

Volume 7
Published on July 2023Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Materials Chemistry and Environmental Engineering (CONF-MCEE 2023), Part II
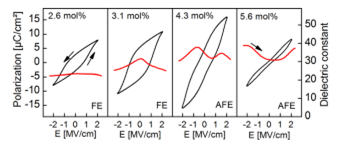
Recently, ferroelectric material is playing a more and more important role in the applications of semiconductor devices, especially in random access memory(RAM) devices, and transistors. Compared with traditional flash memories, FRAMs have advantages such as low operation voltage, a huge number of writes, non-volatile properties, and high write speed. However, in the early stage, the main materials used to produce FRAMs are perovskites with crystal structures. Those materials like PbTiO3/PbZr0.3Ti0.7O3 are restricted by the size and the complementary-metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) technology, which is the common technology used to process semiconductor materials. Hafnium oxide material is a newly discovered material with ferroelectricity when doped with Zirconium(Zr). The Hf0.5Zr0.5O2 thin film is an ideal material for FRAMs, which has a smaller size than perovskites FRAMs and is compatible with current CMOS technology, which means lower cost and higher performance. This article aims to explain some properties of hafnium oxide materials based on different aspects, like dopants, thickness, annealing, and electrodes, and elaborate on the advantages of FRAMs made by hafnium oxide materials.

 View pdf
View pdf


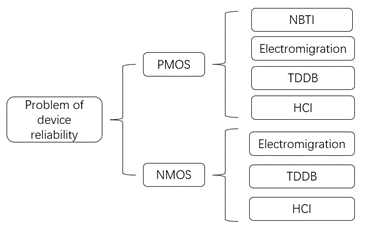
Complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) devices are an important part of integrated circuit (IC), but in the application process, it has many reliability problems, such as negative-bias temperature instability (NBTI), electromigration (EM), time-dependent gate oxide breakdown (TDDB), hot carrier injection (HCI), etc. These reliability problems can affect the threshold voltage and mobility of the device. In order to improve the reliability of integrated circuits, these reliability problems are systematically studied in this paper.

 View pdf
View pdf



Applying a tandem structure to silicon-based sub-cells is the most promising strategy for enhancing efficiency and overcoming the Shockley-Queisser limit, which is an intrinsic limitation of silicon-based solar cells. This study will begin with the various categories of tandem solar cells and then analyze the requirements for optimizing the overall conversion efficiency. Therefore, the characteristics of BaZrS3, a chalcogenide perovskite with high elemental abundance, exceptional photovoltaic properties as well as outstanding stability, are thoroughly evaluated and compared with other previously utilized materials for the top sub-cell. Finally, the most feasible approach for thin film growth which is physical vapor deposition is reviewed based on the available literature from bulk synthesis of BaZrS3. This evaluation may serve as a critical guideline for the future commercialization of BaZrS3.

 View pdf
View pdf


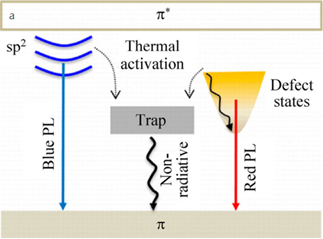
Graphene quantum dots (GQDs) have recently been developed as promising interfacial engineering materials for modifying perovskite solar cells (PSC) surfaces due to their low toxicity and good charge mobility compared to other metallic-based quantum dots in semiconductors. However, the side effect of decorating PSC with GQD is that it creates more structural defects that might cause shallow trap states and non-radiative recombination, leading to decreased PSC performance. This paper reviews the impact of structural defects and trap state of GQDs and the combined corresponding influence on the performance of PSC based on thermally stimulated current (TSC) and density-voltage (J-V) plots. This paper then offers new guidelines to minimize the trade-off of GQD by suggesting a well-controlled fabrication process.

 View pdf
View pdf



Among the wide range of third-generation photovoltaic power generation technologies, there is a widely used type of photovoltaic - heterojunction photovoltaic cells. Although each of the different types of heterojunction photovoltaics has been studied in depth, no one has considered the direct application of the different types of heterojunction photovoltaics at the application level. This paper introduces the composition and advantages of heterojunction photovoltaic cells, and briefly introduces graphene/n-type amorphous silicon heterojunction photovoltaic, organic compound/inorganic heterojunction photovoltaic, and inorganic/inorganic heterojunction photovoltaic represented by CuO and Zn2O, and summarizes the different photovoltaic conversion efficiencies, preparation methods, and other key information of these cells, and compares these information. In particular, whether the photovoltaic conversion efficiency can reach the shockley-queisser limit is examined. Among them, the photoconversion efficiency of graphene/n-type amorphous silicon heterojunction and simple metal oxide heterojunction was not very satisfactory, and finally the heterojunction PV cell constructed by the byorganic cavity-conducting material led by Graezel et al. was chosen among the different research directions of organic/inorganic heterojunction PV cells. Cavity-conducting material combined with a titanium dioxide nanofilm with adsorbed dye as a relatively ideal heterojunction PV cell for comparison was examined in this paper, which provides a proposal for the commercial development of new heterojunction PV cells in the future.

 View pdf
View pdf


In recent years, major industries have been hit hard by the COVID-19 pandemic, and people have become more aware of issues such as environmental health. The development of computer programs, artificial intelligence (AI), has gradually entered the vision of researchers. The product of this technology can help people better manage and improve the current environmental conditions. This paper, through a method of literature review, aims to explain the development history of AI and its application in different fields such as the environment. Through the research, the paper concludes that artificial intelligence can observe in real time for long periods of time without getting tired like humans do. Based on the application of big data analysis and intelligent programs, artificial intelligence can make reasonable plans in a much shorter time than human beings. However, the solution is only based on the operation of the system. In the actual situation, there will be many obstacles. Therefore, it is still necessary for humans to make judgments based on the results of an operation rather than relying entirely on artificial intelligence. Complicated weather conditions can also make the results of the calculation inaccurate. So there will still be a need to evolve computer programs or for artificial intelligence to be able to calibrate the data it is monitoring from the past.

 View pdf
View pdf


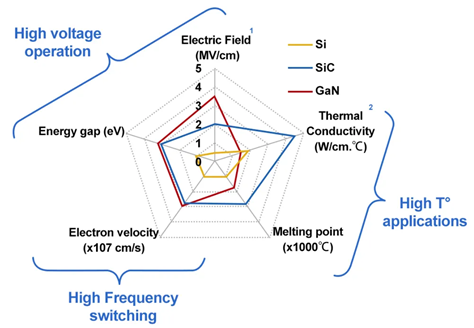
Various devices made of the third-generation semiconductor have been gradually applied to various fields with the rapid development of the third-generation semiconductor materials equipment, manufacturing technology, and device physics represented by SiC and GaN. Firstly, the characteristics of the third-generation semiconductors is analyzed in this paper. Compared with the first-generation and second-generation semiconductors, the third-generation semiconductor has a wider band gap width, higher breakdown electric field, higher thermal conductivity, higher electron saturation rate and more expensive price. Then this paper will talk about the application of the third-generation semiconductor. The third-generation semiconductor materials can be mainly used in three fields, which are photoelectric, microwave radio frequency and power electronics. In terms of the photoelectric aspect, this paper takes the blue LED as an example. The blue LED is produced because of the wide band gap of the third-generation semiconductor. In the microwave RF aspect, the paper takes the 5G communication system as an example. Third-generation semiconductors make the high-frequency, high-power devices needed for 5G communications systems. In the power electronics aspect, the paper cites new energy vehicles as an example. Third-generation semiconductor components have a number of features needed for new-energy vehicles. For example, third-generation semiconductors can work at high temperatures. Finally, this paper will introduce the development trend of it. In the future, larger wafers will become mainstream. The third-generation semiconductors will be used in more fields. In addition, the new material systems will gradually mature.

 View pdf
View pdf



Beta-blockers are generally prescribed for cardiovascular treatment and sometimes as sedative drugs for professionals such as musicians and athletes, which can cause serious side and adverse effects when the dosage is high. Additionally, beta-blockers are maintained as prohibited drugs for athletes by World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA). It is urgent to develop quick, simple and affordable analytical tools for beta-blockers. Electrochemical sensors have been favored by researchers for their simplicity, portability and quick detection. Therefore, this review discusses the most common voltammetric sensors for beta-blockers, along with two important features for effective determination: sensitivity and selectivity, which are realized by chemically modified electrodes.

 View pdf
View pdf


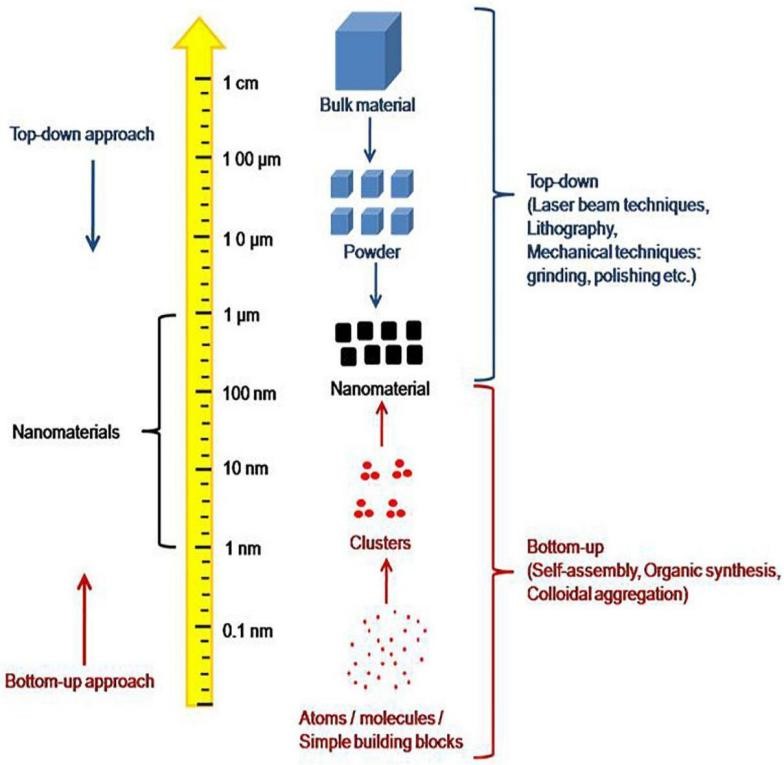
An innovative approach that blends nanotechnology technologies with supramolecular chemistry can accelerate the creation of complex nanoparticle-based goods, self-assembly is used in the production of nanoscale self-assembled systems with desired properties with great versatility and potential. One of the most intriguing classes of material that can be constructed by self-assembly is colloids which is widely used in many areas, especially in the pharmaceutical and industry.

 View pdf
View pdf


In recent years, conductive polymer materials have become a hot topic in scientific research due to their wide applications. Conductive polymer materials are mainly divided into composite type and structural type. Due to the poor oxygen stability and mechanical properties in the air of the doped materials of the structural conductive polymer, its application is limited. However, the composite conductive polymer has become the most widely used conductive polymer material in the market because of its easy processing, wide application range, good corrosion resistance and the conductivity can change according to the electrochemical reversible reaction. In this paper, the composite conductive polymer materials with different doping types are reviewed, and their applications in the fields of stealth technology, battery materials, and sensors are studied. The research significance of this paper is to summarize the research progress of composite conductive polymer materials by scientists in various countries in recent years, and provide scientific and theoretical support for other researchers in this field.

 View pdf
View pdf




