

Volume 163
Published on February 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Business and Policy Studies
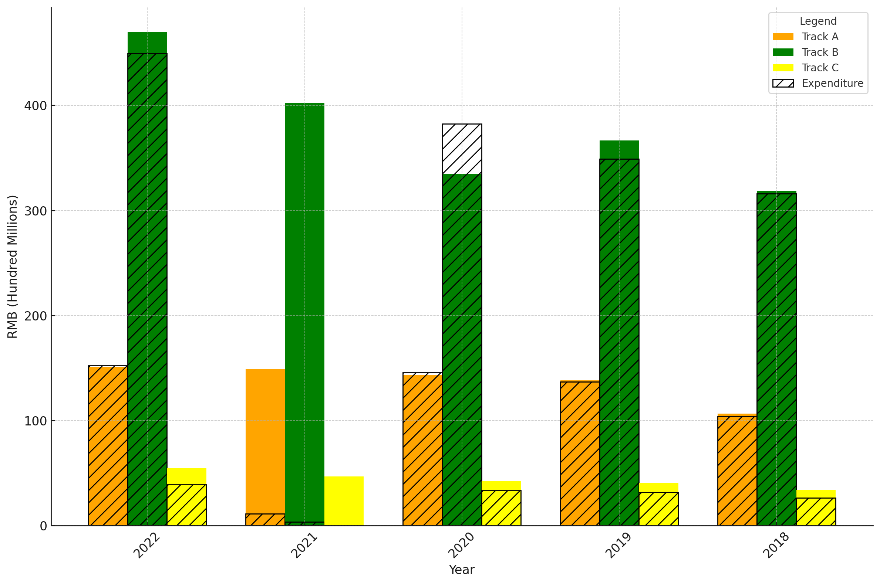
The pension system reforms in China since 2014 have aimed to address significant structural challenges, focusing on the feasibility, sustainability, and equity of the system. This paper evaluates these reforms, particularly their impact on three main pension tracks: public employees, enterprise employees, and rural residents, represented by track A, B, and C, respectively. Despite merging certain pension schemes and introducing a universal basic pension, disparities persist, particularly for rural populations, who remain underserved with low replacement ratios. The analysis reveals systemic inequalities, financial imbalances, and unsustainable funding trajectories exacerbated by China's aging population and declining fertility rates. Drawing lessons from Japan and other nations, the paper proposes policy recommendations, including raising the pension eligibility age, rebalancing pension benefits, and enhancing individual pension accounts through tax incentives and improved financial literacy. These reforms aim to mitigate existing disparities, promote fiscal sustainability, and ensure equitable retirement outcomes, emphasizing the need for structural adjustments to achieve long-term effectiveness in China's pension system.

 View pdf
View pdf


Hebei Province, located in northern China, is a key player in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei coordinated development strategy. Despite steady economic growth, Hebei faces significant challenges in achieving sustainable, high-quality development due to its reliance on traditional heavy industries like steel, chemicals, and building materials. The digital economy offers a transformative opportunity to address these challenges by enhancing industrial transformation, promoting green production practices, and fostering technological innovation. This paper examines the current economic structure of Hebei, the progress of digital economic development, and its integration with traditional industries. It also explores the potential for digital technologies to optimize industrial efficiency, improve resource allocation, and support Hebei's transition from a resource-dependent to an innovation-driven economy. The study identifies the gaps in technological innovation and industrial capabilities and proposes strategic recommendations to strengthen Hebei’s position within the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei coordinated development framework. Future research should focus on regional differences, workforce education, environmental impacts, and policy effects on industrial and digital innovation.

 View pdf
View pdf



In today’s digital era, enterprises are accelerating their digital-intelligent transformation processes to enhance competitiveness and operational efficiency. This paper employs theoretical analysis and case studies to examine the specific impact of digital-intelligent transformation on audit fees. The findings reveal that such transformation can reduce audit fees by improving information transparency, optimizing business processes, and mitigating audit risks. Using China Mobile and Haier Smart Home as examples, the study identifies three mechanisms through which different transformation measures affect audit fees: efficiency enhancement and burden reduction, quality improvement and empowerment, and precise risk prevention and control. These findings offer new insights into cost reduction and efficiency optimization for enterprises, helping to streamline cost structures and providing valuable guidance for the audit industry’s transformation and upgrade in the digital-intelligent era.

 View pdf
View pdf


The global ageing problem has become a heavy issue; this brings us to a question: how can such a huge group survive. Relying on the government, the company, or on their own. China has the worst ageing problem; most older people choose to re-employment. Using their remaining energy, they can not only reduce the financial burden of their family but also refresh the whole labor market. However, the re-employment of the elderly is quite difficult because their outdated skills cannot fit today's requirements, and the digital divide appears. The key to supporting older workers' re-employment lies in addressing the digital divide of them. Through collection and summary of the Chinese age structure, status of the Chinese elderly re-employment, and the digital divide of the Chinese elders, this paper analyzes these aspects and conclude that although the technological gap of China's elderly re-employed is obvious, with the joint efforts of the government, enterprises and society, this digital divide will continue to narrow and will be bridged in the future. This paper also aims to find the key of rapidly alleviating the digital divide of Chinese elderly re-employment, and excavate the new solutions to build the bridge.

 View pdf
View pdf


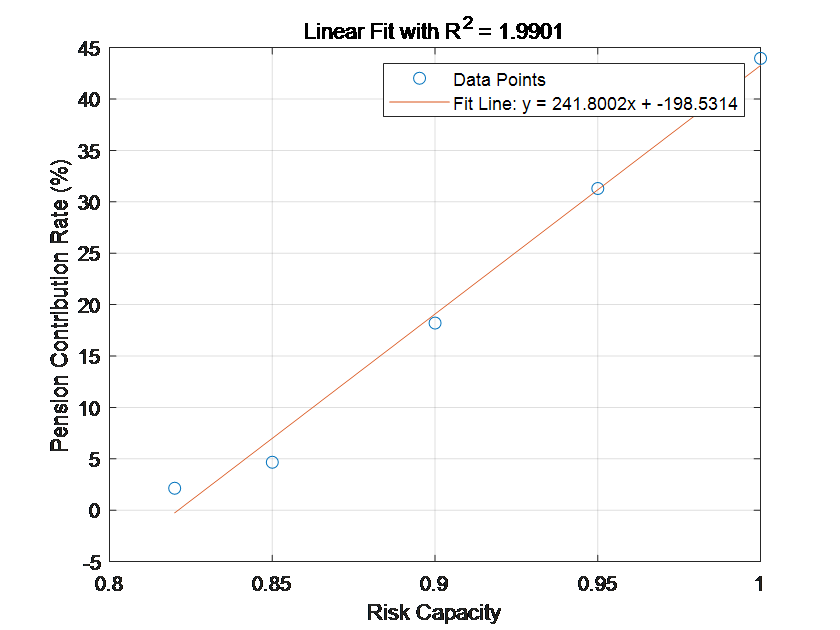
In the context of China's intensifying aging population, the economic security of the elderly has emerged as a pivotal concern. As of 2023, China's elderly population aged 60 and over has reached 297 million, accounting for 21.1% of the total population. Against this detailed background, the purpose of this essay is to investigate the status, problems, and economic impact mechanism of personal pension consumer risk assessment in China. To achieve this, a quantitative analysis was conducted using a large-scale socioeconomic survey, which collected data on age, gender, educational background, risk appetite, and pension contribution rates. The method employed linear regression models to examine the relationship between risk-taking ability and pension contribution rates, as well as the influence of age on consumption willingness. The results indicate that consumers' risk-taking ability has a significant positive effect on their pension contribution rates, suggesting that individuals with higher risk tolerance tend to allocate a larger proportion of their income to pension savings. Furthermore, age was found to influence both risk preference and consumption behavior, with specific age groups exhibiting unique patterns. In conclusion, these findings provide valuable insights for policymakers and financial institutions to better design incentives and products that cater to the diverse needs of the aging population.

 View pdf
View pdf


This study aims to explore the impact of ESG factors on the overall development of JD.com in depth by analyzing the annual report and ESG report released by JD.com. The author studied JD.com's annual and ESG reports of specific years in detail, extracted data and information about ESG indicators (such as energy conservation and emission reduction initiatives in environmental aspects, employee welfare and community relations in social aspects, etc.), and made a comprehensive analysis. In terms of environment, this paper found that JD.com not only built energy-saving and environmentally friendly logistics parks, but also continuously optimized the structure of diversified employees, and continued to increase employees' salaries. After the implementation of ESG, JD.com's profitability has been greatly improved, leading the industry, winning many awards at home and abroad, and being recognized by investors. To sum up, ESG factors play a crucial role in the overall development of JD.com, which has a broad and positive impact on many aspects of its cost control, brand building, talent management, and financial performance.

 View pdf
View pdf


The rapid development of China's electric vehicle battery industry has significantly reshaped global battery supply chains, creating both opportunities and challenges for the U.S. domestic supply chain. This essay examines the implications of China's advancements in EV battery production and trade on the U.S. domestic supply chain, focusing on multiple aspects such as raw material sourcing, production costs, research and development, international collaborations, and policy-making expenditures. Through a comprehensive literature review, this essay identifies gaps in existing research. There are limited explorations of possible factors contributing current situation faced by the U.S., potential alternatives to the sustainable approach for battery raw material supply and applicable policies for supporting the U.S. domestic battery supply chain. To bridge the existing literature gap, the analysis delves into key challenges faced by the U.S., including rising production costs and limited technological advancements, and explores potential international partnerships to enhance supply chain resilience. The conclusion synthesizes the findings and emphasizes the importance of essential measures to address these challenges. The suggestions section proposes systematic policies for the U.S. government, emphasizing investment in domestic production, building international partnerships, and developing a diversified and sustainable supply chain to mitigate risks associated with China's growing influence. This essay aims to contribute to the discourse on strategic responses to China's dominance in the EV battery industry and provide some feasible pathways for U.S. to reinforce its core competence in the global battery market.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the continuous development of the global economy, the public-private partnership (PPP) model is increasingly used in the field of project management. Through in-depth cooperation between the government and social capital, the PPP model achieves optimal allocation of resources and reasonable sharing of risks, brings new solutions to infrastructure construction and the improvement of social public services, and achieves a win-win situation. This article analyzes the main characteristics of the PPP model through the literature review method, discusses the main advantages of PPP project management, focuses on the existing problems of PPP project management, and proposes specific solutions to the problems to help project managers carry out projects under the PPP model. Scientific and efficient project management provides theoretical support and practical guidance to ensure that enterprises maximize economic benefits, improve project quality, and promote the healthy and sustainable development of the PPP model in more fields.

 View pdf
View pdf


The aim of this paper is to explore the impact of the Green Total Factor Productivity (GTFP) factor on the excess returns of quantitative investment strategies in the secondary market of China's capital market. The study integrates the GTFP factor into the Fama-French five-factor model and employs the Newey-West regression method for empirical analysis. The results indicate that the GTFP factor has a significant positive impact on stock excess returns across various industries, with the second-order lag model showing improved statistical significance compared to the first-order model. This finding highlights the importance of considering environmental sustainability factors in investment decision-making and provides investors with investment strategies based on green factors. Furthermore, the results offer insights for policymakers in promoting the development of green finance. This paper enriches the literature in the field of asset pricing and offers a new perspective for both the theory and practice of green finance.

 View pdf
View pdf


Artificial intelligence (AI) has become a major force for change in the healthcare industry, especially in diagnostic systems, where AI plays a key role in improving the accuracy, speed, and efficiency of diagnosis. The deep integration of AI with internet-based platforms has revolutionized the way healthcare is delivered, especially in low-resource settings, where AI provides a scalable solution for healthcare systems. This article explores the application of artificial intelligence in medical diagnosis, focusing on how AI technologies such as machine learning and deep learning can be integrated into areas such as medical imaging, disease prediction, and telemedicine. The article also discusses the rapid development of the internet-based healthcare system, emphasizing the role of AI in improving diagnostic models through real-time data collection and analysis. At the same time, the article also analyzes current challenges, such as data privacy, ethical issues, and regulatory challenges, which limit the widespread application of AI in clinical practice. Through a comprehensive review of existing research, this article outlines the potential and limitations of AI in medical diagnostics and provides insights into its future development trends. The findings show that although AI has great potential to improve the quality and accessibility of healthcare, its application in clinical practice still needs to carefully consider many factors such as ethics, technology, and regulation.

 View pdf
View pdf




