and synergistic effects with other anticancer drugs.

 View pdf
View pdf


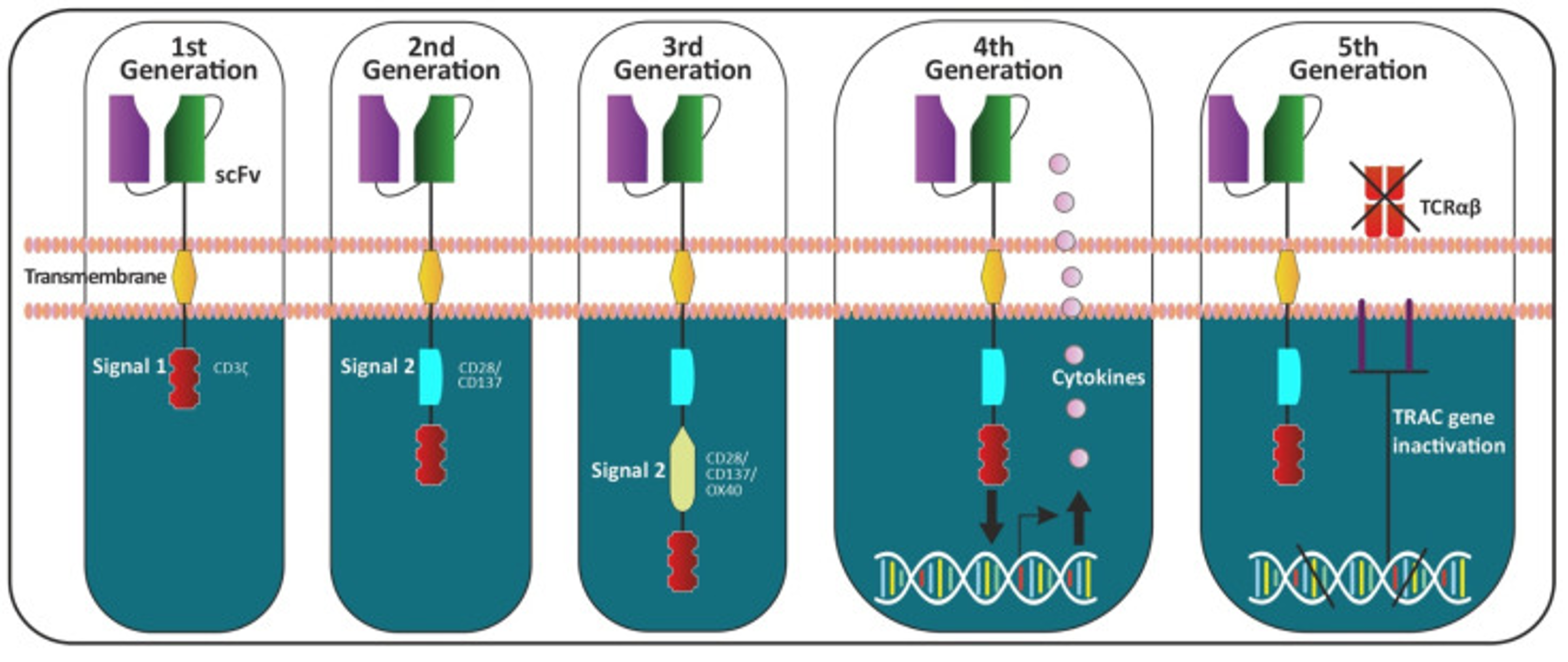
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML), a malignant clonal disease originating from hematopoietic stem cells. In the past few decades, AML treatment has been dominated by a "3+7" regimen (anthracyclines + cytarabine), and the survival curve has stagnated. However, these procedures are associated with serious adverse effects. The development of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell treatment provides a viable alternative, with decreased non-relapse death rates. Despite its potential, CAR-T cell therapy for AML confronts significant obstacles due to the disease's heterogeneity and accompanying toxicity. Genetic alteration strategies are being investigated to improve its safety and efficacy. Engineering CAR-T cells to express inhibitory receptors or suicide genes can help regulate T cell activity and prevent excessive immune activation. In summary, while CAR-T cell treatment has promise for AML, overcoming its hurdles through genetic modification and target refining is crucial. This review focuses on the existing landscape and future directions of CAR-T cell treatment for AML.

 View pdf
View pdf


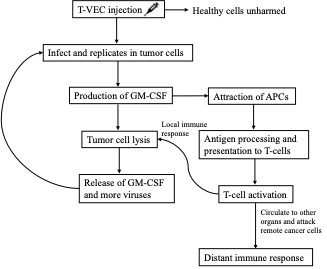
Over the past several decades, immunotherapy as a novel cancer treatment has made tremendous progress. Several categories of immunotherapy have emerged, all designed to stimulate the patients’ immune system to fight cancer. Cancer vaccines, specifically virus-based cancer vaccines, is a subcategory of immunotherapy that can trigger both innate and adaptive immune response by targeting tumor-specific and tumor-associated antigens. This review summarizes the mechanisms of different types of virus-based cancer vaccines, including inactivated/live attenuated/subunit vaccines, oncolytic virus vaccines, and viral vector vaccines. Furthermore, this review introduces the clinical applications of virus-based cancer vaccines, including oncolytic virus vaccine T-VEC against metastasized melanoma, and Pexa-Vec and PROSTVAC that are currently in clinical trials. Virus-based cancer vaccines have shown encouraging results in numerous studies in enhancing overall survival, relapse-free survival, and overall response rate among patients with solid tumors. This review underscores the necessity for future research aimed at improving the efficacy of virus-based cancer vaccines and investigating combination therapies with other immunotherapies to achieve optimal treatment outcomes.

 View pdf
View pdf


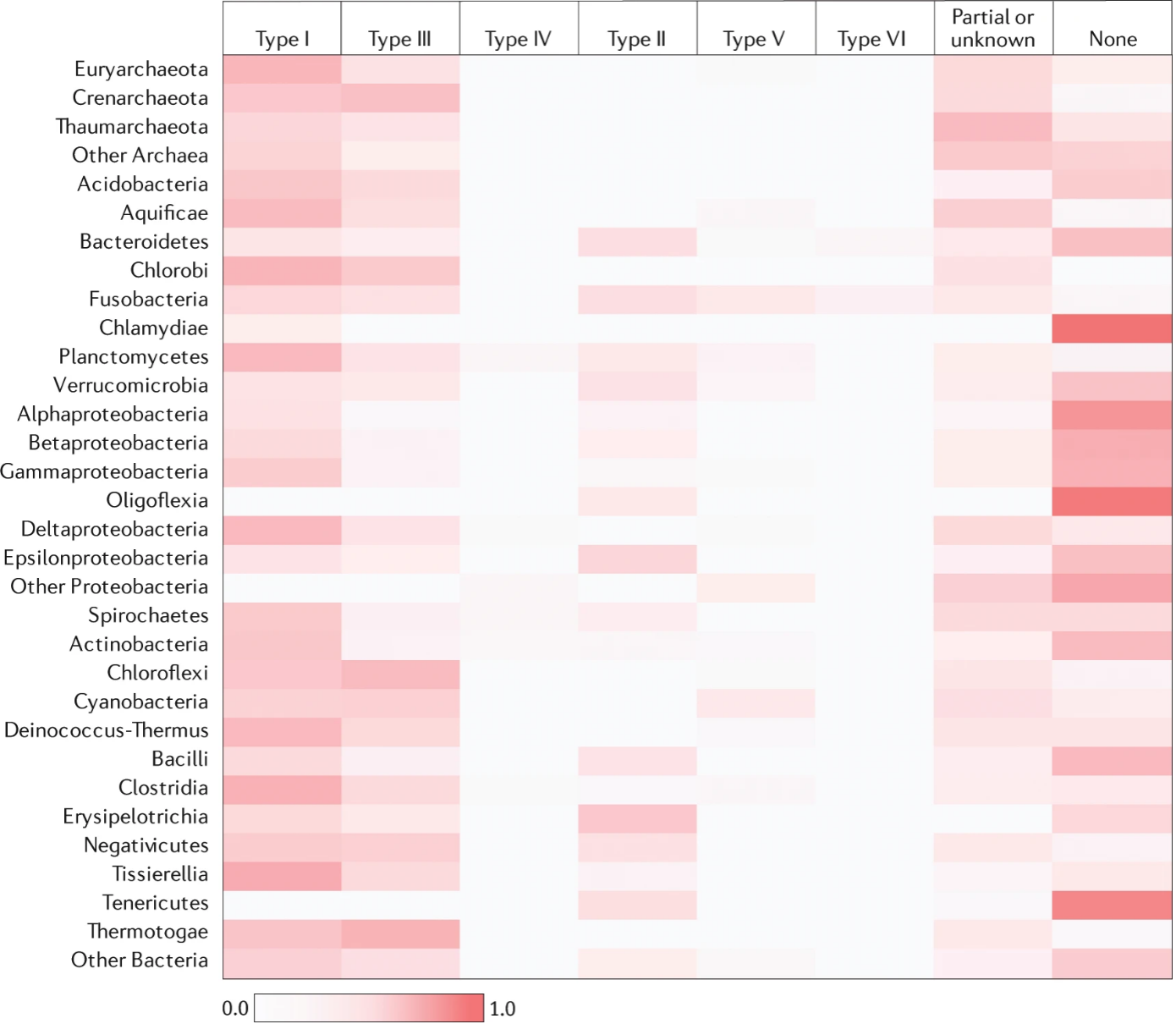
The Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR) system is an adaptive immune system derived from bacteria which is designed to recognize and cleave invading DNA, such as viruses and plasmids. The advent of this innovative gene-editing technology has emerged as influential force in the category of medicine, delivering unprecedented precision in targeting and modifying genetic material. This review explores the potential and challenges of CRISPR in the context of human diseases. Specific applications in diseases affecting hemoglobin, muscle, the eye, and the liver are examined, demonstrating the versatility of CRISPR in addressing both monogenic and complex diseases. The use of CRISPR for gene therapy in conditions like sickle cell disease, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, retinal degeneration, and liver disorders is discussed, showcasing early clinical trials and preclinical studies that underscore the promise of CRISPR in medicine. Finally, it is expected that CRISPR will be able to play a greater role in human health and bring more precise and personalized treatment plans to patients.

 View pdf
View pdf


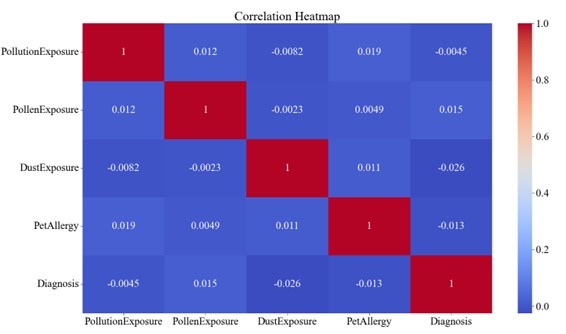
Asthma, being a leading chronic disease globally, involves molecular mechanisms that are quite complex to facilitate easy diagnosis—more especially in the presence of environmental factors, which play an underrecognized role. The current study intends to assess the relationship shared by four allergy risk factors (pollution, pollen, dust, and pets) with the development of asthma. Logistic regression and random forest models were developed using data available from the "Asthma Disease Dataset" sourced from Kaggle to determine the predictive power of these factors. The SMOTETomek technique was applied for data preprocessing due to class imbalance; while relationships and model performance were assessed using the Pearson correlation matrix, box-and-whisker plots, and confusion matrices. Results indicated that pollen exposure is highly predictive of asthma. Dust and pet allergies are negatively associated with an asthma diagnosis. Pollution exposure does not indicate a clear link to asthma. The logistic regression model was less accurate in distinguishing between classes than the random forest model. Therefore, based on accuracy and class distinguishability, the random forest model outperformed logistic regression. These findings contribute to the understanding of environmental and allergy factors in asthma development and underline the feature of such an aspect in predictive modeling. Longitudinal data should be the focus of future studies, along with more objective measures to ensure enhanced reliability for these models.

 View pdf
View pdf




