

Volume 64
Published on December 2024Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biological Engineering and Medical Science
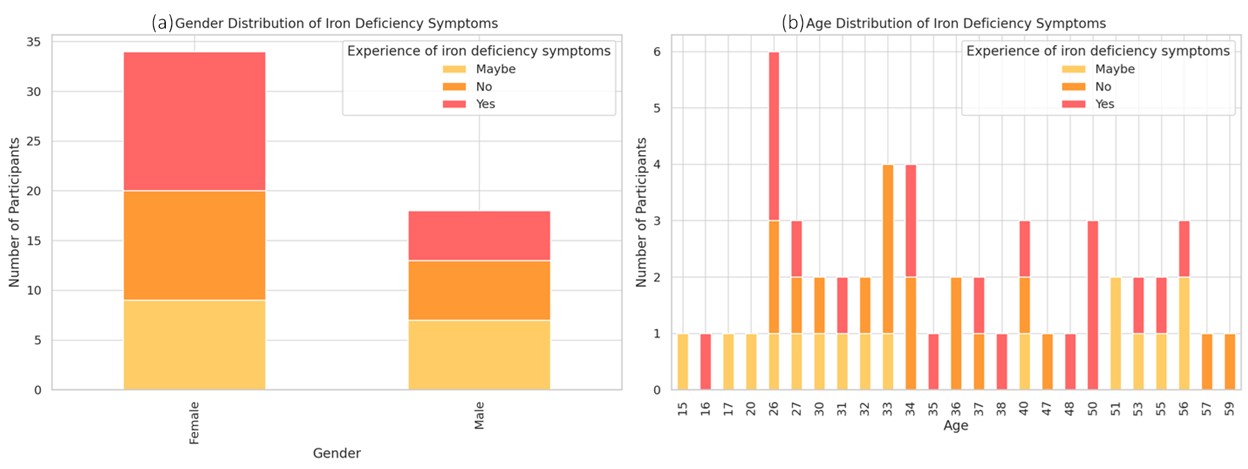
Iron is an essential mineral that plays a critical role in athletic performance, particularly through its involvement in oxygen transport and energy metabolism. This study investigates the awareness, perceptions, and dietary behaviors related to iron intake among athletes, focusing on the prevalence and impact of iron deficiency. A survey of 60 participants aged 16 to 59 revealed that 34% experienced symptoms of iron deficiency, with higher rates among females (41%) and those engaged in intense exercise. The study found a positive correlation between the consumption of iron-rich foods and self-assessed athletic ability, emphasizing the importance of diet in maintaining optimal iron levels. However, the frequency of iron-rich food consumption did not significantly impact recovery speed, suggesting that other factors, such as exercise intensity, play a more significant role in recovery. The findings underscore the need for targeted nutritional strategies and educational initiatives to address iron deficiency, particularly in high-risk groups. The study also highlights the complexity of athletic nutrition, where multiple nutrients and factors contribute to overall performance. Future research should explore the long-term effects of iron supplementation and the specific needs of different athlete populations to optimize performance and health.

 View pdf
View pdf


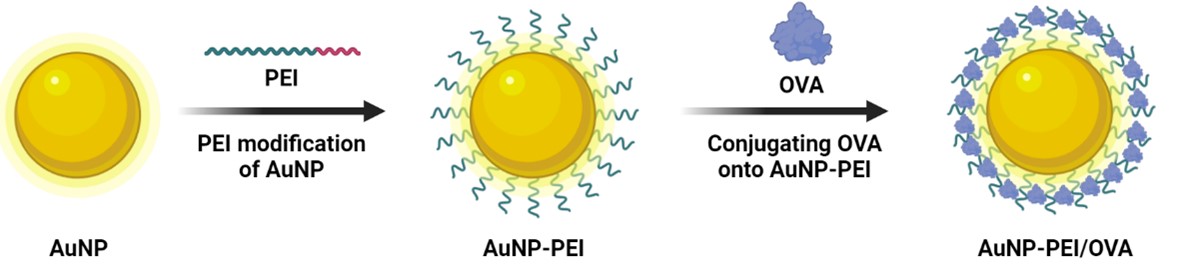
Cancer vaccines have the potential to initiate immunotherapy by utilizing antigens to activate T cells for a targeted immune response. However, Existing drug delivery techniques frequently face challenges such as low antigen delivering efficiency and potential toxicity which impede the effectiveness of treatments. This study designed a gold nanoparticle-based polyethyleneimine (PEI)-modified nanoparticle (AuNP-PEI) following the Turkevich method. Briefly, trisodium citrate dehydrate solution (3%, 1 mL) was added to hydrogen tetrachloroaurate (III) trihydrate (HAuCl4·3H2O) solution (0.25 mM, 100 mL) and stirred for 10 min to form AuNP, then PEI solution (2%, v/v) was prepared added to a stirring solution of AuNPs in 0.005% (v/v) concentration. After stirring for 1 h with the PEI solution, the synthesized AuNPs were coated with PEI. By electrostatic force, AuNP-PEI effectively load model antigen ovalbumin (OVA) to form AuNP-PEI/OVA nanovaccine which realized effective antigen delivery while possessing low cytotoxicity towards RAW264.7 and DC2.4 cells. Further, AuNP-PEI/OVA nanovaccine stimulate dendritic cells (DCs) to become mature, promoting the expression of CD86 and CD80 which are the marker of mature DCs mediating activation of CD8+ T cells. This study explores the potential of AuNP-PEI applied as vaccine vector. Despite further verifying experiments needed, the successful and effective of AuNP-PEI/OVA in this study offer not only a new design strategy for cancer vaccine but also a potential solution to the limitations faced by conventional drug delivery methods.

 View pdf
View pdf


Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a severe and progressive neurodegenerative condition that is marked by a gradual deterioration of cognitive functions, leading to grievous dementia and profound functional impairment. As the disease progresses, individuals lose the ability to carry out routine tasks and daily activities, often leading to bedridden confinement and an increased risk of complications such as pneumonia. Despite considerable research efforts, the precise mechanisms underlying AD pathogenesis remain elusive. The cholinergic hypothesis, one of several proposed pathogenesis hypotheses for AD, suggests that the disease arises from the death of neurons releasing acetylcholine. This hypothesis highlights the critical role of acetylcholine in maintaining cognitive function and implies that the degeneration of these neurons contributes to the progression of AD. To better understand the mechanisms and factors contributing to acetylcholine nerve cell death in AD and how they ultimately lead to disease progression, this research aims to explore the intricate relationship between acetylcholine and AD. We examine the intricate interplay between genetic, molecular, and environmental factors that converge to promote the demise of cholinergic neurons. Ultimately, understanding the complex interplay between acetylcholine and AD pathogenesis could smooth the path for novel treatment strategies aimed at preserving neuronal function and improving patient outcomes.

 View pdf
View pdf


Recent advancements in deep brain stimulation (DBS) technology have shown significant promise in treating neurological disorders. However, research across different diseases often lacks a holistic approach, leading to limitations in treatment strategies and the selection of feedback signals. To facilitate the classification development of DBS technology, a systematic analysis of the similarities and differences among various diseases is essential for optimizing adaptive deep brain stimulation (aDBS) feedback signal selection. This paper examines the commonalities and distinctions in the pathophysiological mechanisms of Parkinson’s disease (PD), epilepsy, and major depressive disorder (MDD), along with their associated aDBS feedback signals. Through comparative research on these conditions, the study explores their respective neurobiological markers and adaptive stimulation strategies. This research provides empirical support for the stratified development of DBS technology, highlighting the importance of optimizing feedback signals based on the characteristics of different diseases, thereby laying a theoretical foundation for future treatment strategy design.

 View pdf
View pdf


Tourette Syndrome (TS), a complex neurodevelopmental disorder featured by persistent motor and vocal tics, has seen Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) emerge as an efficacious treatment option for refractory cases. This study aims to systematically review and compare the roles of open-loop and closed-loop DBS modalities in treating TS, to elucidate their respective strengths, priorities, and clinical outcomes. Through a comprehensive literature review and data analysis, this paper delves into the mechanisms, technical advantages, and effectiveness of both DBS paradigms in managing TS symptoms, mitigating comorbidities, and enhancing quality of life. Furthermore, the disparities in safety, tolerability, long-term efficacy, and the influence of patient-specific requirements on therapeutic strategy selection are evaluated. Besides, this paper also culminates with a summary and outlook, advocating for ongoing exploration to refine closed-loop DBS pathways and concurrent appraisal of open-loop DBS within specific patient cohorts, thereby advancing the precision and personalization of TS therapy.

 View pdf
View pdf


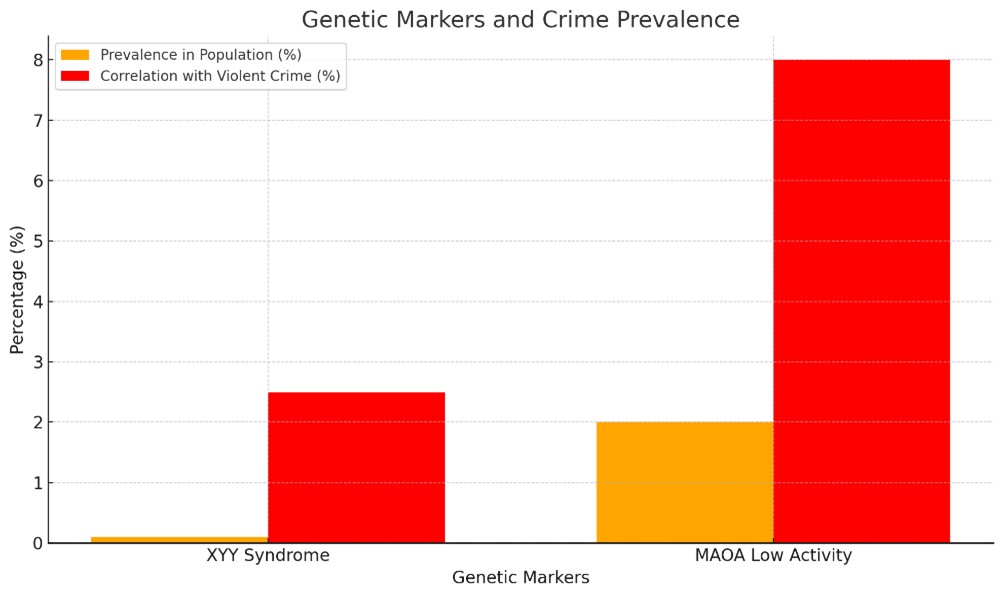
In this extended project, I consider a variety of causes for violent criminality, and show how genetic, environmental and psychological elements converge to contribute to an individual’s likelihood of offending. This review covered some fundamental genetic markers (i.e., XYY syndrome, the MAOA gene variant), with those carried on by environmental influences in the form of own characteristics and immediate factors (i.e. socioeconomic status, familial dynamics) to personal psychological qualities as psychopathy. The results show that genetic influences on a disposition to engage in criminal behavior do not lie dormant but act together outside the confining space of bare biology. In reality, many environmentally and psychologically trigger the actual act of criminal activities. This is not to say that any one of these factors determines whether violent criminal behavior will develop, but rather, that criminal behavior emerges from the interaction of all the elements discussed in this review. Such a nuanced perspective is important for our legal systems, as it emphasises the need of seeing every individual separately and assessing an individual on several levels while also implementing measures that take into consideration some reference to genetic predisposition, surroundings and psychological profile. Further longitudinal and interdisciplinary studies are needed to better understand the relationships between these factors as well as to develop prevention and intervention strategies in the future.

 View pdf
View pdf


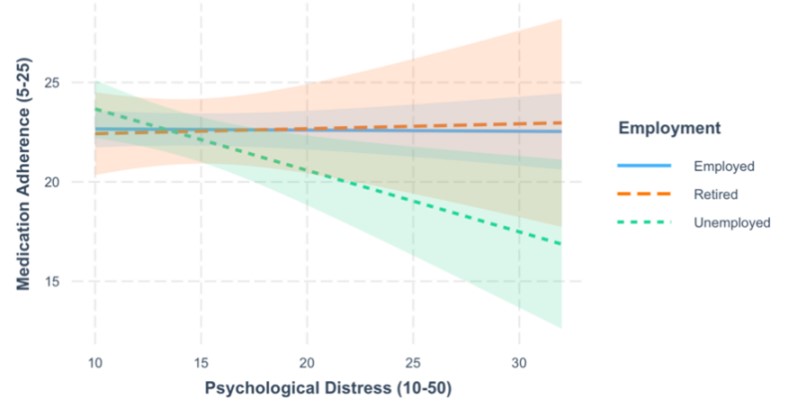
Prevalence of inadequate drug adherence is observed among patients diagnosed with hypertension. Individuals with hypertension may experience psychological discomfort as a result of elevated blood pressure and the adverse effects of therapy, which can impact their mental well-being. Psychiatric disorders are crucial variables to consider when examining the influence on medication compliance. Discrepancies in the research regarding the link between medication adherence and psychological discomfort, such as anxiety and depressive symptoms, emphasize the need of investigating other variables that could impact this link. Previous research has examined the correlation between employment status and psychological distress, as well as the correlation between employment status and adherence. However, none have tested the association between psychological distress, employment status, and the adherence to medication. This study aimed to explore whether employment status influences the effect of psychological distress (including symptoms of anxiety and depression) on medication adherence in adult patients with hypertension. The results of multiple linear regression analyses for secondary data indicated that employment status had a significant effect on the association between psychological distress and medication adherence. More precisely, when compared to those who were working, the adverse effect of psychological distress on the adherence to medicine was more pronounced within the unemployed population. In addition, medication adherence was poorer among younger participants, those who were employed, and those with higher systolic blood pressure. The study indicates that future research should reassess this correlation in samples with a more equitable and varied work status or contemplate using pharmacy data to assess medication adherence.

 View pdf
View pdf


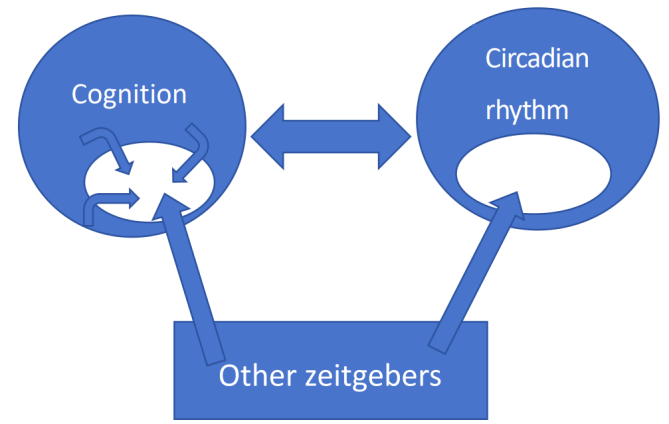
Disruptions in circadian rhythms and their detrimental effects on physical health have become deeply ingrained in daily life. Traditional treatments, such as pharmacotherapy, electromagnetic therapy, and cognitive behavioral therapy, have each explored their own paths but still possess structural limitations, particularly for those who are reluctant to seek treatment for rhythm disorders. "Autonomous Cognitive Instant-Engagement" can be viewed as a new therapeutic approach. It acknowledges the potential of autonomous, immediate cognitive engagement to have an immediate impact on the body and regulate circadian rhythms. However, this concept has not received sufficient attention because cognition as a zeitgeber (time-giving factor) has been under-discussed in the past. This article reviews existing literature on the objective evidence for "Autonomous Cognitive Instant-Engagement" in regulating circadian rhythms and discusses its potential mechanisms and future directions.

 View pdf
View pdf



Aging has emerged as a significant issue in human society, warranting intensified research efforts. Despite this, there is a noticeable dearth of research on genetic factors that could potentially extend lifespan. The genetic role of TOR/let-363 and its interactome was delved into in the model organism C. elegans. Utilizing RNA interference (RNAi), the impact of predicted interactors within the TOR pathway were explored on aging, with a particular emphasis on healthspan. This was achieved through comprehensive lifespan and pumping rate assays. Of the 20 genes examined, only the knockdown of F56F11.4 resulted in a reduction in both lifespan and early-stage pumping rate. To elucidate the interplay between F56F11.4 and TOR/let-363, double knockdown and RT-qPCR assays were employed to reveal their intricate regulatory roles in the aging process. Additionally, the conserved nature of F56F11.4 and let-363 across five well-studied organisms (C. elegans, H. sapiens, M. musculus, R. norvegicus, and D. melanogaster) was identified using bioinformatics analyses. The discovery of the influence of F56F11.4 on healthspan through the modulation of TOR/let-363 signaling suggests a promising target for the development of novel therapeutic strategies aimed at enhancing healthy aging.

 View pdf
View pdf


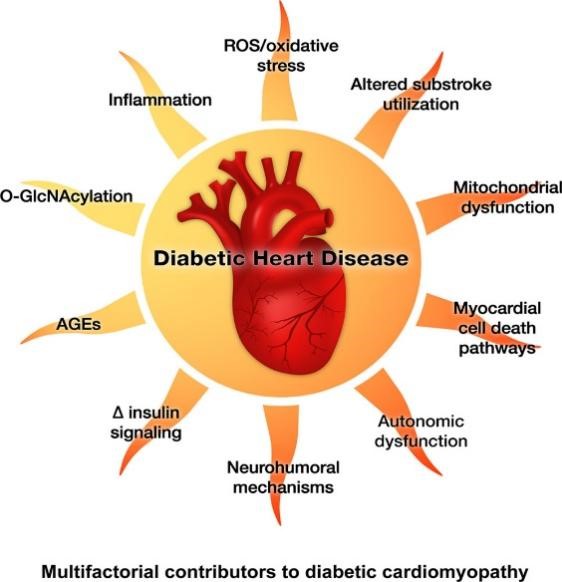
People with diabetes mellitus are more likely to develop heart failure, and those with both conditions often experience a worse prognosis compared to heart failure patients without diabetes. This paper will summarize the pathogenesis of diabetic heart failure and propose treatment and prevention options for diabetic patients with heart failure based on the existing literature and data results. Both types of diabetes lead to high blood sugar levels, which, along with diabetes itself, exert different effects on the heart. As time goes on, it causes heart failure. The outcome demonstrates how chronically elevated blood sugar levels can lead to inflammation and accelerate the development of heart failure. Significant roles are also played by oxidative damage, insulin resistance, and other variables. It has been demonstrated that altering one's lifestyle can avoid diabetic heart failure and improve the quality of life for individuals with asymptomatic diastolic dysfunction and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).

 View pdf
View pdf




