

Volume 146
Published on May 2025Volume title: Proceedings of SEML 2025 Symposium: Machine Learning Theory and Applications
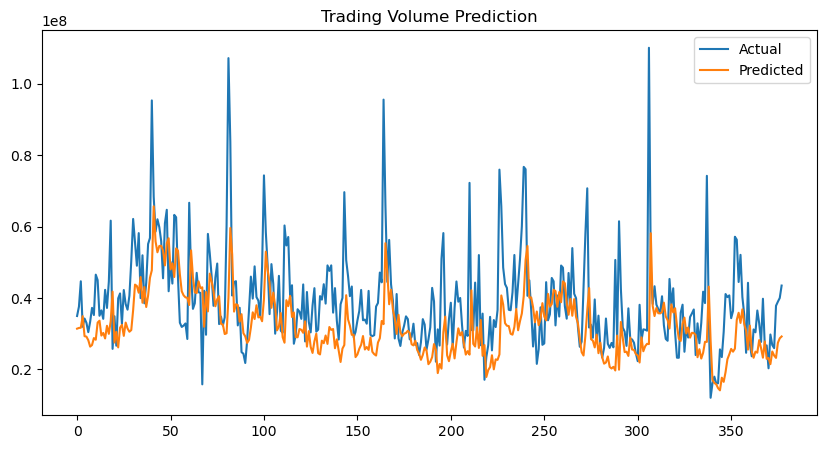
Time series analysis plays a pivotal role in diverse domains, facilitating critical tasks such as forecasting, classification, and anomaly detection. This paper introduces a multi-task learning (MTL) model utilizing a deep learning framework to simultaneously predict three key financial indicators: trading volume, closing price, and volatility. By leveraging shared representations across tasks, the MTL model captures intricate dependencies and enhances generalization, outperforming single-task benchmark models—ARIMA and univariate Deep Learning (DL). The MTL model achieves over 50% reduction in MAE and RMSE compared to ARIMA and approximately 10% improvement over DL. The results demonstrate the ability of MTL to exploit inter-task relationships, delivering more accurate and robust forecasting for stock markets. This work highlights the potential of multi-task learning framework in enhancing financial time series forecasting.

 View pdf
View pdf


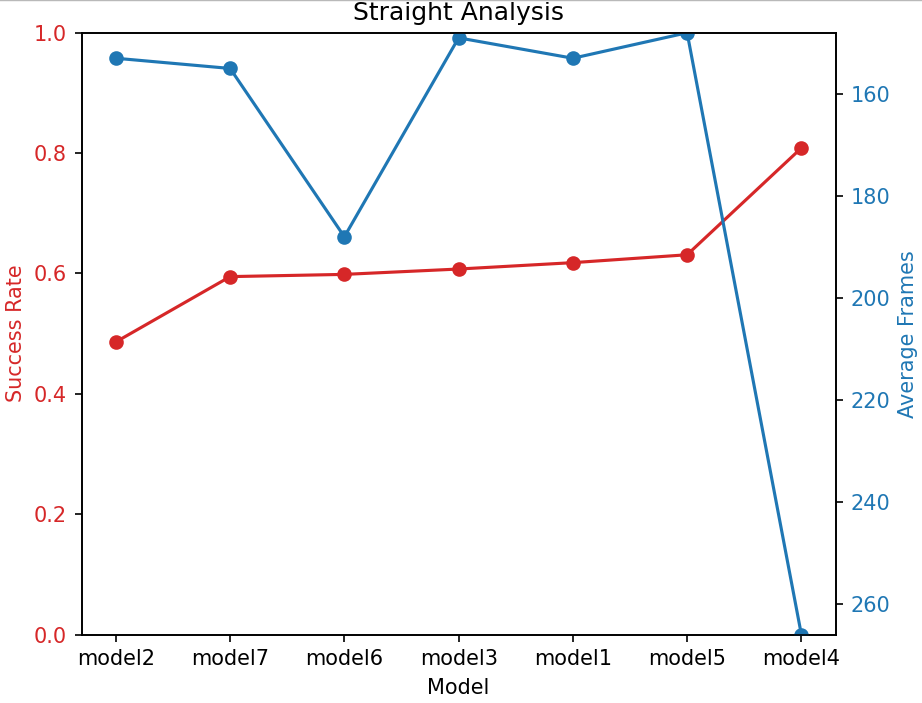
Autonomous driving, leveraging artificial intelligence and reinforcement learning (RL), has made significant strides in improving traffic efficiency and safety. However, current RL-based approaches often focus on single-objective optimization, such as maximizing either efficiency or safety. In real-world driving, multiple conflicting objectives—such as safety, efficiency, and comfort—must be balanced simultaneously, which remains underexplored. This paper proposes a multi-objective reward function design to balance safety and efficiency in autonomous driving. Using the Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) algorithm, we train seven autonomous driving models with varying collision penalty strategies in the MetaDrive simulation environment. The results show that dynamic collision penalties outperform fixed penalties in balancing safety and efficiency, with Model 5 achieving the best overall performance. Despite this, all models underperform in left-turn scenarios, highlighting the need for further optimization in lateral control. This work provides insights into effective reward design for multi-objective reinforcement learning in autonomous driving.

 View pdf
View pdf


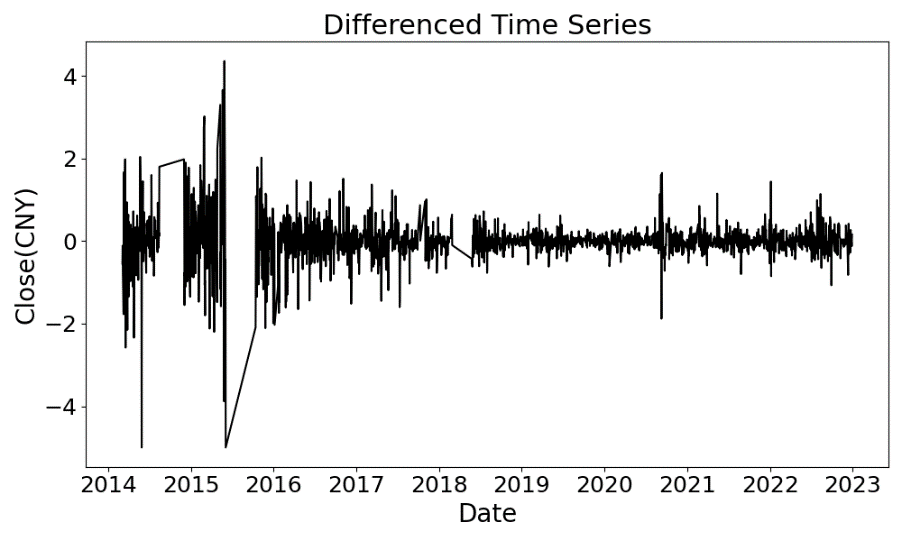
This study proposes a stock price prediction model integrating Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) and Random Forest (RF) to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of closing price predictions. Using historical data of Zhongchuang Environmental Protection (300056.SZ) from 2014 to 2022, the model incorporates features such as opening price, EMA, and RSI. The ADF and Ljung-Box Q tests confirm the stationarity and autocorrelation of the differenced time series. PSO optimizes RF hyperparameters (e.g., n_estimators, max_depth). Results show: (1) The PSO-RF model achieves high performance with R²and MAE reaching 0.943 and 0.030 respectively. (2) The DM test indicates statistically significant prediction accuracy compared to benchmark models (PSO-SVM, Grid-RF, GA-RF) with p-values < 0.05. (3) The synergistic effect of PSO's global optimization and RF's generalization ability effectively captures short-term market trends, demonstrating superior predictive performance and broad application potential.

 View pdf
View pdf


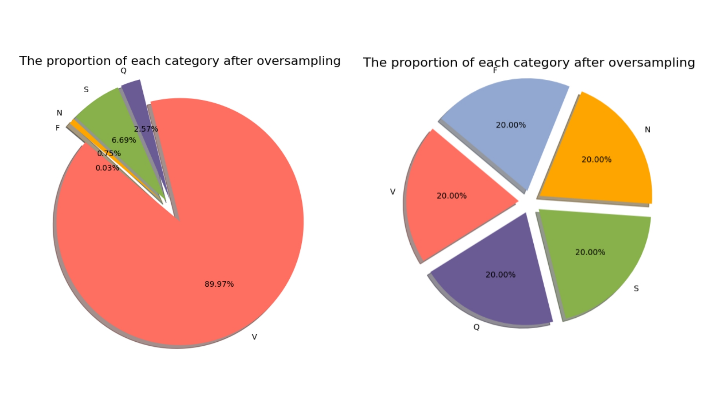
Electrocardiogram (ECG) signal classification is a critical task in arrhythmia diagnosis, and its accuracy directly affects the effectiveness of clinical decision-making. However, ECG signals usually contain noise and have uneven category distribution, which poses a great challenge to the classification task. To this end, this study proposes a classification method for ECG signals based on wavelet noise reduction and random forests. Specifically, we first remove the noise from the signals using the wavelet transform, then we select an oversampling technique to alleviate the problem of category imbalance, and finally we use a random forest model to train the classification. We conducted comparative experiments to demonstrate the significant advantages of our algorithm in the ECG signal classification task. In addition, to validate the effectiveness of the proposed method, we designed ablation experiments to demonstrate the important role of wavelet transform noise reduction and oversampling in improving the model performance. This paper proposes a method which obviously improves the accuracy of ECG signal classification, and at the same time provides reliable technical support for the automatic diagnosis of cardiac arrhythmia.

 View pdf
View pdf


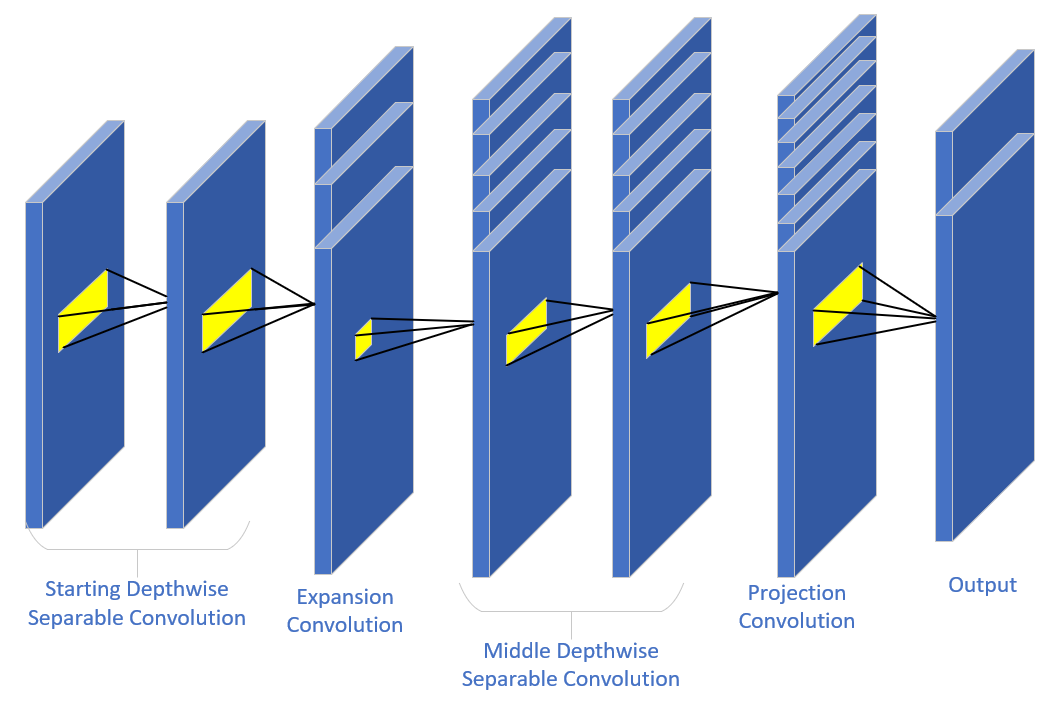
Deep learning and neural networks have become widely applied in signal modulation recognition, offering numerous advantages in performance. Traditional approaches to modulation recognition using neural networks typically focus on improving model accuracy, which often results in increased model size and computational complexity. This makes deployment on mobile devices challenging. Therefore, this study aims to reduce the model size while ensuring recognition accuracy and proposes a lightweight neural network architecture based on MobileNetV4. The network incorporates an inverted bottleneck structure, which helps reduce the model’s running time through depthwise separable convolution and residual concatenation. The performance of the model was evaluated on the public dataset RadioML 2018.01A dataset across multiple signal-to-noise ratios and compared with convolutional neural networks and residual networks. The results show that the proposed network reduces the running time to approximately 1/2 to 1/3 of the original models while maintaining comparable or even slightly improved recognition accuracy.

 View pdf
View pdf


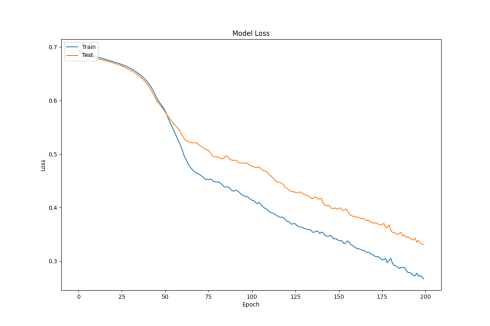
This paper addresses the issues of weak model transferability and poor environmental adaptability in cross-domain gesture recognition within wireless sensing technology. A time-series data classification model integrating Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) and attention mechanism (W-LSTM+A) is proposed. By introducing a feature selection weight matrix to reconstruct the LSTM gating mechanism and combining a dynamic attention allocation strategy, the model’s ability to capture key spatiotemporal features in channel state information is significantly enhanced. Experiments based on a WiFi signal dataset collected in a real office environment compared the performance of CNN, LSTM, and LSTM+A models. The results show that the LSTM+A model achieved a test accuracy of 87.3% after 200 training epochs, significantly outperforming CNN’s 81.9%. Although the LSTM model had a higher final accuracy, its convergence speed was significantly slower than that of the LSTM+A model. Further analysis indicates that the attention mechanism, by strengthening key time-step features, enables the model to quickly capture effective patterns in the early stages of training. However, due to limited sample size, its potential has not been fully realized. This study provides new solutions for the cross-scene adaptability of wireless sensing technology and has application value in smart homes, health monitoring, and other fields.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the era of digital transformation, big data has emerged as a pivotal resource driving innovation across various sectors. The effective utilization of big data, however,is fundamentally contingent upon robust governance frameworks. This paper conducts a comprehensive exploration of the multifaceted domain of big data governance, with a focus on three critical dimensions: key technological implementations, policy-system architecture, and application prospects. By employing a combination of literature review, case analysis, and comparative research methods, it addresses several key research questions, such as how to improve the efficiency and quality of data management in big data governance, how to construct a scientific and reasonable policy system, and how to better apply big data governance in different scenarios. The research findings demonstrate that advanced techniques, particularly data wrangling, play an indispensable role in data preprocessing and quality enhancement. Furthermore, the study reveals that a sophisticated, multi-tiered policy system involving multiple stakeholders is progressively evolving in the realm of policy-system construction. In terms of application, big data governance has achieved remarkable results in areas such as government decision-making and business operations, but challenges remain. Overall, this research provides valuable insights for promoting the development and application of big data governance.

 View pdf
View pdf


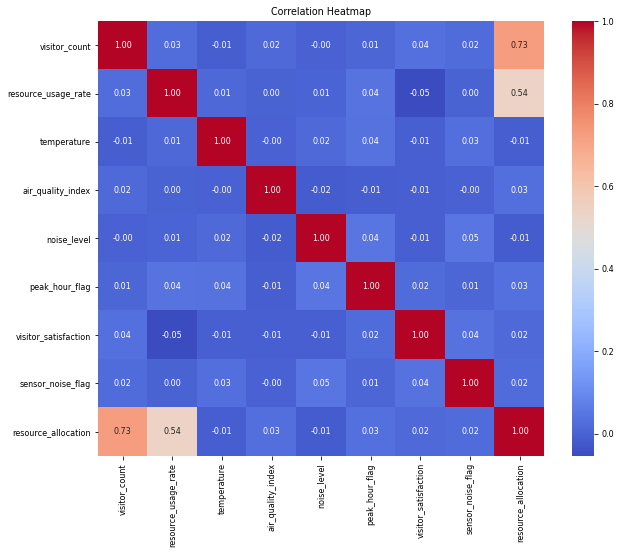
In this study, an innovative prediction framework for intelligent management and allocation decisions of tourism resources is constructed by integrating the iterative local search strategy and the sparrow search algorithm to co-optimize the random forest model. The experimental results show that the tourism resource allocation level and the number of tourists show significant correlation (Pearson coefficient 0.73), and this indicator as a core driver directly affects the resource allocation decision; the resource utilization rate, as a secondary correlation variable (correlation coefficient 0.54), and the scenic spot operational efficiency form a two-way feedback mechanism, which together constitute the key influencing factors of the dynamic allocation of tourism resources. Through the quantitative analysis of the confusion matrix, the optimized model achieves 100% perfect fit in the training set, and maintains 95% prediction accuracy (190/200 samples are correctly classified) in the independent test set, and the performance degradation of only 5% fully proves the success of the algorithmic improvement strategy in avoiding overfitting, and its excellent generalization characteristic breaks through the limitations of the traditional prediction model in cross-scene applications.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the environment of the continuous development of the new energy industry, the traditional software engineering methods have been gradually backward in the face of the ever-complex demands, so this paper analyses the successful implementation of the charging pile cloud service project of Company T as an example, and explores how the modern software engineering methods can promote the development efficiency and the development quality of the cloud service project. This paper adopts the case study method and comparative analysis method. It is found that after applying the new software engineering methodology, the development quality and development efficiency of the project are significantly improved, and the final product has high reliability and stability, which meets the current market demand. Compared with the products developed using the traditional methodology, the products developed using the software engineering methodology have gone through the development process of requirements definition and system design, agile development and continuous integration, and have an advantage in the development cycle and development quality. In the subsequent operation and maintenance, the new software engineering approach uses DevOps thinking to incorporate post-operation at the time of development, which allows for continuous updating of the product operation and maintenance, and reduces costs through automated operation and maintenance. This paper supplements the theory of software engineering methodology for cloud service project development and further illustrates the significance of applying the new methodology to software development projects, which can provide reference suggestions for the development of the industry.

 View pdf
View pdf


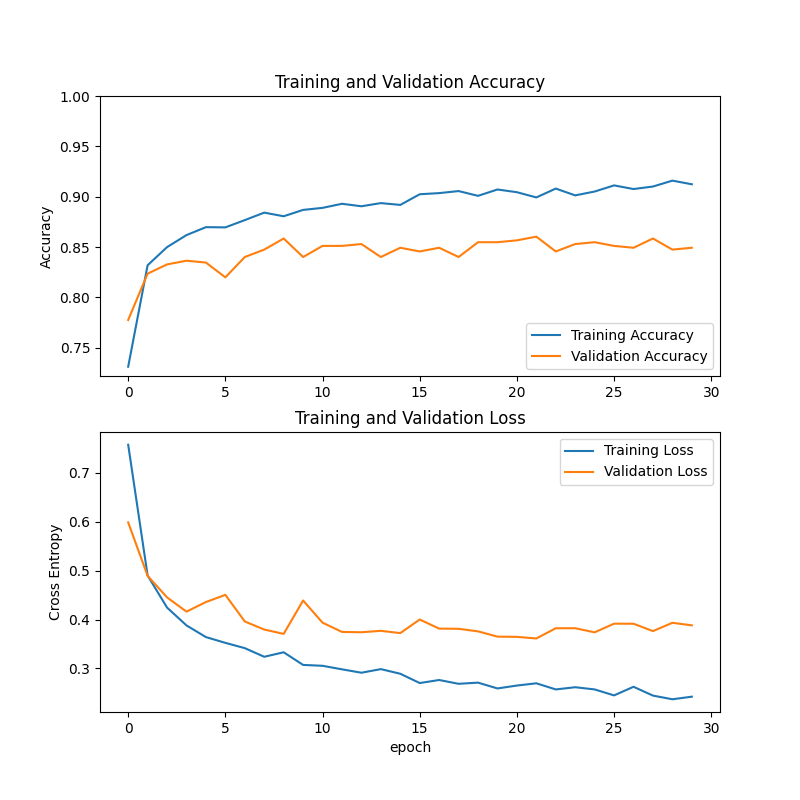
In the process of global sustainable development, waste recycling has an important strategic position, especially in the dual dimension of resource protection and environmental protection plays a key role, and becomes an important means to alleviate resource tension and ecological pressure. It is worth noting that the recycling and sorting of footwear products faces special challenges: the level of automation is relatively weak, the dependence on manual sorting is too high, and the traditional technology is difficult to accurately deal with the footwear products of multiple composite materials, resulting in limited resource conversion efficiency. In view of this technical bottleneck, the development of efficient intelligent sorting solutions has become an urgent need for the industry. This study systematically sorts out the recycling paths and existing problems of waste clothing and footwear, focuses on analyzing the technical features of deep learning architectures such as ResNet, Vision Transformer and MobileNet, and demonstrates their application efficiency in footwear sorting based on actual test data. The test data show that the target model achieves about 85% recognition accuracy in footwear sorting tasks, effectively verifying the application potential of intelligent algorithms in this field. The research results have practical guiding value for realizing intelligent sorting of footwear resources, improving the utilization rate of renewable resources and reducing environmental load, providing a feasible scheme reference for technological upgrading in related fields, and helping the construction of circular economy system.

 View pdf
View pdf




