

Volume 49
Published on November 2024Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biological Engineering and Medical Science
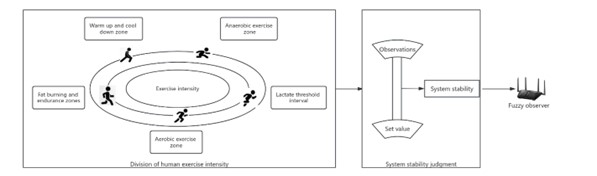
With the progress of society and the improvement of people's living standards, people's requirements for physical fitness are also increasing. Especially for middle-aged and young men, they often need to work at their desks for a long time in their daily work and life, and their physical fitness is relatively poor, making them prone to various diseases. Therefore, this article focuses on the study of motion intensity evaluation algorithms based on fuzzy observers. By classifying human motion intensity and establishing corresponding fuzzy observers, the difference between the output of the fuzzy observer and the set value is used to determine whether the human motion intensity is too high or too low. The research results indicate that the fuzzy observer has a good performance in evaluating exercise intensity, with an evaluation accuracy of up to 94%.

 View pdf
View pdf


The immune system has three basic functions: defense, surveillance and homeostasis. It helps us monitoring and timely eliminate mutant cells and distinguishing between “alien” components to maintain self-stability. However, once it loses these abilities, it could cause the autoimmune disease. In this article, I mainly discuss about the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), a type of autoimmune diseases which is mediated by type Ⅲ hypersensitivity. SLE patients suffer from chronic inflammatory responses, leading to tissue damage and organ dysfunction. Therefore, purpose of therapeutic schedule is to inhibit the overactive immune system and relieve the inflammatory response. Nowadays, there are three major therapies: Glucocorticoids (GC), immunosuppression agents and belimumab. Glucocorticoids suppresses inflammatory responses and generate anti-inflammatory factors. Immunosuppression agents can not only control SLE and raise the survival rate of long-term prognosis for SLE patients. Belimumab inhibits the survival of B cells by obstructing the interaction between soluble B cell activating factor (BAFF or BLys) and receptors on B cells. This action promotes the apoptosis of auto-reactive B cells, leading to a decrease in auto-antibodies present in the serum. With the development of biotechnology, more and more advanced treatments have emerged and brings new hope to SLE patients.

 View pdf
View pdf


Physical treatment is useful in reducing the many COVID-19 problems, according to recent studies. The significance of physical therapy in the all-encompassing management of the new coronavirus has been brought to light. Physical therapy is the main body of rehabilitation therapy, including a wide range of techniques (such as sound, light, cold, heat, electricity, force (movement and pressure) and other physical factors for treatment, as well as breathing, muscle training, for local or systemic body dysfunction or lesions, The use of non-invasive, non-drug treatment, reinforcement strategy exercises, immediate relief of symptoms and overall improvement of the patient’s physical function and restoration of the patient’s original body physiological function. This integrated approach enables patients to return to their previous level of activity and quality of life by highlighting the entire context of treatment. Physiotherapy is not without its limitations, though. Physiotherapy requires patient-specific care, because there aren’t enough doctors or patients during a pandemic. To ensure the provision of effective rehabilitation services, creative solutions are required to address issues including the shortage of specialists, the requirement for training units, and the return of telemedicine. Furthermore, further research efforts and interdisciplinary collaboration are required to establish effective practices and improve patient outcomes related to physical therapy engagement in COVID-19 recovery programs. As a result, the pandemic has brought attention to and strengthened an important shift in the role of physical therapy in the management of post-viral syndromes, opening the door for future advancements in the field of infectious disease medicine.

 View pdf
View pdf


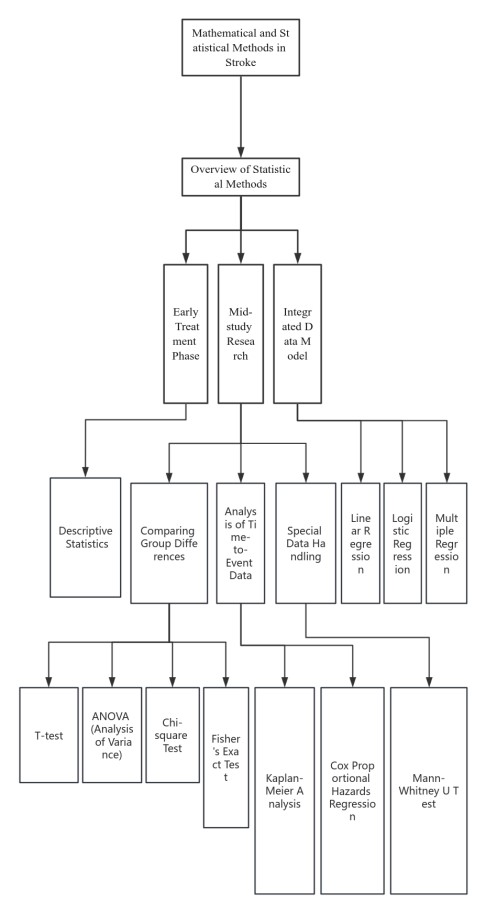
Stroke is a serious illness, with a global disability rate of over 50% and a mortality rate of up to 30%, making research on stroke prognosis prediction of significant societal importance. This paper comprehensively analyzes the application of mathematical statistical methods in stroke prognosis prediction, aiming to explore how these methods can enhance the accuracy of prognosis predictions, thereby providing patients with personalized treatment plans and improving their long-term rehabilitation process. Initially, the article introduces the severity of stroke and the importance of prognosis prediction, outlining the diversified development trends in current stroke prognosis prediction research. Subsequently, the article detailedly summarizes 11 statistical methods commonly used in stroke prognosis prediction, dividing these methods into three categories: methods suitable for analysis at the initial stage of treatment, methods suitable for data processing during the mid-study phase, and methods for integrating all data to establish regression models. Through specific case studies, this paper demonstrates the application of these statistical methods in actual research, including the use of descriptive statistics in MRI image analysis, the application of T-tests and ANOVA in comparing different treatment effects, and the importance of regression analysis in establishing prognosis models, including linear regression, logistic regression, and multiple regression analysis when considering multiple independent variables. This research not only provides a precise method for predicting the prognosis of stroke patients but also offers theoretical support for medical teams to formulate personalized treatment plans, enabling researchers to more accurately predict the prognosis of stroke patients, providing more personalized and effective treatment options. This contributes to reducing the risks during the patient’s rehabilitation process and improving the quality of life.

 View pdf
View pdf


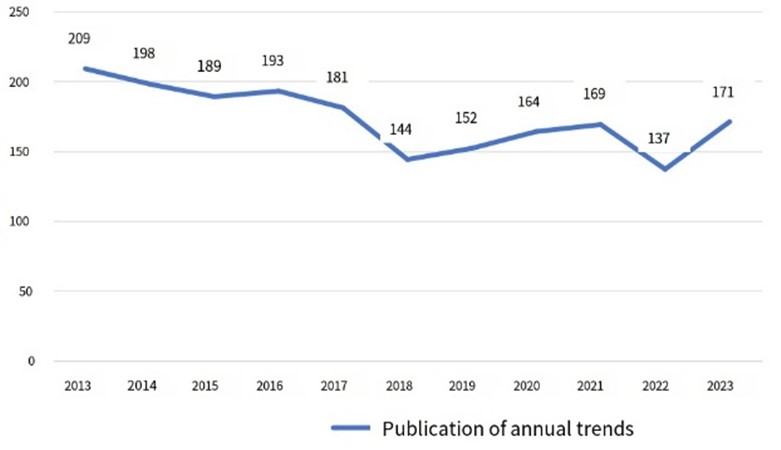
Purpose: Chronic heart failure (CHF) is a serious cardiac disease and has become a common and high-incidence disease worldwide. This study aims to investigate the current status and trends of research on CHF over the past decade (2013-2023), in order to understand the latest developments in this field and future research directions. Methods: Using the China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) as the data source, visual analysis software CiteSpace 5.5 R1 was employed to visualize and analyze CHF-related research, exploring authors, institutions, keywords, and development trends of relevant studies. Results: A total of 1907 articles were included. Visual analysis revealed that research authors were relatively dispersed, with few collaborative publications. The collaboration among main research teams was insufficient, and the main research institutions were also relatively dispersed. Hot keywords included chronic heart failure, heart failure, chronic congestive heart failure, cardiac function, quality of life, prognosis, ventricular remodeling, brain natriuretic peptide, etc., forming nine clusters. Conclusion: The publication volume of CHF over the past decade showed a trend of gradual decrease followed by an increase. The impact of cardiac function on patients’ prognosis and quality of life has received relatively high attention in the field of chronic heart failure.

 View pdf
View pdf


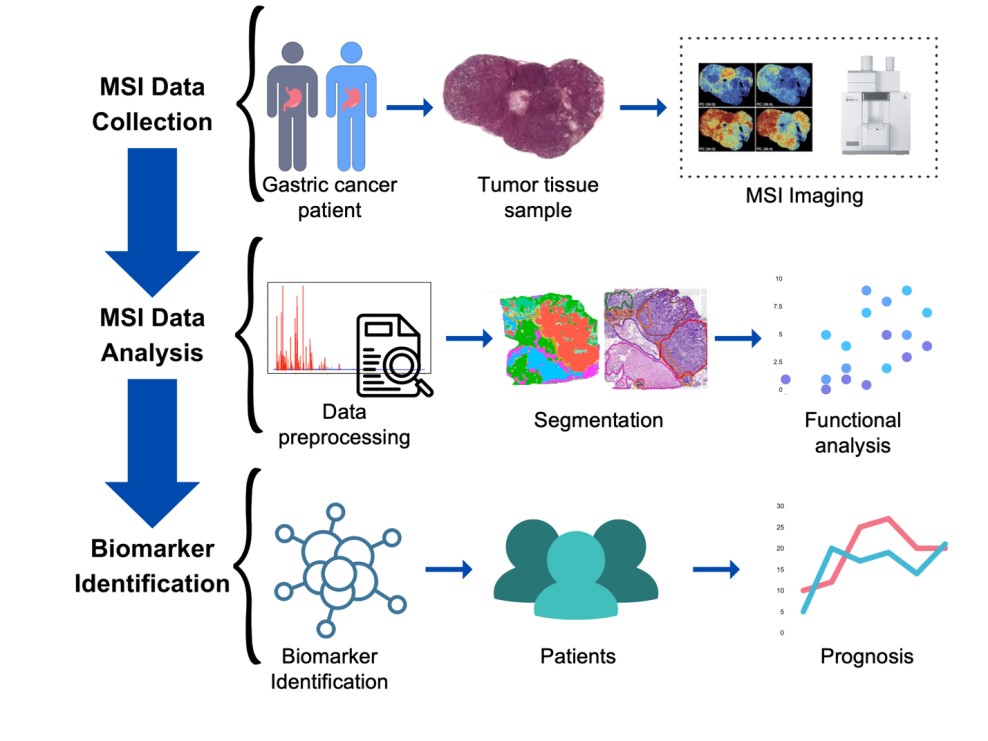
Gastric cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the world. It is estimated that gastric cancer would cause 12,000,000 deaths by 2030. Gastric cancer diagnosis in its early stages is often challenging due to the lack of specific symptoms, while early diagnosis is pivotal to patient survival. The discovery of tumor-specific biomarkers plays a crucial role in effectively diagnosing gastric cancer. Metabolomics-based approaches provide qualitative and quantitative measurements of the metabolic signatures that are unique to cancerous tissue. Recently, mass spectrometry imaging (MSI)--based metabolomics enables untargeted investigation of molecular species concerning spatial distribution across tissues, elucidating the heterogeneity of gastric cancer. In this study, a computational imaging segmentation-based pipeline that analyses the spatial distribution of metabolite for gastric cancer using MSI metabolomics data is developed, which leads to the discovery of differentially expressed metabolites and the identification of biomarkers across different tissue subtypes in gastric cancer.

 View pdf
View pdf


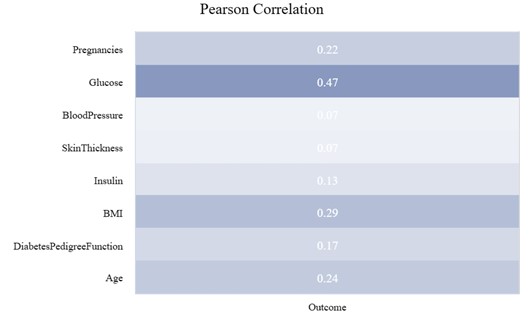
Type 2 diabetes has become a serious chronic disease, which poses a great threat to human health. In previous research, the author found that people at higher risk for type 2 diabetes had unchanged characteristics - family history, age, having diabetes during pregnancy and being overweight at birth. Additionally, there are many reasons why people develop type 2 diabetes, such as weight, physical activity, blood pressure, cholesterol levels, smoking, diet, alcohol, stress and health, and sleep. However, with the development of technology in recent years, the influencing factors may have changed. This study mainly collected and analyzed examples of 768 women, including 8 variables such as pregnancy, glucose and so on. The target variable is whether the woman has type 2 diabetes. In this study, the accuracy of both the testing and training model is in a good state at 77%, so the binary logistic regression is acceptable. In order to better understand the influencing factors of type 2 diabetes, more comprehensive data support and more advanced analysis are needed. This model sets the stage for the factors that influence type 2 diabetes in women.

 View pdf
View pdf


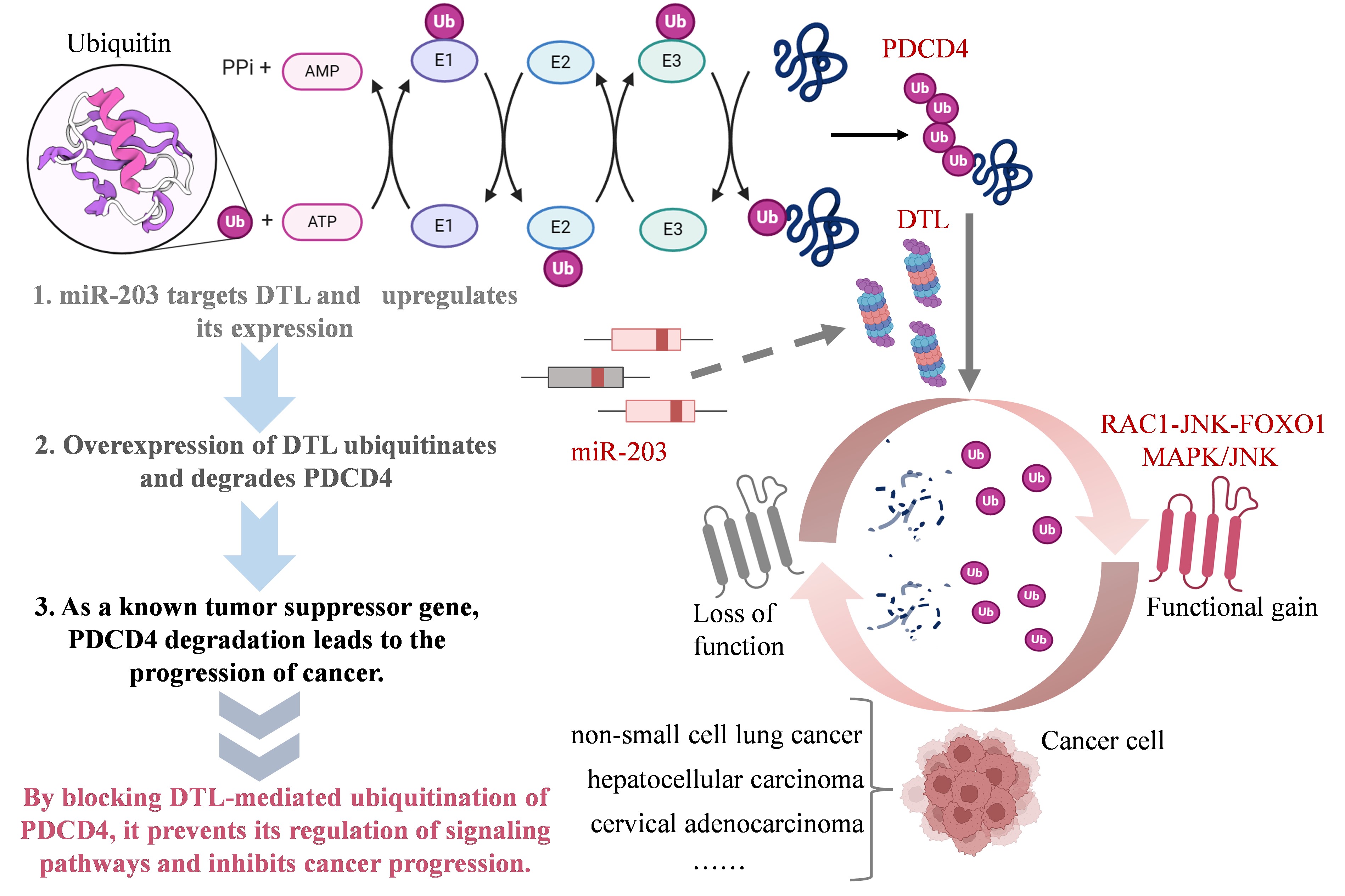
DTL (denticleless E3 ubiquitin protein ligase homolog) is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that is highly expressed in a variety of tumors and is closely related to the occurrence and development of tumors. Here, we review the latest progress in DTL regulation in various cancer data, including the mechanisms by which changes in its expression affect multiple pathways, ultimately leading to cell cycle arrest and tumor proliferation. Future research should further elucidate the molecular mechanism of DTL and its relationship with tumorigenesis, which is of great significance for the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of tumors. In addition, multi-omics data need to be used to further explore the differential expression and regulatory network of DTL at the single cell level, which is crucial for finding tumor suppressor drug targets.

 View pdf
View pdf



In this study, we established a sterile propagation and regeneration system for Mongolian willow in order to study its salt tolerance and adaptation in depth and to provide methods for future genetic improvement. Mongolian willow, belonging to the genus Willow in the family Populus, is valued for its high salt tolerance and ability to ameliorate high pH soils. However, its distribution in specific saline soil areas and sensitivity to drought and rainless environments make its reproduction limited. In this study, by stem segment induction method, we aseptically cultured apical and lateral shoots of Mongolian willow, respectively, and found that the apical shoots performed best in MS medium supplemented with 0.1 mg/L IBA, while the lateral shoots grew well in MS medium supplemented with 6-BA, IBA and TDZ. In addition, this study investigated the effects of different combinations of phytohormones on healing tissue induction and found that the combination of NAA and 6-BA had the highest success and value-added rate. Further addition of TDZ significantly increased the induction rate. The study also dealt with the application of DNA methylation inhibitors in inducing adventitious shoots, and the results showed that the addition of this inhibitor in specific culture medium could significantly increase the induction rate of adventitious shoots. In this study, the regeneration system of Mongolian willow was successfully established, which provides a basis for its future genetic research and wide application.

 View pdf
View pdf


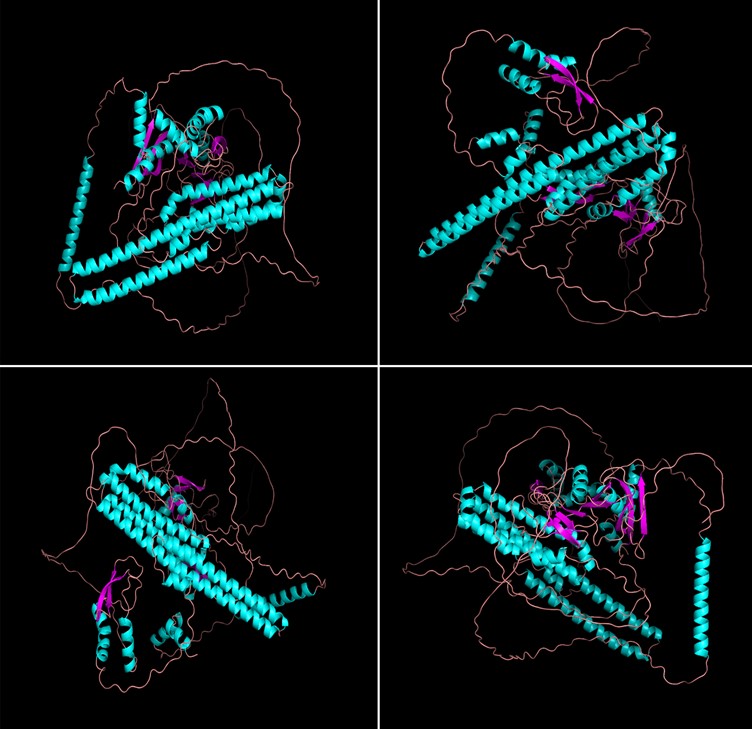
Amyloid-beta (Aβ for short) is a protein intricately linked to Alzheimer’s disease (AD for short). In the brains of AD patients, Aβ forms abnormal deposits known as amyloid plaques, which are considered one of the key factors in the progression of AD. These plaques may disrupt communication between neurons, leading to cell death and a decline in cognitive function. Therefore, this study aims to utilize Computer-aided drug design (CADD) techniques to screen and optimize potential therapeutic agents targeting Aβ. Through literature review and UniProt, we identified the active sites of Aβ and constructed a three-dimensional structural model using AlphaFold. We employed Molecular docking technology to virtually screen a compound library for candidate molecules that may bind to Aβ. The selected candidates were then subjected to Molecular dynamics simulation to verify their stability, and their molecular structures were further optimized using Pharmacophore modeling. Our research results indicate the successful screening of a series of candidate compounds with high affinity and selectivity. These compounds can form stable complexes with the active sites of Aβ, thereby inhibiting its aggregation and deposition. Current structural determination methods for Aβ have certain limitations. Techniques such as cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) can observe the morphology of Aβ fibrils but typically do not provide atomic-level structural information. Additionally, Aβ proteins tend to form non-specific aggregates in vitro, presenting challenges in preparing samples suitable for structural analysis. The innovation of this study lies in the combination of various computer-assisted technologies, offering new perspectives and methods for the drug treatment of AD and laying the groundwork for the development of novel therapeutic agents targeting Aβ.

 View pdf
View pdf




