

Volume 78
Published on January 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biological Engineering and Medical Science
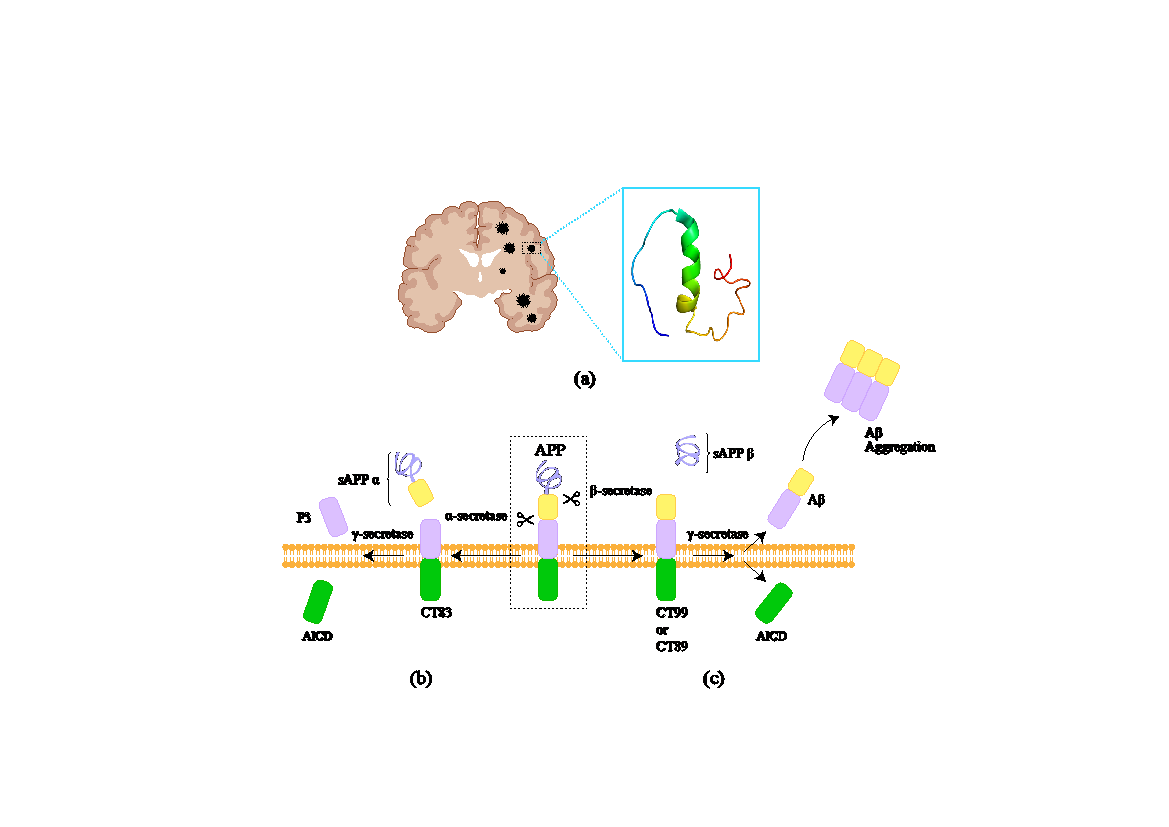
Alzheimer's disease (AD), a brain disorder marked by memory loss and cognitive decline, is pathologically characterized by amyloid-beta (Aβ) plaques and tau neurofibrillary tangles. Recent studies link AD to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress from misfolded proteins buildup. This review explores molecular mechanisms of ER stress in AD, focusing on how persistent ER stress exacerbates Aβ and tau pathologies and contributes to neuroinflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and autophagy disorder. Additionally, the review examines the viral hypothesis of AD, highlighting how certain viral infections, particularly Zika virus, may accelerate AD progression through the ER stress pathway. These insights enhance understanding of AD pathogenesis and potential therapeutic strategies targeting ER stress and viral factors.

 View pdf
View pdf


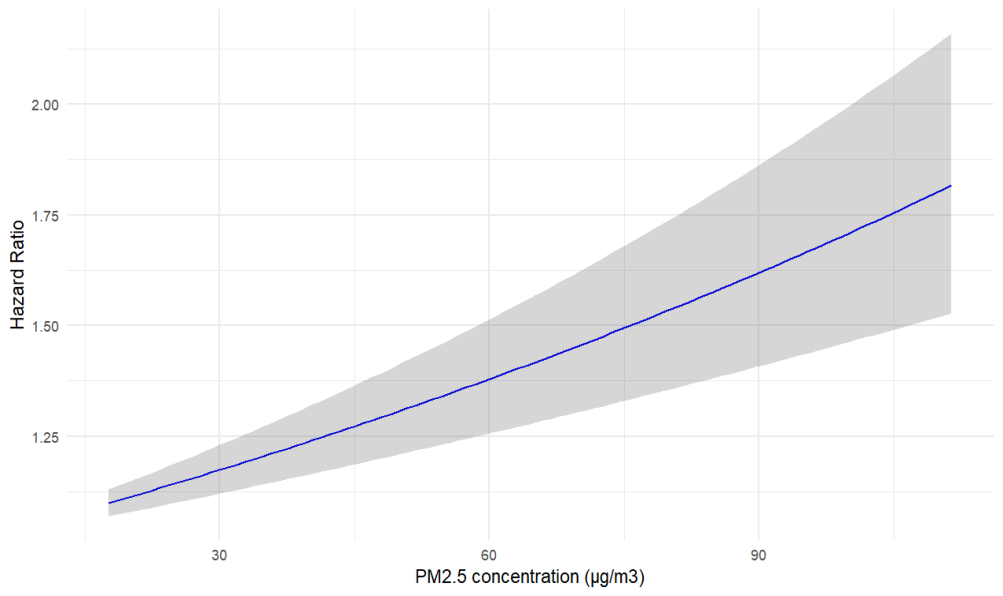
Air pollution has significantly impacted China’s economy and public health. Over the past few years, there has been numerous research conducted to investigate the relationship between air pollution and the mortality of the Chinese elderly. However, little research has investigated the factors(disease etc.) related to air pollution in the elderly population. This study aims to find out which factors under the impact of PM2.5 contribute to the resilience of the elderly. In the China Longitudinal Healthy Longevity Survey (CLHLS), 11,999 participants(Average 87.1) with follow-up from 2000 to 2018 were analyzed with a time-varying cox model, exploring whether PM2.5 has an effect on the relationship between mortality of the elderly and the elderly’s status, including ADL, smoking, age, sex, chronic respiratory, stroke or CVD, hypertension, diabetes. Rises of 10 µg/m³ in PM2.5 were associated with increases in all-cause mortality of 0.54% (95% confidence interval [CI]:0.38–0.69%). In stratified analyses, elderly people diagnosed with diabetes (HR = 1.0131, 95% CI:1.0016 ~ 1.0248) and hypertension (HR = 1.007, 95% CI:1.003 ~ 1.011) were more vulnerable to PM2.5 exposure. Contrary to our understanding, Older adults with impaired physical function have a reduced risk of PM2.5-related death(HR=1.0107, 95% CI:1.0007~ 1.005).

 View pdf
View pdf


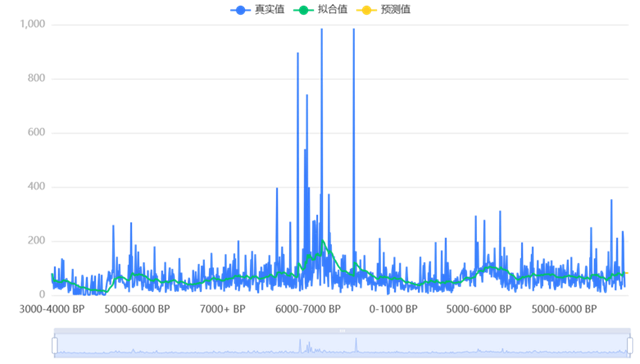
The Holocene period spans some 11,700 years and has witnessed major climatic changes that have had a profound impact on the dynamics of European vegetation. This study begins by collating existing scholarly research. Combined with pollen data, temperature and precipitation records, the response of European vegetation to climate change during the Holocene was investigated. Using datasets from sources such as Pangaea, AGU and NOAA, we performed time series analyses, correlation analyses and kernel density estimates to explore these interactions. Our findings suggest that there are important relationships between climatic variables and vegetation distribution. It also validates the findings of other scholars in this area. The findings highlight regional differences in vegetation response, suggesting complex interactions between climatic factors and plant ecology over millennia. This study provides insights into past climate-vegetation interactions.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper reviewed recent advancements in surgical suture technologies, focusing on coating based antibacterial sutures, therapeutic delivery systems, and biosensors. Silver nanoparticles and Triclosan were two antibacterial coatings that combat infections effectively. Additionally, innovative therapeutic delivery systems for suture coatings enable localized delivery of drugs using the strategies of nanoparticle coating, drug or bioactive mixture adhesion and hydrogel coating, which enhances wound healing. The review also covers smart suture sensors designed for monitoring infection, tensile strength, and pH conditions of suture or suture sites, which would improve post-surgical outcomes. These innovations signify a leap forward in surgical care, enhancing both patient recovery and surgical precision.

 View pdf
View pdf


This study investigated the efficacy of two chemotherapeutic regimens, which ECF stands for Epirubicin, cisplatin, and 5-fluorouracil. DCF stands for docetaxel, cisplatin, and 5- fluorouracil. Their efforts on quality of life in patients with developed esophageal cancer. The research investigated the mechanism of action of these drugs: Epirubicin inhibits DNA replication by inhibiting topoisomerase II and generating free radicals, cisplatin induces DNA cross-linking to trigger apoptosis, and 5-fluorouracil disrupts nucleotide metabolism to inhibit DNA synthesis. This study included 65 patients divided into ECF and DCF treatment groups. The results showed that while both treatment regimens were effective, the DCF regimen resulted in greater improvements in the quality of life and overall functioning of the patients, especially after multiple cycles of treatment. Despite a higher incidence of certain toxicities, DCF has a higher overall response rate and improvements in survival and overall survival without progression. Restrictions of the study include a small sample size and a short duration of QOL assessment. The findings suggest that DCF may be a more favorable 1st line therapy for the therapy of further esophageal cancer, necessitating larger studies and longer follow-ups.

 View pdf
View pdf


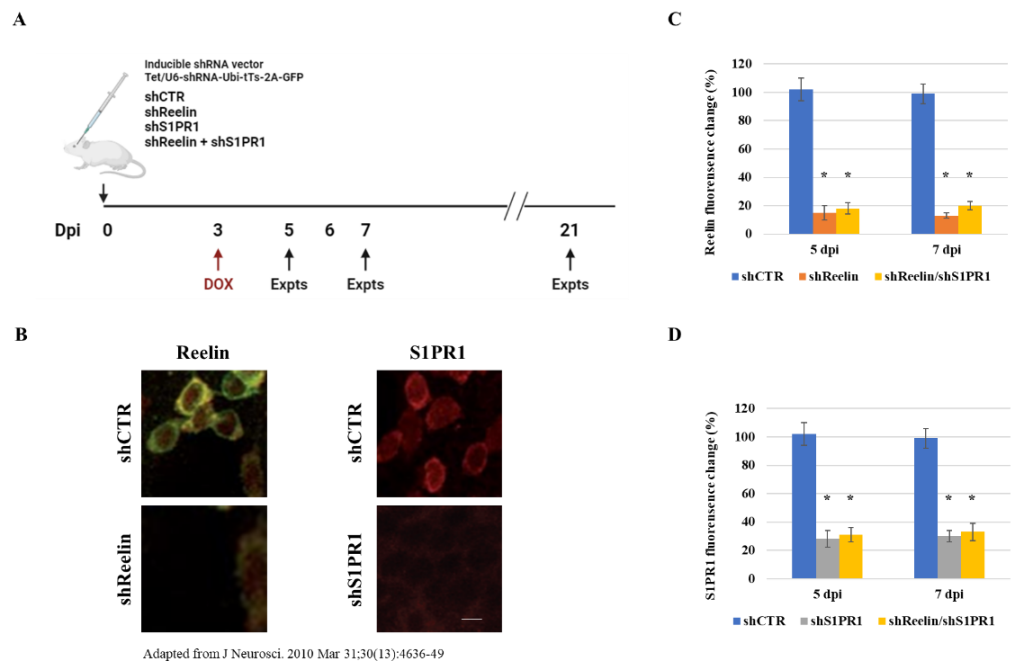
Adult neurogenesis is a process that brain generates new neuron and integrates them into the existing circuits. This process is regulated by many different factors. Reelin is one protein that plays an important role in adult neurogenesis. It is a secreted glycoprotein that can initiate the downstream signaling of the Reelin pathway, which promotes new neuron maturation and circuit integration. More recently, the S1P pathway has also been found to contribute to the maturation of new neurons. However, it is unknow if there is any correlation between these two pathways. To study their relationship, I will utilize shRNA knockdown techniques and fluorescent microscopy to assess the impact of the loss of their expression. The findings from this project may deepen our understanding of the mechanisms underlying adult neurogenesis.

 View pdf
View pdf


In modern society, the fast pace of life and sedentary work habits have led to a growing prevalence of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes (T2DM), obesity, and hypertension. These conditions pose serious health risks and place a significant burden on public healthcare systems. This review explores the positive impact of aerobic exercise on managing and alleviating symptoms of these chronic diseases. By analyzing a wide range of studies, it was found that aerobic exercise can significantly improve key physiological indicators, including blood glucose, blood pressure, and body weight. These benefits not only reduce disease symptoms but also decrease patients' reliance on medication and enhance their quality of life. The review also compiles exercise recommendations from authoritative guidelines, addressing factors such as frequency, intensity, and duration to help individuals tailor their exercise plans. Understanding the crucial role that aerobic exercise plays in preventing and managing chronic diseases is key to promoting healthier lifestyles and forms a basis for further research in chronic disease treatment.

 View pdf
View pdf


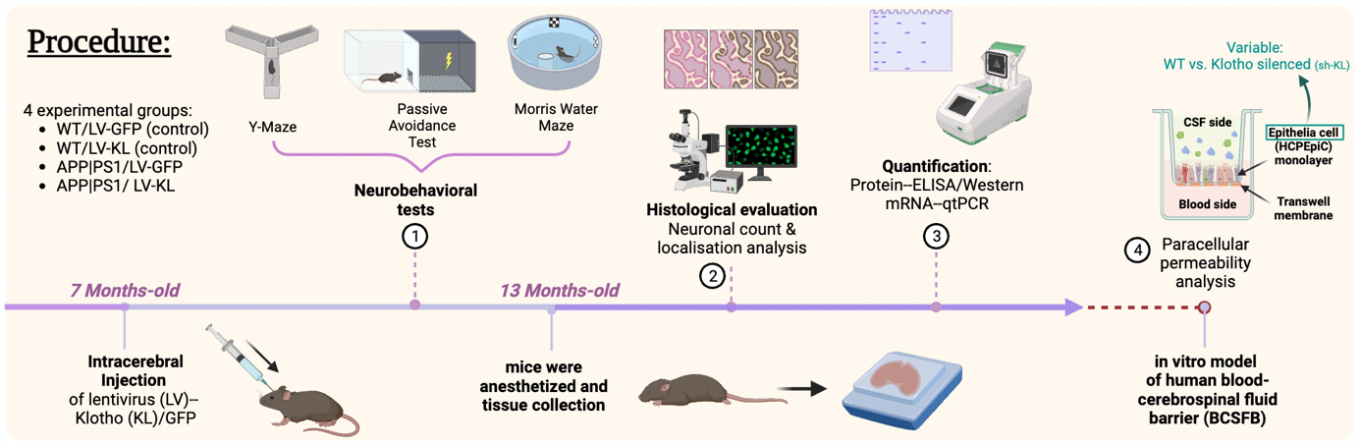
Alzheimer's Disease (AD), the most common neurodegenerative disorder, is characterized by cognitive decline and neurodegeneration. This review explores the intersection of AD pathology and Klotho, a protein linked to aging and cognitive enhancement. Klotho modulates aging-related processes, including amyloid-beta dynamics and neuroinflammation, through mechanisms such as autophagy enhancement, oxidative stress reduction, and amyloid-beta clearance. Research has indicated Klotho's potential in mitigating AD symptoms in murine models, such as APP/PS1. However, methodological challenges, including variability in experimental models and inconsistencies in Klotho administration, complicate the translation of these findings. This review synthesizes current research, highlights experimental limitations, and proposes methodological improvements to enhance the reliability and applicability of Klotho as a therapeutic target for AD, providing a foundation for future investigations that could revolutionize neurodegenerative disease management.

 View pdf
View pdf


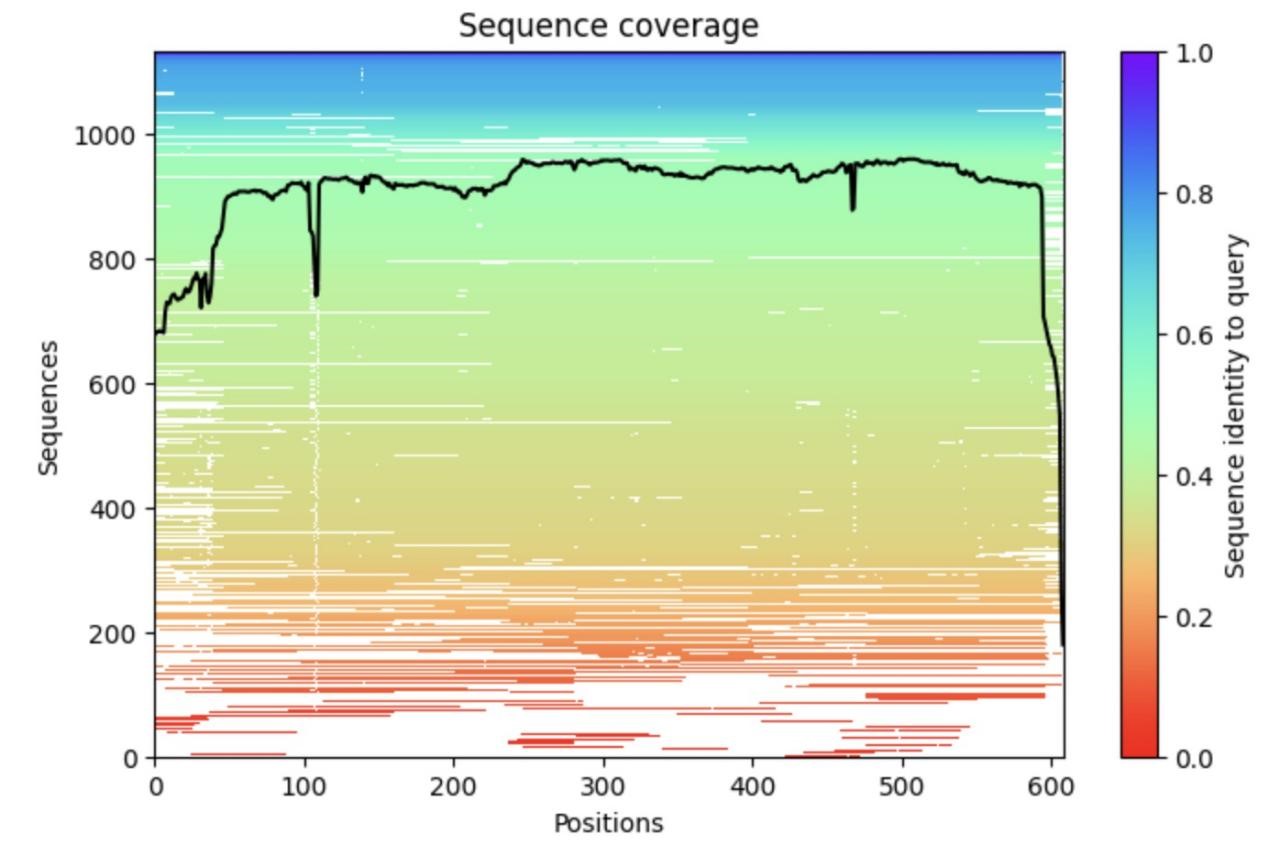
With the increase of drug research and development activities, the demand for resources for clinical medical experimental research grows year by year, and the traditional biological experimental methods can no longer meet the requirements of saving the existing resources, so this paper proposes a new method combining protein drug structure prediction and AI artificial intelligence to perform structure-based drug design on the computer. Considering that the medical community has not yet obtained the complete three-dimensional structure of human albumin, it is taken as a full-text research object for subsequent analysis and research. Firstly, the standard amino acid sequence of HSA was extracted from the uniprot protein database and imported into alphafold2 for structural prediction with atomic accuracy, and then the prediction results were fed into the plip tool for non-covalent bonding interactions to explore the potential binding sites and drug pockets. The experimental results indicate that human serum albumin has high drug activity and is a suitable choice as a ligand drug, which needs to be further investigated by related scholars. This study provides a novel method to guide the drug development, which is expected to play an important role in future protein applications and drug repositioning.

 View pdf
View pdf


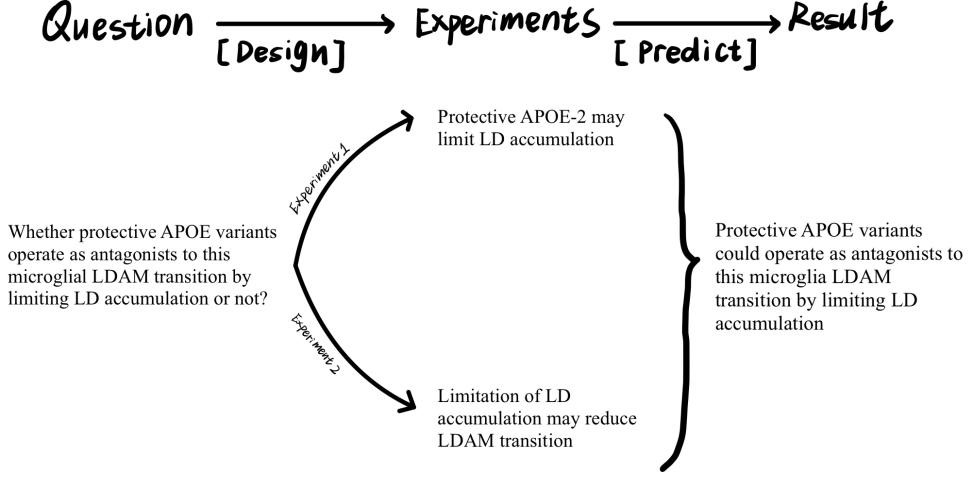
Recent studies have suggested the relationship between genetic risk factors related to lipid droplets accumulation such as APOE4 and Alzheimer’s disease pathology. However, whether certain APOE variants act as inhibitors of transition to LDAM by limiting LD accumulation remains unknown. This paper raises a research proposal for this question by trying to illustrate it in two steps. First, experiments performing immunostaining on mice suggest that APOE2 could limit lipid accumulation, proving that APOE2 could efficiently clear myelin debris and microgliosis is dramatically increased upon acute demyelination. Then, several experiments are performed to prove that limited lipid accumulation could reduce microglial LDAM transition, illustrating that the differences in ability of phagocytosis, ROS production and immune signaling exist if there are differences in the content of lipid accumulation. Finally, some insights about the related therapies are mentioned. If the hypothesis in the proposal is proved to be true, some related potential therapeutic strategies for treating Alzheimer’s disease would appear.

 View pdf
View pdf




