

Volume 86
Published on February 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Computing Innovation and Applied Physics
This thesis examines vortex and wake formation mechanisms in automotive aerodynamics and their impact on vehicle performance, emphasizing strategies to mitigate adverse airflow effects through optimal design and computational techniques. It demonstrates that vortices and wake turbulence elevate drag, diminish fuel efficiency, and compromise high-speed vehicle stability. Streamlined body design, optimized rear-end shape, and underbody airflow management can effectively reduce wake turbulence and vortex intensity, enhancing aerodynamic performance. This paper also introduces a variety of computational techniques, including theoretical analysis, wind tunnel experiments and Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), and explores the application of these methods in the real-world design process. CFD simulation demonstrates its advantages in evaluating airflow characteristics and optimising design solutions, enabling engineers to carry out efficient iterative design. Future research directions include the application of active aerodynamic systems and the integration of intelligent design algorithms for more efficient airflow control and vehicle performance enhancement.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the current context of global energy structure transformation and climate change response, the development and utilisation of wind power, as a kind of clean and renewable energy, has received extensive attention. However, the intermittency and uncertainty associated with wind power present challenges to its stability and reliability in power system scheduling. This paper provides an in-depth analysis of the application of robust optimization algorithms in wind power systems, focusing on how these algorithms can enhance the efficiency and stability of wind power within power systems. This paper discusses the specific methods of robust optimisation algorithms for solving problems in wind power systems from various perspectives. For example, by constructing a robust optimisation model that takes into account the uncertainty of wind power output, the scheduling flexibility and economy of the wind power system can be effectively improved. At the same time, the application of robust optimisation algorithms is analysed in terms of improving the anti-interference capability of wind power systems, optimising the combination of wind turbines, grid integration and wind farm planning, and improving the accuracy of wind power forecasts. The effectiveness of the algorithms in solving the problems encountered in the scheduling of wind power systems is analysed, and the challenges and opportunities for future development are discussed.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper explores the continuum fitting method for estimating the spin of stellar-mass black holes in X-ray binaries. By fitting the thermal emission created by the accretion disk to theoretical models, this method provides a precise and accessible way to estimate the spin of black holes. Key developments, including the use of KERRBB and SIMPL models, improve accuracy by accounting for disk structure and Compton scattering effects. This paper reviews recent applications of this technique and compare it to the X-ray reflection method, noting that continuum fitting is highly accurate for black holes with strong thermal emission. This paper also gives the new spin measurement of some black hole, especially the Cygnus X-1, that has the spin a_*>0.976, but also use it to prove that the continuum fitting method which relies heavily on knowing the black hole’s three parameters. Finally, this paper discusses both the advantages and challenges of this method, with an expectation of future improvements in modeling and observations that can expand its use.

 View pdf
View pdf


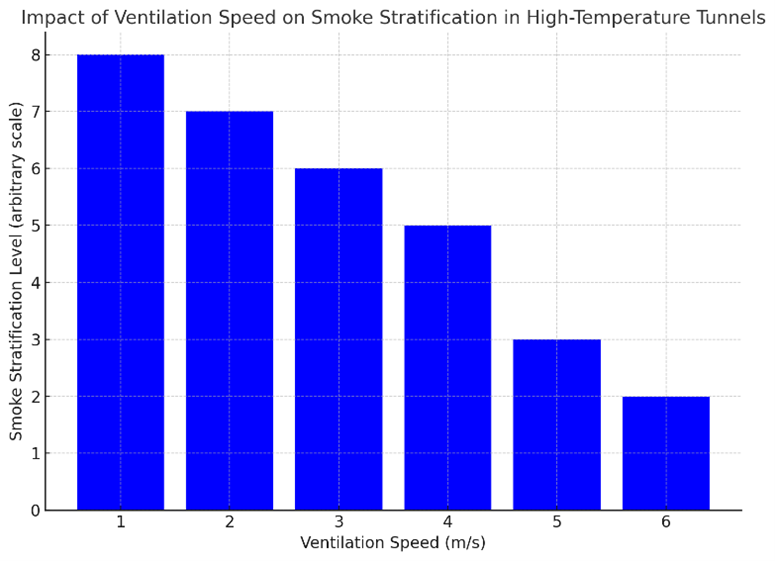
When high-temperature geothermal conditions occur within road tunnels, the safety of emergency exits becomes more challenging, especially in cases of fire. The high background temperature increases the speed of the smoke stratification process, and therefore, is unfavorable for people rescue and safety evacuation. In China, longitudinal ventilation systems are widely used to control the smoke within road tunnels during emergency fire events and help ensure safety evacuation. This paper aims to evaluate the performance of the longitudinal ventilation system when applied to a high-temperature road tunnel. The results show that the high-temperature geothermal in the tunnel will result in an accelerated stratification of the smoke layer, and the ventilation speed must be reasonably adjusted to meet the demands of smoke control. Under an optimal ventilation setting, the smoke density in the passage was reduced and the visibility was dramatically improved, which tremendously increased the evacuation efficiency. Overall, this study provides some practical suggestions for tunnels exposed to high geothermal temperatures, including the potential for variable-speed ventilation systems and localized smoke extraction strategies.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the era of big data and artificial intelligence, machine learning has become a crucial tool for extracting insights and making predictions across various domains. Bayes’ theorem, a fundamental principle in probability theory, has emerged as a cornerstone in many machine learning algorithms. This literature review explores the main applications of Bayes’ theorem in machine learning, focusing on its role in classification, Natural Language Processing (NLP), and other emerging fields. The study aims to provide an overview of how Bayesian principles enhance learning algorithms, improve decision-making processes, and address complex problems in artificial intelligence. Through a systematic review of academic papers from Google Scholar, this research synthesizes current knowledge on Bayesian methods in machine learning. The methodology involves defining the research scope, conducting a literature search using specific keywords, screening relevant studies, and analyzing the collected data. By examining diverse applications ranging from disease prediction to sentiment analysis, this review highlights the versatility and significance of Bayes’ theorem in advancing machine learning techniques and their real-world implementations.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper discusses the application of time series analysis in financial markets and biological phenomena. It expounds the basic theory of time series analysis, including the concepts and characteristics of time series and commonly used time series models. It also provides an in-depth analysis of its application in financial markets, covering the characteristics of financial time series and specific applications in stock markets and foreign exchange markets, such as stock price forecasting, risk measurement, foreign exchange rate forecasting and volatility analysis. It also discusses the application of time series analysis in biological phenomena, including the characteristics of biological time series and its application in biological growth and development, such as modeling the growth curves of animals and plants, and studying the dynamics of microbial populations. The application of time series analysis in these two fields is summarized, providing a valuable reference for related research and practice.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper explores the integration of Arduino Uno with surface electromyography (sEMG) electrodes for measuring muscle electrical activity and controlling servo motors based on these signals. By analyzing electromyographic signals from various hand postures, such as opening and closing, signal variations were thoroughly evaluated. The study implements a servo control mechanism that adjusts the servo motor’s position based on computed root mean square (RMS) voltage values derived from EMG signals. The experimental results demonstrate that the servo control system effectively mirrors hand movements, providing a feasible solution for biomedical applications and human-machine interfaces. This research highlights the potential for using affordable hardware for sophisticated control systems and suggests future enhancements to improve system accuracy and applicability.

 View pdf
View pdf


Speech Emotion Recognition (SER)’s burgeoning significance within intelligent systems is underscored by its transformative impact across various fields, from human-computer interaction, and virtual assistants to mental health monitoring. Over the rapid development of this technology in the past two decades, studies have continuously confronted and overcome kinds of real-world challenges, such as data scarcity, environmental noise, and cross-language differences. This survey focuses on recent innovations in SER, particularly deep learning architectures, and synthetic data augmentation, and addresses recent developments in cross-domain and multimodal SER techniques, which have expanded the applicability of SER to more diverse datasets.

 View pdf
View pdf


Image recognition has always been a fundamental research task in the computer vision community, aimed at identifying the categories of objects in images and has been widely used in many fields, especially in autonomous driving. Early image recognition technologies were mostly based on machine learning, and their recognition speed and accuracy could not meet the application requirements of complex autonomous driving scenarios. With the great success of convolutional neural networks, image recognition technology based on deep learning has attracted increasing research interest. Taking the autonomous driving scenario as an example, this article introduces the latest research progress of image recognition technology, including representative methods and their basic pipelines. In addition, this paper also introduces the commonly used dataset in image recognition and discusses the existing problems of image recognition in autonomous driving tasks. Finally, this paper looks forward to the future development directions of this field, hoping bring some new insight to advance the further development of image recognition under autonomous driving scene.

 View pdf
View pdf


In recent years, quantum key distribution (QKD) protocols have undergone rapid evolution, thus significantly advancing the field of quantum communications. The exploitation of quantum properties enables quantum communication to achieve superior security, yet many traditional protocols still face challenges in terms of stability and practicality. Since 2019, two new QKD protocols have emerged: mode-pairing QKD and sending-or-not-sending TF-QKD. In this paper, through an in-depth analysis of the existing literature, a simple mathematical derivation of the quantum uncertainty relation is provided, along with a systematic summary of the process for proving the security of these two new protocols. The results demonstrate that sending-or-not-sending TF-QKD can still effectively ensure the security of information in the presence of large bit error rates, showing its potential application in quantum communication. In addition, the paper explores future research directions, including experimental validation in diverse real-world environments, performance optimization, and the development of robust error correction techniques. These studies provide a critical foundation for the practicalization of QKD and promote the further development of quantum communication technology.

 View pdf
View pdf




