

Volume 94
Published on November 2024Volume title: Proceedings of CONF-MLA 2024 Workshop: Securing the Future: Empowering Cyber Defense with Machine Learning and Deep Learning
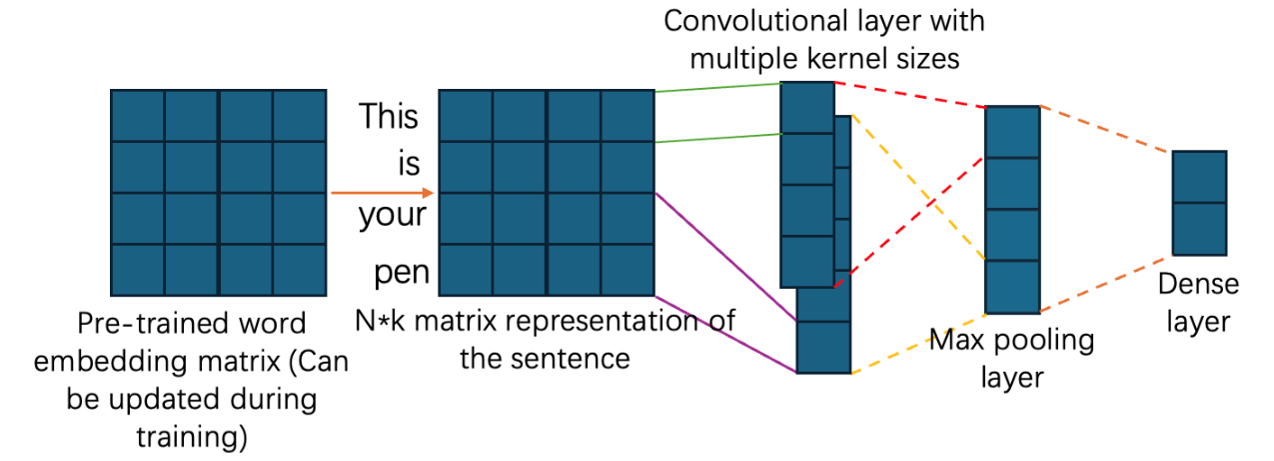
Born from the machine learning (ML) subfield of neural networks (NN), deep learning (DL) has many advantages over other ML algorithms and has become more significant today. As one of the most essential model architectures of DL, the convolutional neural network (CNN) has attracted the attention of many researchers, especially in recent years. Meanwhile, sentiment analysis has become more renowned since the rapid development of various online platforms like blogs, social networks, etc. To study these two heated topics together, this article selects a particular CNN model designed for sentiment analysis and explores its width’s potential influence on the result. During the experiment, four CNN models are created based on the same structure but with increasing width. By forwarding the pre-processed datasets to the four models and comparing their performances from different perspectives using different metrics, it’s concluded that the more expansive the model's width, the better it performs in the training, validation, and testing sections.

 View pdf
View pdf


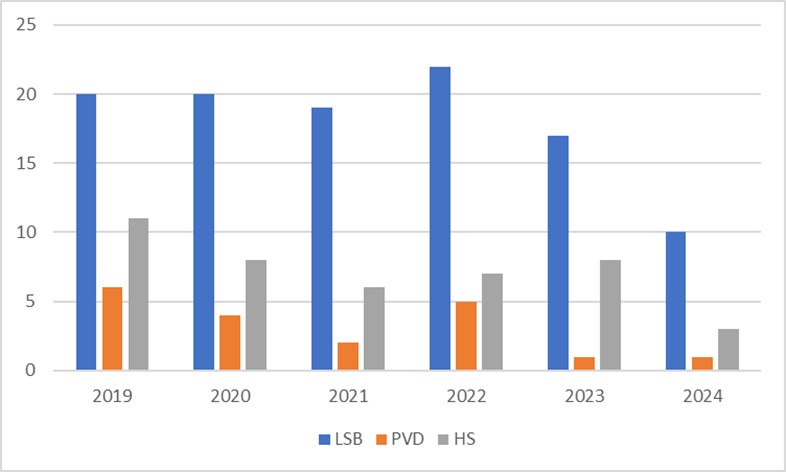
Image steganography, a technique for transmitting secret information hidden within images over public networks undetected, serves as a discreet alternative to cryptography in the field of information security. This article explores new steganography techniques based on the Least Significant Bit (LSB) method, widely recognized for its simplicity in embedding secret data by altering the least significant bit of pixels in the spatial domain. The performance of these LSB-based methods is critically assessed using criteria such as Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR), embedding capacity, and histogram analysis. A comprehensive review of recent literature provides a foundation for this evaluation, highlighting advancements and identifying areas for future improvement. Additionally, the article discusses practical applications of LSB-based steganography in healthcare, government operations, and cloud storage, suggesting directions for further research and development in this subtly powerful area of data security.

 View pdf
View pdf


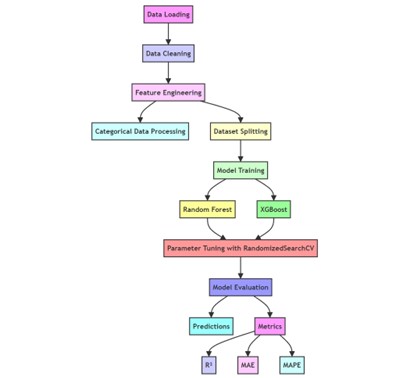
The global film industry has been proved to impose a significant impact on both culture and the economy, with box office revenue serving as a crucial indicator of a film's commercial success. This study utilizes data from the Kaggle "TMDB Box Office Prediction" competition, encompassing 3,000 films released between 1990 and 2018, to predict movie box office revenue using Random Forest, XGBoost algorithms, and deep learning models such as Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (Bidirectional LSTM) and Simple Recurrent Neural Network (SimpleRNN). The goal is to develop a model that accurately predicts movie box office. By comprehensively considering multiple factors such as budget, popularity and film characteristics, this study not only significantly improves the accuracy of box office prediction, but also provides a scientific basis for the formulation of film market strategies. The results demonstrate that the Bidirectional LSTM excels in handling complex time-series data, showing strong trend-capturing capabilities, while XGBoost exhibits greater robustness in dealing with complex data and outliers. These findings can not only provide guidance for making more effective strategies on film production and distribution, but also provide new directions for future research, such as delving into the impact of social media on box office and developing more sophisticated predictive models to adapt to changing market dynamics.

 View pdf
View pdf



As Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies are developing rapidly and are widely used in various domains, it is efficient and convenient for composers to make music using AI to convert sheet music to audio. This research aims to compare the performance of different models in identifying individual notes within sheet music. Compared to traditional technologies like Optical Music Recognition (OMR), deep learning models have a significant advantage in processing blurry images with high efficiency. In the research process, three different models are used in searching for musical notes: OMR, You Only Look Once (YOLO)v5, and YOLOv8. The evaluation index consists of recognition accuracy, mean Average Precision (mAP), inference speed, and parameter quantity. After the experiment, it is found that the YOLO model performs best with high accuracy and fast speed. Based on the above analyses, the thesis finds that the YOLO model can be an efficient tool in composing music, with further research.

 View pdf
View pdf


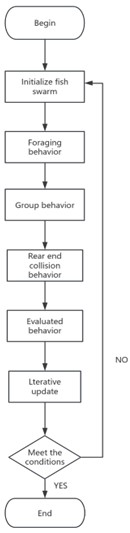
The significance of this research lies in its potential to improve energy efficiency in buildings, particularly in regions prone to high temperatures. By optimizing the thermal performance of heat-reflective glass, buildings can achieve better temperature regulation, leading to reduced dependency on air conditioning systems and lower energy costs. This research specifically targets the optimization of glass thickness, a critical factor influencing the overall effectiveness of heat-reflective glazing. The focus is on minimizing the transmitted light intensity for sunlight within the wavelength range of 300 to 2000 nm, which is vertically incident on the glass. The optimized glass thickness aims to maximize the thermal reflective properties while ensuring adequate natural light within indoor spaces. This study employs the Artificial Fish Swarm Algorithm to explore the optimal thickness of heat-reflective triple glazing. The effectiveness of this optimization method is assessed by comparing its results with experimental findings obtained through a systematic traversal of glazing thicknesses. The results highlight the potential of the Artificial Fish Swarm Algorithm to significantly enhance the thermal performance of heat-reflective glass, offering a practical solution for energy-efficient building design in hot climates.

 View pdf
View pdf


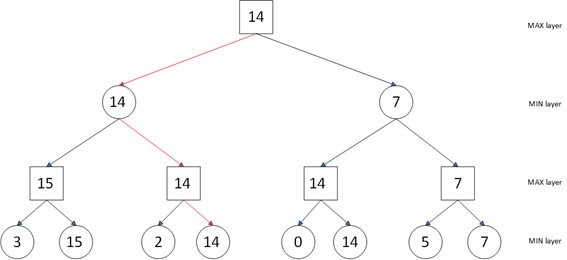
This paper presents the implementation of a Gomoku AI based on the alpha-beta pruning search algorithm and the Negamax algorithm. Gomoku, a traditional board game known for its strategic depth, poses significant challenges in AI development due to the exponential increase in possible moves. The AI leverages the computational efficiency of Alpha-Beta Pruning, which enhances the Negamax algorithm by reducing the number of nodes that need to be evaluated in the game tree. This combination allows for faster decision-making without compromising accuracy. Additionally, a value evaluation function is used to assess board states and guide the AI in selecting optimal moves. In the results the performance of the AI was tested through simulations, demonstrating great performance in move selection and computational efficiency compared to traditional methods. The paper also explores potential improvements, including the integration of reinforcement learning (RL) techniques to further enhance the AI's adaptability and strategic decision-making capabilities.

 View pdf
View pdf



Pathfinding systems are used in many applications today, including navigation systems, autonomous driving systems, and games. The core part of the pathfinding system is the pathfinding algorithm, A Star pathfinding algorithm is a kind of efficient pathfinding algorithm, which is especially suitable for the design of game pathfinding. In this paper, based on the A Star algorithm, Godot game engine and C Sharp language are used to write a pathfinding program. After comparing different pathfinding methods and the estimated function, the A Star algorithm is improved according to the needs of the actual game pathfinding system, so that the pathfinding program can avoid crossing the obstacles through the diagonal by searching the surrounding obstacles and excluding unavailable nodes, and find a shorter path by using the Euclidean distance estimated function. The program applies the improved A Star algorithm in practice, and finally can complete the basic pathfinding needed in the game, which is practical for the design of the game's pathfinding system.

 View pdf
View pdf


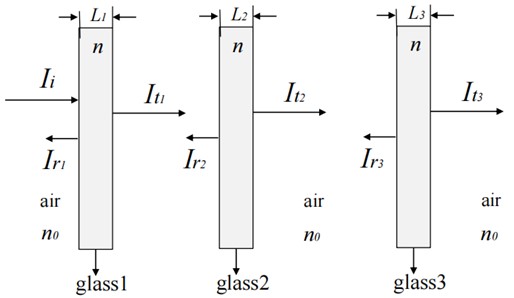
This paper introduces an innovative three-layer window glass design optimized using particle swarm optimization (PSO) to achieve reduced ultraviolet (UV) transmission, particularly targeting the 300–400 nm wavelength range. PSO, recognized for its capability to handle nonlinear optimization problems effectively, was applied to determine the optimal thickness of each glass layer, aiming to minimize UV transmission as quantified by a fitness function based on the total transmitted energy. The outcomes highlight significant enhancements in UV shielding capabilities of the optimized glass structure over traditional designs. This study not only underscores the efficacy of PSO in refining material properties but also positions it as a valuable tool for advancing green building technologies and energy-efficient solutions. By reducing UV transmission, the optimized glass contributes to better indoor environmental quality and health protection, presenting new possibilities for the application of multi-layer glass in various sectors. These results advocate for broader application and further validation of PSO in material optimization, paving the way for innovations in architectural and environmental design.

 View pdf
View pdf


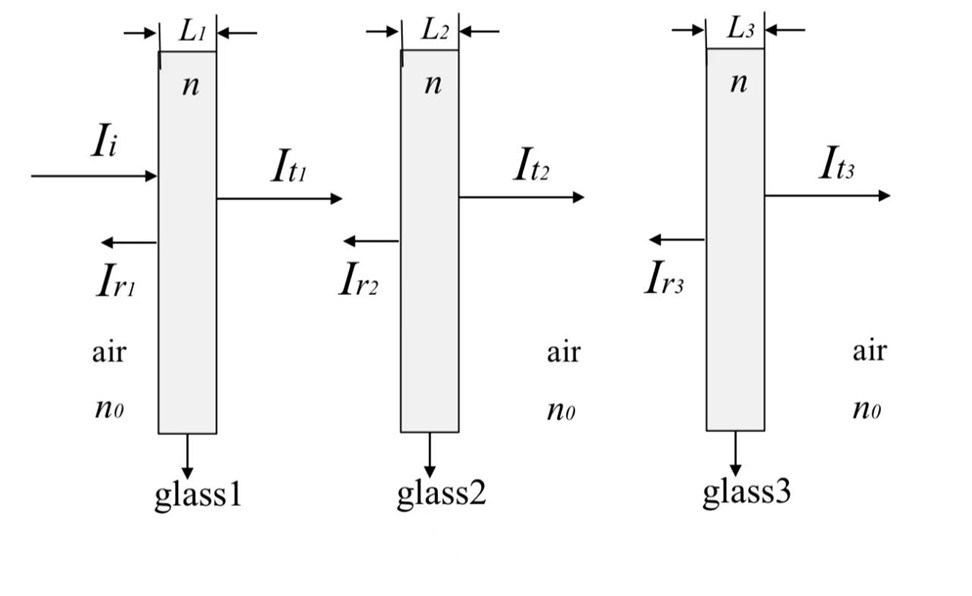
This study investigates the optimization of multilayer glass thickness to maximize solar heat gain in buildings located in cold northern climates, utilizing the Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) algorithm. The research focuses on enhancing thermal comfort and reducing energy consumption by optimizing the thickness of three glass layers, thereby improving solar energy transmission into indoor spaces. ACO, a metaheuristic inspired by the foraging behavior of ants, is employed due to its robustness in handling complex optimization problems. The study incorporates wavelength-specific considerations into the ACO framework to achieve a sophisticated optimization approach, resulting in improved solar energy transmission. The experimental results demonstrate that the optimized glass configuration significantly increases sunlight transmittance, especially within the target wavelength range, contributing to more energy-efficient and comfortable architectural designs. This research highlights the potential of ACO in optimizing building materials and suggests further refinement of the algorithm for enhanced performance in real-world applications.

 View pdf
View pdf


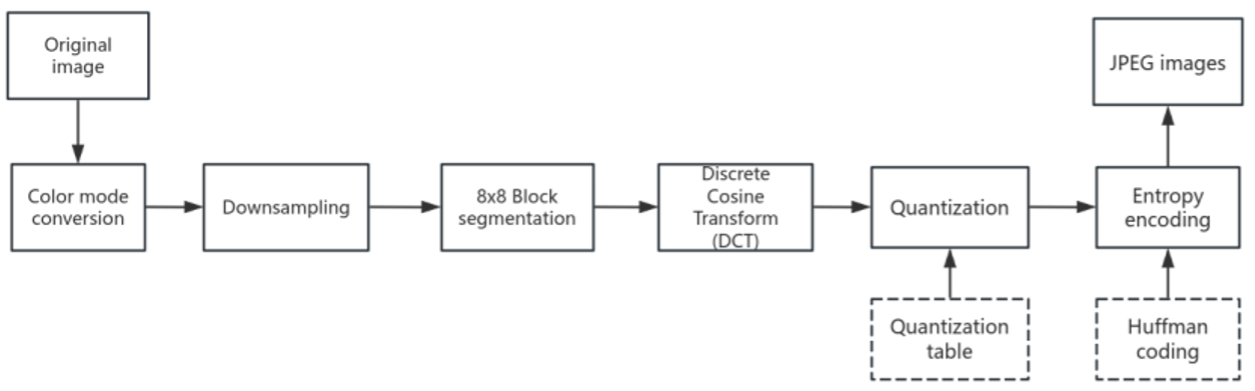
This paper provides an extensive review of recent advancements in reversible information hiding methods tailored for JPEG images, a predominant compression standard crucial for data security and digital copyright protection. It starts by outlining fundamental concepts related to JPEG image structure and reversible data hiding techniques. The analysis then delves into three primary methods: modifications to JPEG quantization tables, adjustments in Huffman tables, and corrections of Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) coefficients, detailing how each technique contributes to effective and secure data embedding. Furthermore, the exploration of potential applications in critical areas highlights the versatile utility of these techniques in safeguarding digital content. Concluding with a discussion on future research directions, this paper emphasizes the significant potential for growth in this field, particularly in enhancing security measures and improving efficiency. Such advancements promise to extend the applicability of reversible data hiding, ensuring robust copyright protection and information security in the digital age.

 View pdf
View pdf




