

Volume 11
Published on November 2023Volume title: Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Mathematical Physics and Computational Simulation
Currently, the relatively popular public key encryption is RSA. It was officially launched in 1978 and given their initials as a name. Different encryption and decryption keys are used in the RSA public-key cryptosystem. Deriving decryption keys from known encryption keys is computationally difficult. Rsa has emerged in various forms since its development. Since the development of RSA, there have been various forms, which means there are various loopholes. Next, we will summarize several interesting attack methods of rsa. It will involve continued fractions and CRT and so on. Through this paper, one can learn a series of knowledge about rsa. As a classic asymmetric password, the value of rsa's existence is relatively high, and exploring its value is something that every password learner should experience. Through this article, one will learn about the most basic attack methods of rsa.

 View pdf
View pdf


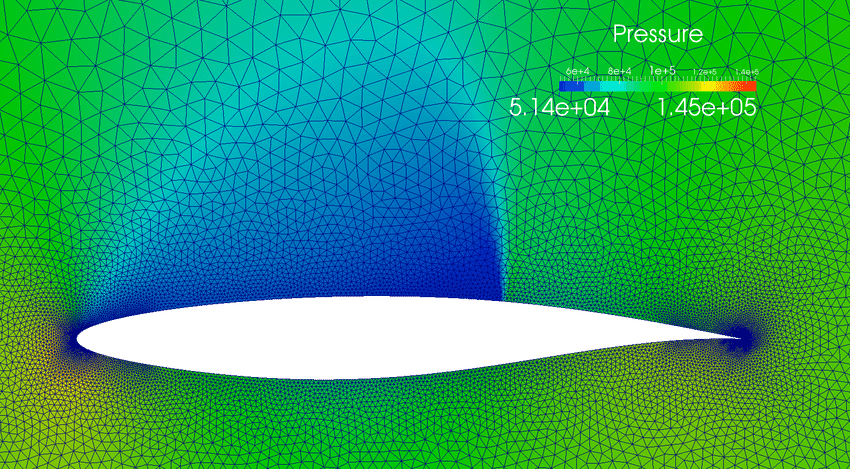
In many industries, there is a need to model the flow of air over structural components. With sufficient information from these models, engineers can better implement these parts into a complete design. The purpose of this paper is to provide a model of specific airfoils using computational fluid dynamics (CFD). With computational fluid dynamics, the characteristics of air around an airfoil can be modeled, providing useful data to engineers who could be designing an airfoil or airplane. The CFD calculations are performed using Python, along with the two packages Numpy and Matplotlib. The governing equations of CFD, including Newton's Second Law, small disturbance equation (SDE), wave propagation, etc. are discretized and transformed into partial differentiation equations (PDE). Using the second order derivative of the wave propagation PDE, the SDE can be solved in iterations and plotted on a graph showing the velocity distributions for a particular airfoil. The results from the CFD calculations show general trends in velocity distributions, regardless of airfoil shape. These include a decrease in x-direction velocity at the ends of an airfoil with an increase at the midsection of the airfoil. Also, y-direction velocity is generally positive and increasing at the front of the airfoil, but negative and decreasing at the end of the airfoil. What is important to understand is how different airfoil shapes can change velocity distributions, moving to using 3D CFD calculations, and the possibility of using CFD for modeling airflow over a multitude of objects.[ Henry Bao, the first author, participated in the Illinois junior academy of science state fair, and abstracts of the regional winners' presentations were posted online. (ilacadofsci.com)]

 View pdf
View pdf


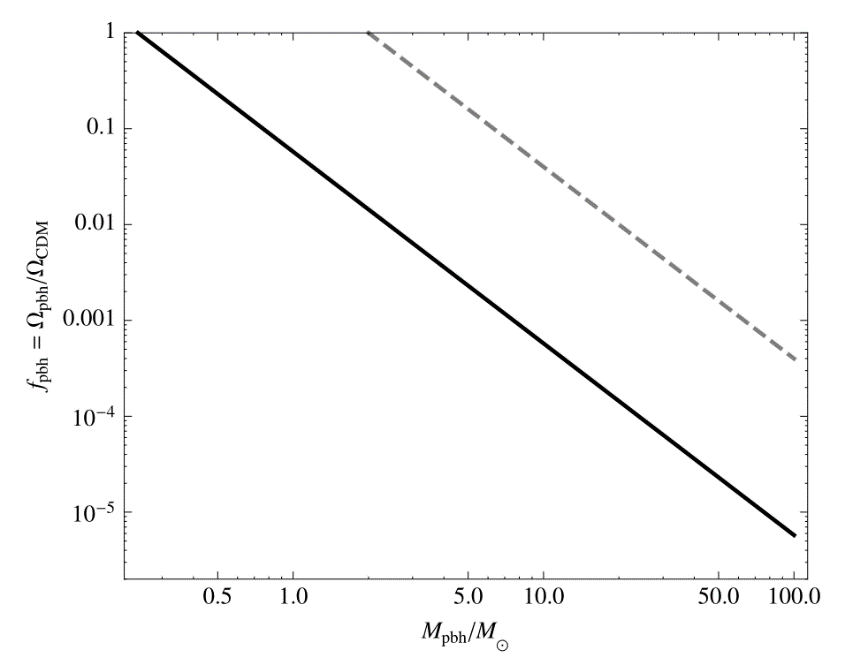
In recent years, the origination and formation of the black holes remains an unsolved issue. On this basis, a large number of scholars have suggested the possible relationship between primordial black holes and dark matter. To be specific, if one can confirm the existence of PBHs, it’s much more likely for researchers to determine the origin and nature of dark matter, and thus come to the solution to one of the most important problems in modern astrophysics. The search missions for PBHs have been on for decades, and amounts of money and time had been put in, yet no direct evidence has come in. In this paper, it is hoped to map out the dark matter distribution in early universe with THESAN simulations. According to the analysis, this study provides the most valuable and worthwhile observation goals for the search of PBHs. Overall, these results shed light on guiding further exploration of black holes.

 View pdf
View pdf


The appearance and generation of O2 has long been discussed by the scientists. It is a fundamental topic as it can not only help us get to know the origin of lives, but can also give us the inspirations of discovering the possibilities of lives on other planets as O2 is vital to most creatures. And the GOE is the most important discovery in the O2-producing period.The appearance of the GOE was marvelous and is a great turning point in the earth’s developing history. Of course, the GOE cannot be simply explained as a coincidence, it is an inevitable development in the earth’s developing history. In this paper, we are going to focus on the mighty causes including photosynthesis in the early stage of earth and O2 storage. Also we are hunting the influences of the GOE and a relating experiment in search of the probabilities of mighty lives in the outer space.

 View pdf
View pdf


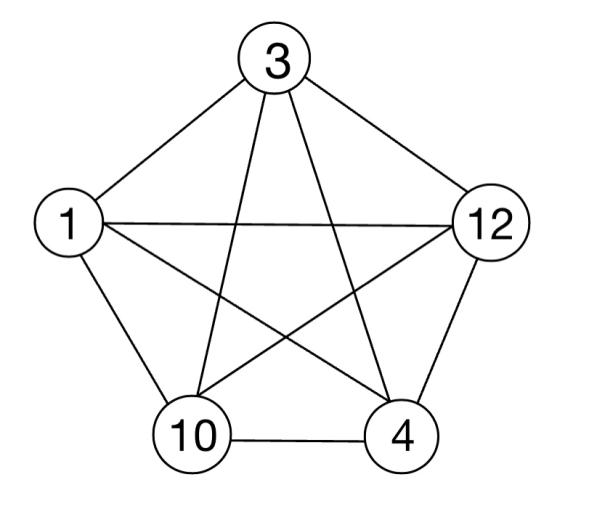
For Disneyland visitors, a well-designed route is often necessary to experience the maximum number of preferred entertainment facilities within a limited time. To construct the best way that optimizes visitors’ satisfaction, a survey is first conducted to estimate the attraction value of each facility, followed by the collection of data that record the traveling time among each facility and the waiting line time. Using collected data and listed constraints, a possible route is listed as an example. To solve the problem, a model is constructed based on integer linear programming. The original, incomplete, and modified formulations are listed in the last part of this paper.

 View pdf
View pdf


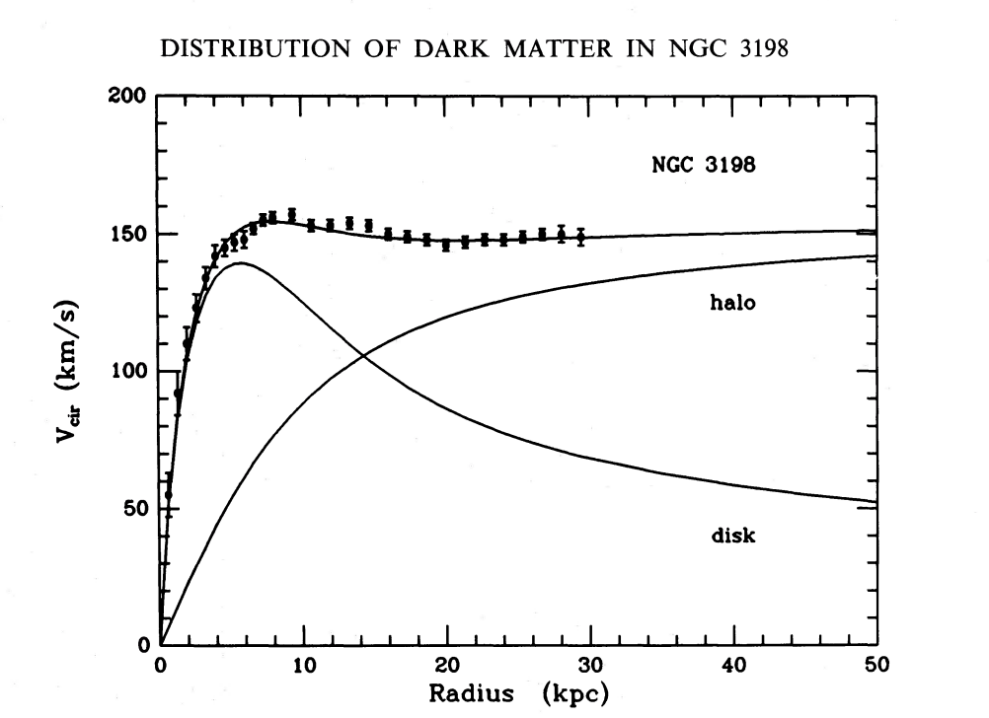
Although several discoveries have proved the gravitational effects of dark matter (DM) on various astrophysical objects, its origin remains one of the main puzzles in physics. These observations can be explained by adding a new particle to the Standard Model that is weakly interacting, massive, stable, and non-baryonic. One of the main characteristics of DM in question, beyond its exact particle nature, is its density in the Universe. In this paper, we use the latest data for the local DM density, total DM mass, and rotation curves in the Milky Way to estimate the density profile of these elusive particles in our Galaxy. We find the density profile parameters that match the current data and analyze the density of the stellar bulge and gas and star in the disk. We show that the stellar bulge dominates the Galactic dynamic for distances below a few kiloparsecs (kpc), the disk plays the most important role at intermediate distances, and DM explains rotation data beyond a few tens of kpc. Finally, we settle on a local DM density of about 0.5-0.7 GeV/ to fit the data well, regardless of the exact function we use to model the density profile.

 View pdf
View pdf



The waterjet propulsion system is a marine propulsion device prevalently used on contemporary high-speed vessels. The performance of a waterjet propulsion system is considerably affected by the nozzle. In this study, the influences of the shape and the outlet area of a waterjet propulsion system on the efficiency of the propulsion system is investigated using the computational fluid dynamics method. A total of 10 different nozzle designs, including cylindrical and conical nozzles with 5 different outlet areas, are analyzed in terms of nozzle efficiency and overall efficiency, and the possible reasons and explanations behind the variations of the nozzle efficiency and the overall efficiency are proposed in this study. The simulated results indicate that the conical nozzles consistently have higher nozzle efficiency than the cylindrical nozzles, and the maximum nozzle efficiency occurs in the conical nozzle with an outlet area of 60% of the inlet duct area. The abrupt change in the flow direction at the transition between the guide vane section and the nozzle, as well as the skin friction on the nozzle wall, are predominant factors affecting the nozzle efficiency. The waterjet propulsion units equipped with conical nozzles generally have higher overall efficiency than their counterparts equipped with cylindrical nozzles, while the maximum overall efficiency occurs in both the cylindrical nozzle with an outlet area of 50% of the inlet duct area and the conical nozzle with an outlet area of 60% of the inlet duct area. The loss of mechanical energy due to viscosity and turbulence in a propulsion unit is the major source of energy loss, while the kinetic energy carried by the exit flow is also a considerable factor affecting the overall efficiencies of the propulsion units equipped with conical nozzles with relatively large outlet areas.

 View pdf
View pdf


Galaxies as the most important structures in the universe and Galaxy formation is a sequential redistribution process.The basic picture of galaxy formation was first proposed by White and Rees.The physical processes involved in galaxy formation are very numerous and complex. We know very little about most of these processes. Therefore, we can only describe them with a few empirical formulas. In this article the popular simulation techniques for galaxy formation are discussed in detail, based on the most recently observed cosmic star formation history. This study will focus mostly on the goals of galaxy development by describing the processes of star formation, gas dispersion, dark matter, and galaxy correlation. In this paper, we do not study the formation process of a specific galaxy, but focus on the formation process of a large sample of galaxies in the framework of the whole cosmology We are also concerned not with the specific properties of a particular galaxy, but with the statistical properties of the whole sample of galaxies.Therefore the paper will next explore hydrodynamic techniques such as N-body simulation, other modified f (R) gravity models, smoothed-particle hydrodynamic simulation, and semi-analytic models to mimic the process of galaxy formation. This article finishes with a summary of galaxy formation.

 View pdf
View pdf


Motivated by results in the literature that use representations and group actions to produce nice geometric results about algebraic varieties, this article studies projective equivalence relations between closures of orbits for several complex algebraic group actions on , where is a complex representation of . In particular, we study the cases when is one of the following:, , , and . On the way, we also obtain some interesting geometric results from studying these orbits.

 View pdf
View pdf


When the wind blows against a building, the resulting force acting on the building at a particular elevation is called the “wind load”. Measuring and minimizing the wind load is crucial to ensure the safety of buildings. Therefore, the objective of this study is to investigate the effect of a building’s roof design on the wind load by evaluating and comparing the wind pressure differences ∆p that different building models experience by leveraging Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations. The 3D CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software SolidWorks was used to construct building models of identical dimensions with the exception of roofs harboring different shapes and angles. By exerting a wind velocity through flow simulation, flow trajectories and cut plot graphs of wind velocity and pressure surrounding the building models are generated. Wind pressure differences ∆p for each situation were calculated and compared based on the CFD results. Wind tunnel experimentation with building models will also executed to test the computed data and prove its reliability and applicability. The data shows that, among all tested roof designs, the barrel-vaulted roof exhibits the minimum pressure difference (of 171.15 Pa) between the windward and the leeward surface and experiences the least wind load and resists strong wind most effectively. It reduces up to roughly 15% of wind load compared to the worst case tested. For symmetric triangular gable roof designs, the greater base angle leads to greater wind load. Overall, this study provides the theoretical basis and scientific evidence for the building designs of the next generation.

 View pdf
View pdf




