

Volume 134
Published on May 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Signal Processing and Machine Learning

Depression is one of the most diagnosed mental illnesses in modern society, with leading causes such as psycho-trauma concerning interpersonal relationships, primarily relationships and familial dynamics, and both physical and psychological disturbances resulting from protracted exposure to stressors. Former research explicitly proved that virtual reality technology is likely to succeed as a major treatment medium for psychological disorders, primarily due to the fact that it is immensely immersive, interactive, and private. However, very little research is available in the literature regarding the treatment through VR, and exposure-based therapies of real-life landscapes. This paper presents an effort in an such direction: using VR technology for the treatment of depression via virtual rehab landscapes and VR exposure desensitization training to reduce emotional stress and enhance the treatment effect. It found that the viewing of virtual natural scenes resulted in significantly improved moods of the subjects and reduced their stress, with increased interactivity being more effective. One study observed elevation among the patients, where the degree of anxiety also decreases gradually eventually leading to better tolerance of treatment and treatment effectiveness. All these findings confirm the claim that such virtual natural environments and exposure desensitization trainings would be effective for depression treatment because they allow for a new pathway of non-pharmacological interventions.

 View pdf
View pdf


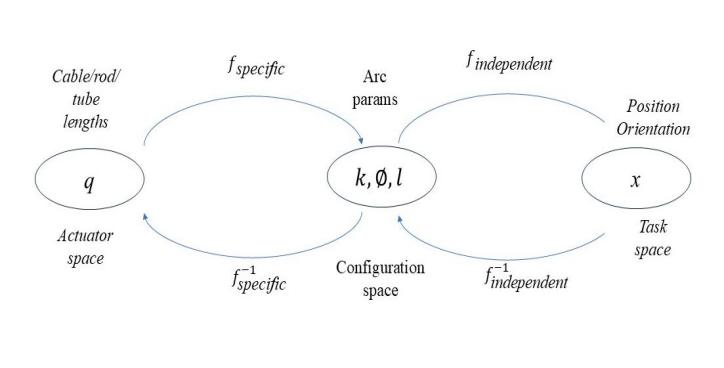
Tendon-driven continuum robots (TDCRs) are extensively employed in medical equipment, rescue, and other fields. Currently, most studies solve the workspace of continuum robots based on a specific number of segments. There is no comparison between different numbers of segments. In this work, we explored the workspace of single- and two-stage TDCRs and compared the shape volume of the workspace. We implemented a kinematic modeling approach based on the constant curvature model to analyze the impact of segment numbers on the workspace. This efficient approach allowed us to compute the workspace of two different TDCRs with less computation time and draw the workspace volume. Therefore, we observe the effect of different numbers of segments of continuum robots on the robot's workspace. The results show that increasing the number of segments significantly enhances the robot's workspace and changes its shape and volume. This research provides practical insights into the effect of segment numbers on the workspace of TDCRs. This analysis can guide future TDCR planning and control, helping to identify the optimal segments for a given workspace and design strategies to maximize workspace efficiency.

 View pdf
View pdf


As an emerging force born in the 19th century, industrial design has continuously embraced and integrated cross-field elements, gradually evolving into a complete system. With the advent of the new era of Industry 4.0, emerging technologies such as virtual reality, augmented reality, and interactive technologies have been booming. The integration of intelligent technologies into industrial design has emerged as a significant contemporary issue. With the expansion of the industrial designer team, the defects in the field of industrial design education have become increasingly exposed. This paper focuses on the deficiencies in the field of industrial design education. Firstly, it explores the connotations and current situations of industrial design and mixed reality disciplines. Furthermore, it proposes three educational means of integrating mixed reality technology: building an interactive design platform, developing a new AR - CMF real - time projection software, and constructing a DIY experience platform for product innovation design. These means aim to enhance the interactivity, convenience, and efficiency of education, and at the same time promote collaboration and learning between teachers and students.

 View pdf
View pdf


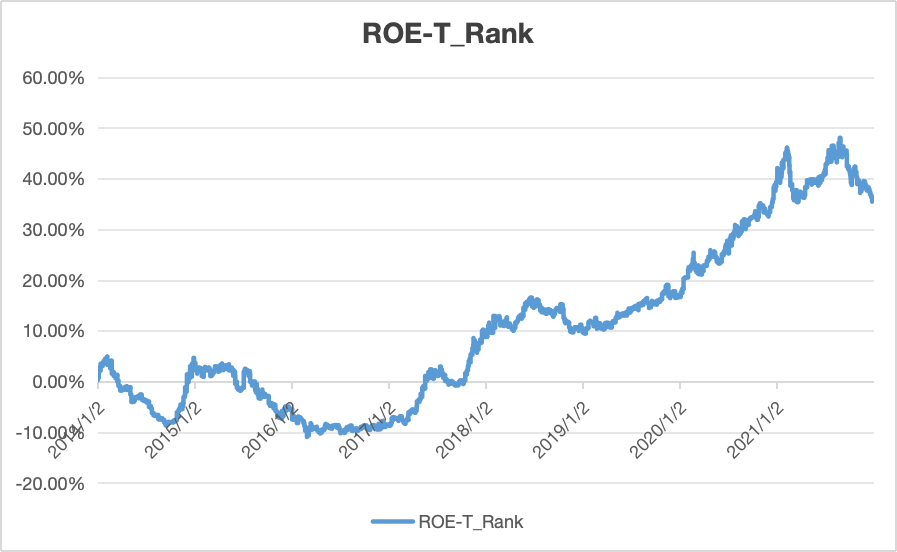
In previous research, the integration of fundamental and technical analysis in predicting the stock price has been proved successful when compared to fundamental model or technical model partially. Meanwhile, considering the rapid growth and diversification of Chinese stock market in recent years, it is promising to apply a hybrid strategy to CSI 300. The strategy implemented in this research is a momentum strategy that combines Technical Momentum and Fundamental Factors. In this paper, this strategy is implemented in CSI 300 data from January 1, 2014 to March 31, 2024 and it turns out that the annualized volatility of portfolio falls to more than half that of CSI 300 index after sector neutralization and ranking filter. Although this strategy does not demonstrate an outstanding annualized return, this research is still a valuable exploration in improving the stability in stock selection and enhancing risk management.

 View pdf
View pdf


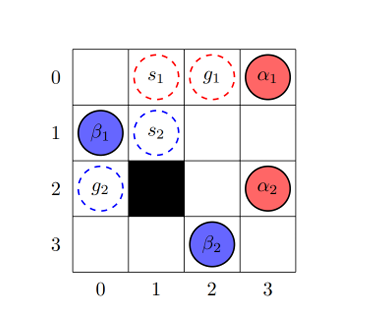
Multi-agent pathfinding (MAPF) is a problem focused on coordinating multiple agents to navigate from starting positions to goals in shared environments while avoiding collisions. This capability is important for applications in areas such as computer gaming and robotics, where efficient and safe navigation in complex environments is required. Although advancements have been made, challenges remain in areas such as multi-agents cooperation, MAPFunderdynamicenvironments, and real-time MAPF. This paper reviews three advanced MAPF algorithms: Cooperative Conflict-Based Search (Co-CBS), which extends the traditional CBS algorithm by introducing cooperative planning; Dynamic Incremental Conflict Based Search (DI-CBS), which adapts to environmental changes through integration with ECTand SLPA* algorithms; and Bounded Multi-Agent A* (BMAA*), which enables agents to independently plan paths using real-time heuristic search without explicit coordination. Experimental results highlight the distinct characteristics and advantages of each algorithm across different scenarios

 View pdf
View pdf


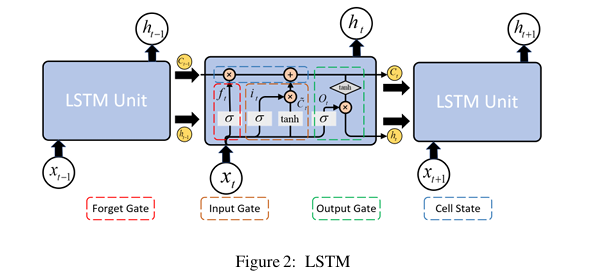
In this study, we evaluate the forecasting effectiveness of the classical ARIMA model and the deep learning-based LSTM model in the financial domain. An investment portfolio comprising equal shares of gold, the S&P 500, and 2-year U.S, is constructed to predict future trends, thereby accounting for market factors and risk-free interest rates. Various historical data are used to train the model and forecast the value of protfolio respectively. For the ARIMAmodel,predictions are made by segmenting the model into three groups based on the time span of the training data. The LSTM model utilizes 80% of the data as the training set and 20% as the test set. Furthermore, by employing diverse initial states for parallel training and averaging, errors are reasonably reduced. Key indicators, such as the portfolio’s expected annual returns, daily logarithmic returns, volatility, and value at risk (VaR), are calculated.The findings suggest that both the forecasting models and the constructed portfolio are effective. Future research could focus on using prediction models to optimize and dynamically adjust portfolios, thereby enhancing returns

 View pdf
View pdf


Path-finding plays an important role in the computer game industry. Generally, the A* algorithm and its various extensions are used in traditional path-finding methods, but they can only find a path for a single agent once a time. Recently, some potential field path planning methods have been proposed. These methods can be accomplished by multiple agents simultaneously with little additional computation. This paper reviews three different Potential Field path-planning methods for games. The main method is based on Potential fields, and we also introduce two Hybrid Potential Fields of Navigation in games and a method of implementing the algorithm with a hyper-target that people set. The first paper shows the performance of a potential field algorithm and tries to solve some problems in the algorithm. A hybrid navigation algorithm is introduced in the second paper, utilizing A* and potential fields, to handle the problems in RTS games better. The Third paper presents a real-time Voronoi-like path planning method using a combination of flow field and A* algorithm to navigate dynamic environments with obstacles, addressing issues of local minima and providing a flexible, efficient solution for collision-free navigation.

 View pdf
View pdf


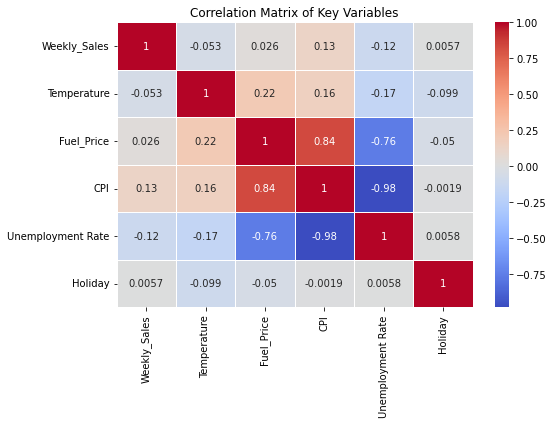
This paper, a model for predicting the sales of Walmart is demonstrated with the VARMAX technique (Vector Autoregression with Exogenous Factors). By incorporating sales data along with variables like holidays as well as economic indicators such as temperature fluctuations, fuel costs, CPI (Consumer Price Index) and unemployment rates, the Walmart’s weekly sales figures can be precisely forecasted by this model. Impressively, the performance metrics of thi model achieved an RMSE of 18, 961 and a MAPE of 4%, outperforming forecasting models such as ARIMA. Considering these influences, the model successfully recognized seasonal sales growth and considered economic changes that may affect consumer habit.

 View pdf
View pdf


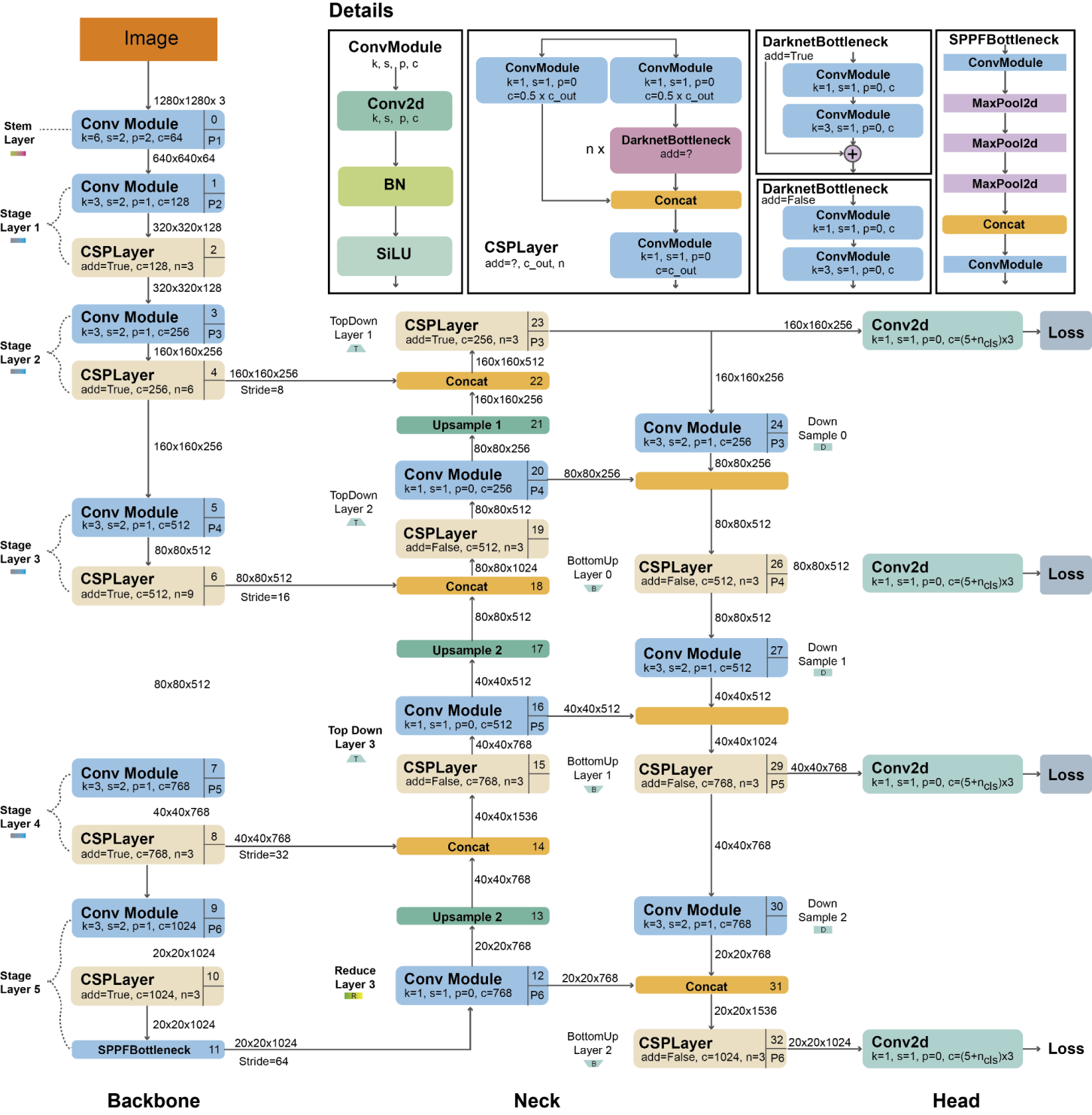
Object detection has become an important task in the field of computer vision, where the goal is to recognize and classify objects in images or videos. This paper presents a comparative analysis of different object detection models, focusing on convolutional neural networks (CNN) and transformer-based architectures. CNN-based models (e.g., the YOLO family) have made significant progress in real-time object detection by efficiently extracting local features via convolutional operations. In contrast, transformer-based models, such as the Visual Transformer (ViT), use self-attention mechanisms to capture global dependencies, improving performance on large-scale datasets. This research explores the evolution of these models and examines their foundations, strengths, and weaknesses. Through experimental evaluations, we show that CNNs continue to dominate when data and computational power are limited, while Transformers exhibit superior scalability and accuracy in complex environments. Our results highlight the complementary nature of these approaches and emphasize the need for hybrid models to achieve optimal performance in different object detection tasks.

 View pdf
View pdf


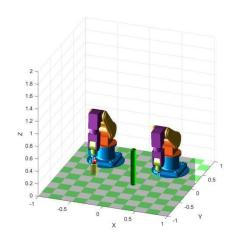
In this project, to ensure the practicality and dissemination value of the results, the subject team will verify the feasibility and reliability of the dual robotic arm system in the actual working environment. Through a series of experiments and simulations, the group expects to provide solid technical support for similar heavy-lifting scenarios. The group will use two options, one option is to import the stl file created in solidwork and then simulate and test it in matlab, the other option is not to import the file created in solidwork but just use matlab to set up the robotic arm, then the research group will use solidwork and matlab to develop and simulate the Then, the research team will use solidwork and matlab to create and simulate the movement process of the robot arm to simulate the final result of the movement.

 View pdf
View pdf




