

Volume 9
Published on November 2023Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Computing Innovation and Applied Physics

This work investigates the vertical and horizontal characteristic velocities of salt-finger convection over different density ratios by experimentally adding various concentrations of salty, hot water into cold, fresh water in a water tank. salt fingers are visualized by dye and its displacement over time is obtained by recording and analysing video. These experiments effectively generate the phenomena resembling salt-finger micro-structure in the ocean. The vertical velocity is significantly increased by lowering the density ratio corresponding to a larger salinity difference between the top and bottom showing a stronger destabilizing effect. Tilted fingers that resemble the experimental and oceanography observations are also observed. We also observe a non-zero horizontal velocity implying the presence of staircases. Finger widths obtained from the experiments are compared with that predicted from the linear stability analysis, which is within the same order of magnitude.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the era of big data, survival analysis, a statistical method for analyzing the expected duration of time until one or more events happen, has gained significant importance, especially in medical and biological research. This paper primarily focuses on the comprehensive exploration and understanding of survival analysis modelling, from traditional to modern approaches, and identifies the existing challenges and future prospects of these models. We commence by discussing foundational models such as the Kaplan-Meier and Cox proportional hazards models, and then transition into the exploration of the more flexible Accelerated Failure Time model. Acknowledging the current challenges faced in survival analysis, such as dealing with high-dimensional data, lack of labelled data, and data quality and reliability, we further delve into the potential solutions provided by modern techniques like deep learning, transfer learning, and semi-supervised learning. Additionally, the paper highlights the issues of interpretability and transparency of complex models, offering an overview of interpretability methods such as LIME and SHAP. Despite certain limitations, our study offers a valuable reference for understanding the evolution of survival analysis and sparks further discussions about its future development, emphasizing the profound significance of survival analysis in the realm of statistical research.

 View pdf
View pdf


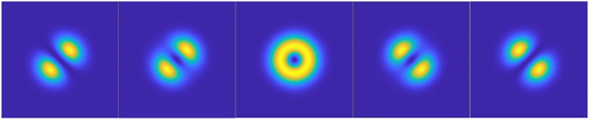
Structured beams have been extensively studied in the last ten to twenty years. Due to its excellent spatial characteristics, it has been widely used in the fields of optical communication, optical tweezer and particle manipulation. This paper first analyzes and summarizes the formation mechanism of structured beams. Then, based on the eigenmode superposition theory, the numerical simulation was carried out for the first three-orders of Hermitian-Gaussian (HG) eigenmodes. At the same time, some complex structured beams were obtained through experiments. The structured beams obtained from experiments are in good agreement with the numerical simulation results, which further verifies that the eigenmode superposition method is an effective way to realize complex structured beams.

 View pdf
View pdf


A mapping that satisfies two specific axioms provides a common notion of group action. A homomorphism translating from a group to a symmetric group of a certain set can also be used to describe group action. Therefore, any example of the group actions can be stated based on the second equivalent definition, such as the regular action, natural matrix action, coset action, and Z^2 acting on R^2, etc. It is necessary to examine the concepts of the orbit and stabilizer of a group in order to reveal the orbit-stabilizer theorem. After the preparatory work, the orbit-stabilizer theorem can be proved by defining a mapping from the orbit to the stabilizer and then checking that the mapping is well-defined and bijective. To derive Burnside’s lemma, it needs to introduce the set of fixed points which is related to the concept of the stabilizer. Through the orbit-stabilizer theorem along with the fact that a set is a disjoint union of orbits, Burnside's lemma can be confirmed. Moreover, it is natural to compose a group action with a linear representation, and then a representation would be obtained, which is permutation representation. Further, one must calculate the character of the permutation representation, the dimension of the fixed subspace, and the dimension of CX^G. Then it can show Burnside’s lemma in another way by permutation representation.

 View pdf
View pdf


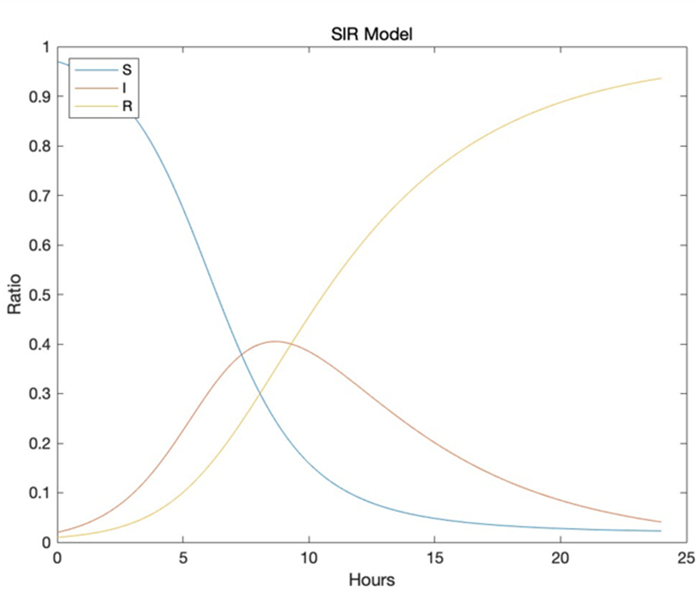
The SIR model was used to better comprehend and analyse the transmission dynamics of COVID-19. This mathematical framework splits the population into three compartments: suspectable, infectious, and recovered, allowing disease spread to be simulated across time. After making some essential assumptions of SIR model, the project illustrates the rate of suspectable, infected, recovered individuals over time by constructing several differential equations using specific parameters. Also, SIR model gives insights into expected disease trajectories, the impact of therapies, and other pertinent discoveries by including critical factors and assumptions. Researchers successfully anticipate disease trajectories using this simulation, indicating the usefulness of actions in preventing viral propagation. Researchers have found that the incubation period of COVID-19 has vital impact on the epidemic curve, which results in a slower growth in the number of infected people overtime and a delay in the upward slope of the infectious in the epidemic curve. The SIR model’s examination of epidemic curves has assisted in identifying the peak of infections, estimating the duration of outbreaks, and assessing the efficiency of public health measures in various context. Further study, continued data collecting, and integration with real-world data will improve the accuracy and usefulness of the SIR model, enabling evidence-based ways to combating COVID-19’s issues.

 View pdf
View pdf


The Chinese remainder theorem (denoted it as " the theorem" in this article) was originally an important theorem in number theory. It played a vital role in the integer solution of the congruence equation in ancient times. With the continuous development of the algebraic system, the theorem naturally has different forms. This paper will show some research and applications based on the theorem. For example, the theorem in polynomial form, the theorem in the form of group theory, the theorem on unitary rings, the theorem on polynomial ring modules, etc. It is not difficult to know that integers and polynomials are special rings, so this the two forms of the theorem are the theorems that can be covered on the unitary ring. In fact, the theorem in the form of group theory is also covered. This paper will elaborate the first three forms of the theorem and give their specific applications.

 View pdf
View pdf


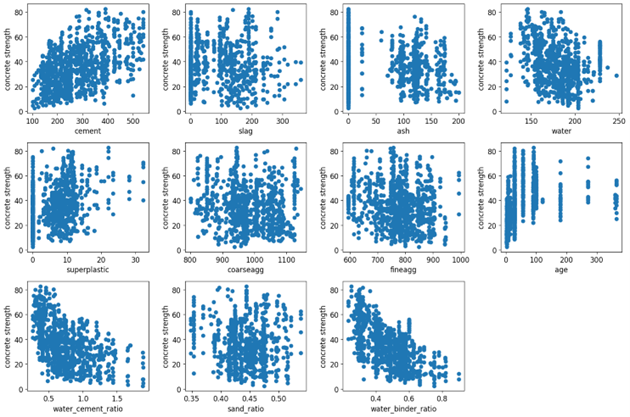
Concrete strength prediction is a complex nonlinear regression task that involves multiple ingredients and age as key factors. In order to achieve accurate predictions, the Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) and Gaussian Process Regression (GPR) techniques are employed. The dataset, sourced from Kaggle repositories, comprises a comprehensive collection of 1030 data points. Alongside the existing features (content of ingredients, age and strength), we introduce new ones, including water-cement ratio, sand ratio, and water-binder ratio, to enhance the model's credibility. To determine the optimal kernel function, the dataset is partitioned into training and testing subsets. Notably, the MCMC method yields an R2 of 0.41, while GPR demonstrates a significantly improved R2 of 0.89. Further investigation is warranted to refine the model's fit and optimize its predictive capacity.

 View pdf
View pdf


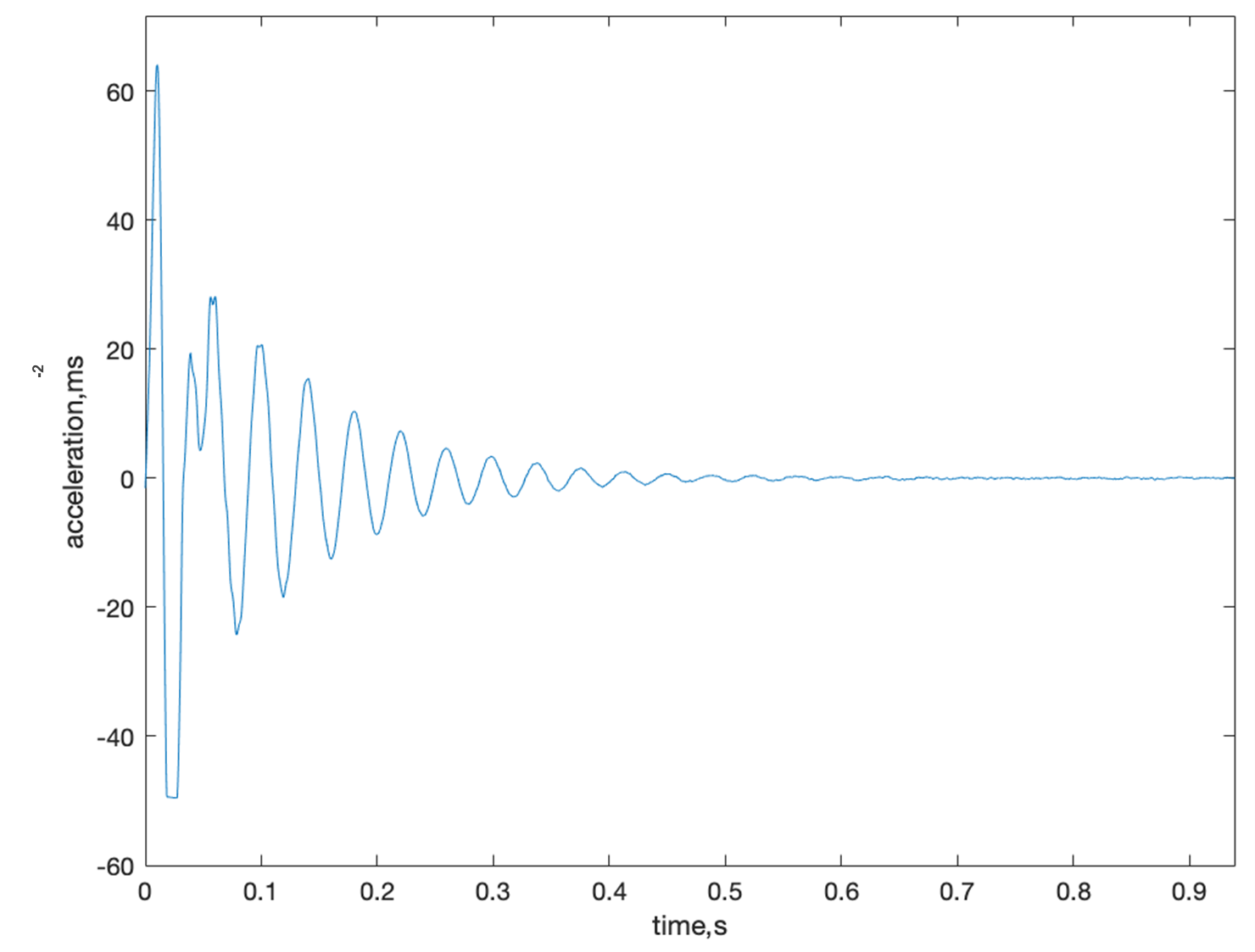
Frequent global earthquakes lead to catastrophic property damage and casualties due to building collapses. However, the 1976 Tangshan Earthquake showcased an exception: the Forbidden City, constructed with wooden materials and featuring mortise-tenon structures, remained unscathed among surrounding destruction. This study investigates the earthquake-resilient attributes of wooden mortise-tenon joints utilizing economical high school equipment. An innovative low-cost sensor system, featuring custom instrumented hammer, is developed and validated. Calibration of the hammer's impact force employs correlation with acceleration data from a standardized scale weight during impact. The system's reliability is tested by comparing resonance frequencies from Finite Element modal analysis and experimental data for a cantilever beam. Impact hammer tests assess frequency response and damping across buildings with various joint configurations. Mortise-tenon joints display augmented frictional damping due to internal displacement. Through simulated vibration acceleration responses, a crucial finding emerges---integration of mortise-tenon joints translates to an impressive 11.0% reduction in earthquake vibrations. This research underscores the potential of accessible high school devices in advancing seismic engineering insights.

 View pdf
View pdf


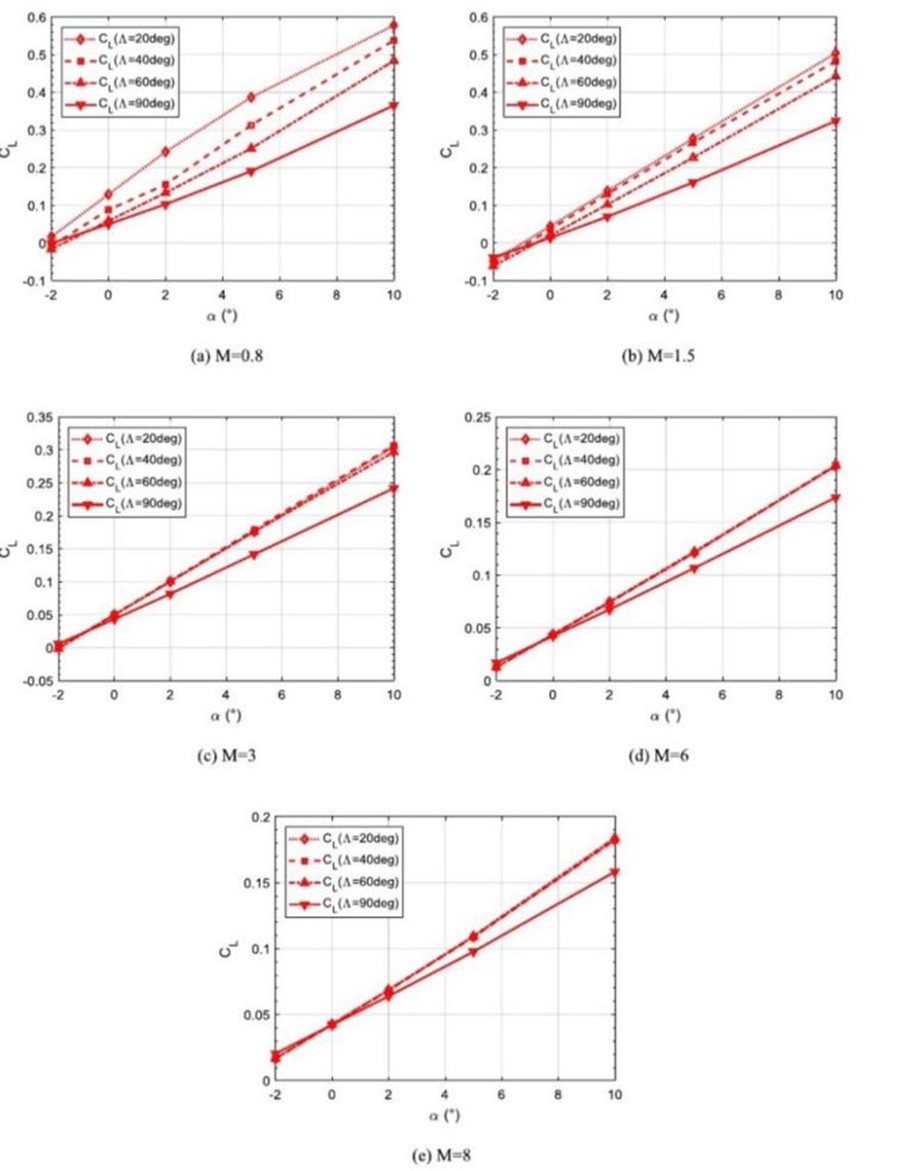
With the development of science and technology, more and more civil and military aircraft have adopted swept-back wing shapes. this paper explores the relationship between the angle of swept-wing and the lift, drag and lift-drag ratio of the aircraft, and expounds it in combination with the actual swept-wing aircraft, such as Boeing737 and MIG-23 to find the best sweep angle of the aircraft in the appropriate range and analyze the effect of swept wing angle on flight speed. This paper studies and analyzes the data through literature retrieval and data processing and cites data models from many academic journals. The experimental data are mainly derived from computational fluid dynamics and wind tunnel simulation. This paper finds that a wider sweep angle can result in better aerodynamic performance, suited for supersonic flight, while a smaller sweep angle can result in a better lift-drag ratio, it is suitable for takeoff and landing of aircraft and low-speed flight attitude.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the past decades, taking an airplane has become one of the fastest travel methods, including transportation between two cities far away from each other or between two different countries across the earth. Jet engines take over most of the engine market on airplanes; while having over 20% of the cost to build a plane, economic efficiency is the first thing to consider. After that, due to the pollution of its fuel-burning process, environmentally friendly became another thing that needs to be valued. In this paper, the history and the basic principle of the jet engine will be demonstrated. Some recent improvements in jet engines would be provided, such as the Diverterless Supersonic Inlet (DSI) and a way to improve the component’s strength in building process solidification crystallization control technology. A way to improve both the service life and the component strength would be to discuss different materials, along with the looking-forward perspectives on jet engine advancement.

 View pdf
View pdf




