

Volume 107
Published on May 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Computing Innovation and Applied Physics
With the rapid development of fuel vehicles, fuel consumption has gradually become a concern of people. How to effectively improve fuel efficiency is also a challenge. This study explores the application of cutting-edge materials such as carbon fiber, ceramics, aluminum alloys, and titanium alloys in the automotive industry to improve lightweight design and performance. The assessment encompasses the unique advantages, corrosion resistance, and compatibility with high-temperature environments demonstrated by each material. This paper will compare the strength and corrosion resistance of these four materials. Carbon fiber composites offer exceptional weight reduction capabilities and corrosion resistance properties that render them highly suitable for constructing electric vehicle body structures. Aluminum and titanium alloys exhibit commendable strength-to-weight ratios; however, they encounter challenges when exposed to extreme conditions while also being relatively costly. These findings emphasize the significance of meticulous material selection in optimizing both vehicle performance and efficiency.

 View pdf
View pdf


Advanced materials are significant to the improvement of vehicle fuel economy. Lighter materials are easier to accelerate than heavier materials, requiring smaller amounts of energy, therefore, lightweight materials have great potential to improve the efficiency of vehicles. Based on this motivation, four materials were selected: titanium alloys, magnesium alloys, and aluminum alloys respectively. All these materials can reduce the car's weight because their densities are lower than traditional materials such as cast Iron. However, they have different material properties. In this paper, the quantity of ultimate stress is utilized to compare the specific strength of different materials after they experience heat treatment, and the appearance of cracks can be seen as an important indicator to compare the fatigue life of various materials. Other effective methods are also mentioned in this paper. For example, aluminum alloys are widely used in car engines. Yet, it does not have high toughness at high temperatures. Thus, scandium can be added to this alloy to increase its heat resistance and heat toughness. As for magnesium alloys, PLA coatings can resist the appearance of cracks so that fatigue life can be exceeded. The subsequent ageing treatment can increase the tensile strength of this material. Finally, changing the lattice structure of titanium can increase the specific strength and fatigue life simultaneously.

 View pdf
View pdf


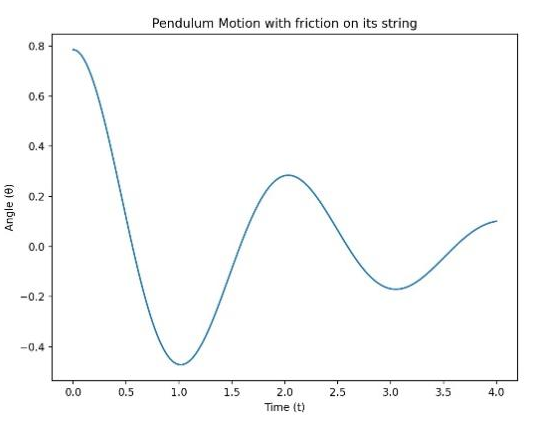
One of the main topics in classical mechanics is the study of pendulum motion, which makes it possible for us to know how objects move and swing. In this study, two approaches—numerical and analytical—for simulating pendulum motion under various beginning conditions are compared. It also looks at more intricate situations. Pendulum research was first developed in the late 16th century by Galileo Galilei and further advanced by Christiaan Huygens, the man who invented the pendulum clock. With the passage of time, scientists were able to describe pendulum motion with much greater accuracy because of developments in mathematics, such as the differential calculus created by Leibniz and Newton. The development of digital computers and numerical techniques made it possible to solve difficult issues, such as pendulum motion. This research investigates the motion of the fundamental pendulum by assuming only modest oscillations and eliminating air resistance. Analytical procedures construct mathematical equations using Newton's principles when numerical processes divide motion into tiny steps for approximative solutions. The research investigates and assesses the advantages and disadvantages of various approaches. The results show that for real-world scenarios such as air resistance, numerical methods perform better than purely analytical methods. This comparison highlights the need to use both approaches to fully understand mechanical systems and may be useful for future motion research.

 View pdf
View pdf


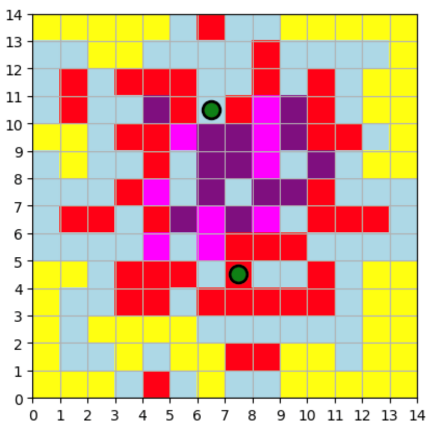
Whether for environmental protection or as a means of transportation, the use of shared bicycles has been expanding. This has also brought about the management problem of shared bicycles and how to optimize the placement of stations. The main goal of this paper is to optimize the location of shared bicycle stations during the peak hours of shared bicycle use in Manhattan so that shared bicycle companies can achieve more effective placement at the minimum cost. The method used can be divided into three parts. First, a grid is established to simulate the layout and construction of the city, assuming the values of the variables; the second part establishes a linear function, modifies the objective function for different variable factors, and applies it to the grid of the first part to test whether it is the optimal placement location; after verification, the third part combines the model with the actual situation in Manhattan and calculates 10 optimal locations for the placement of shared bicycle stations. This paper determines the optimal way to place stations by minimizing costs and combining actual needs, thereby improving the effectiveness and timeliness of future shared bicycle rentals.

 View pdf
View pdf


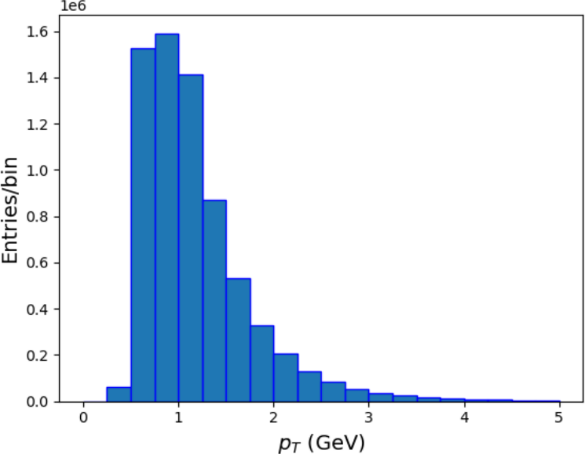
This paper presents the analysis of the hydrodynamic properties of Quark-Gluon Plasma (QGP) in PbPb collision events collected by the sPHENIX detector, focusing on the elliptic flow () and triangular flow () by analyzing azimuthal angle distribution of particles. The two-dimensional correlation function between azimuthal angle difference () and pseudorapidity difference () that excludes collision pairs with was analyzed. The shape of the graph suggests the hydrodynamic flow during PbPb collisions explicitly. The value of and were compared with the value of the weighted average of eccentricity () and triangularity () with the same centrality (4050%) of the simulated dataset generated by the PHOBOS Glauber Monte Carlo (Glauber MC) code. The trend of elliptic flow and triangular flow as a function of transverse momentum of the experimental data was also examined, and general increasing trends that agree well with that predicted by a multi-phase transport model (AMPT) were found.

 View pdf
View pdf


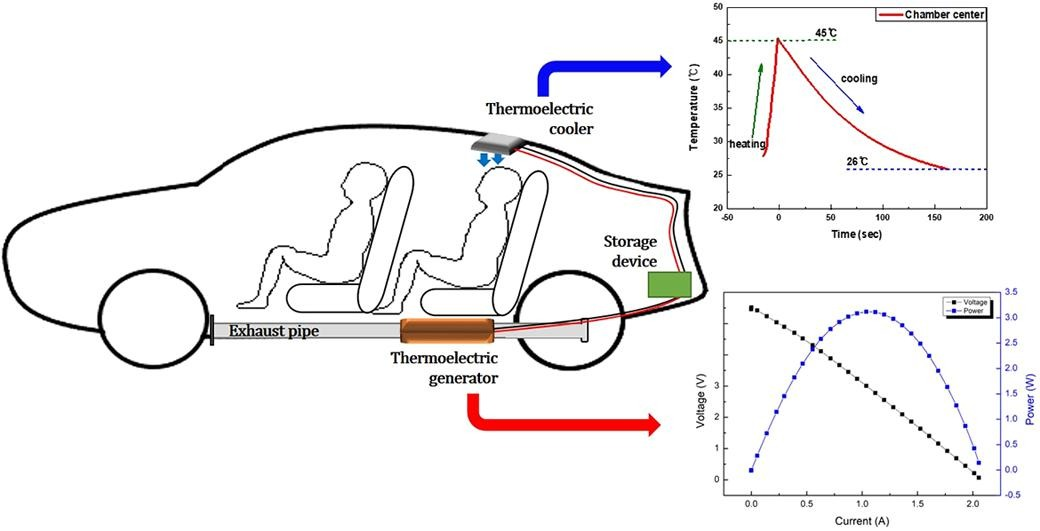
The application of hybrid and electric vehicles is gradually becoming widespread for the purposes of reducing environmental pollution, saving energy, lowering operating costs, and reducing dependence on petroleum resources, thus the significance of energy recovery has emerged as a crucial area of focus. How to improve energy utilisation, extend battery life, reduce noise and environmental pollution have become urgent issues. And energy recovery systems have the potential to solve these problems. This review examines five key energy recovery mechanisms: regenerative braking, flywheel systems, thermoelectric generators, the Rankine cycle, and electric turbochargers. The objective is to evaluate these methods, emphasizing their potential to improve energy conversion efficiency and their feasibility in real-world applications for both hybrid and purely electric vehicles. By synthesizing information from a wide range of literature, this study provides a comprehensive overview of the energy recovery and conversion efficiencies demonstrated by each technology. The analysis explores both theoretical foundations and practical implementations across various vehicle models, highlighting recent scientific advancements aimed at optimizing energy recovery performance. In conclusion, this review underscores the potential of diverse energy recovery mechanisms to enhance the performance and sustainability of hybrid and electric vehicles.

 View pdf
View pdf


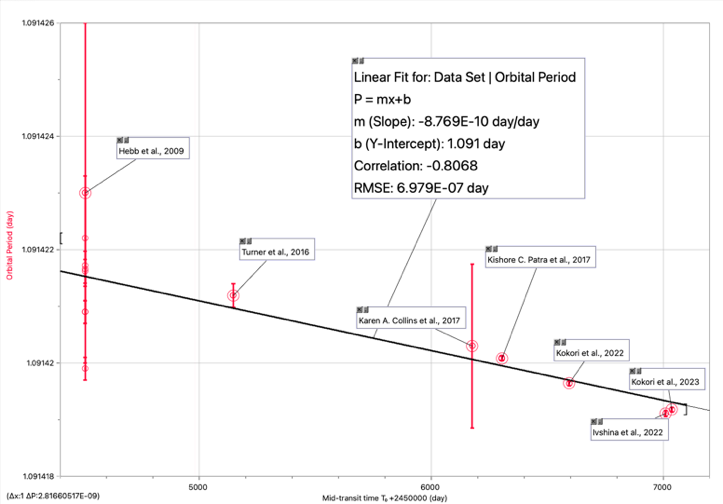
This article synthesizes past and recent articles which study WASP-12b, including its discovery, refined system parameters, and the mechanisms behind its orbital decay. This study mainly focuses on the orbital decay, whereas the orbit of WASP-12b is not persistent. A compilation of more than 15 years of literature on WASP-12b is utilized to extract its orbital data, revealing that its orbital period is diminishing at a rate of 32.53 milliseconds per year. The mechanism behind the decay can be traced to the tidal dissipation effects, where the planet's tidal interaction with its parent star leads to a gradual contraction of the orbit.

 View pdf
View pdf


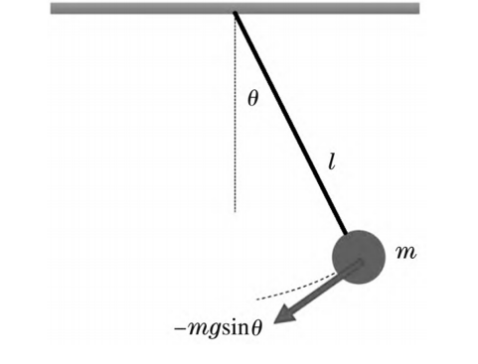
The objective of this work is to conduct numerical simulations and analyses to derive the equations of motion of a non-torque pendulum. For the sake of obtaining pendulum motion equations under various circumstances, such as with and without a drag force, Taylor expansion, second-order differentiation, defined differential equation and other mathematic methods are employed. Moreover, Python is utilised for the calculation of precise values and the generation of graphs, thereby facilitating a more comprehensive understanding of the object's motion law and the interrelationship between its constituent elements. The article will predict the position of the ball in different conditions when there is a change of length, initial velocity or derivative angle. In this paper we first show the basic theory deduction and divided into two cases which are without drag and with drag. When there is no drag force, two conditions are discussed. One is Simple Harmonic Motion, and the other one is Regular Pendulum Motion. For both two cases, numerical and analytical solutions will be deduced. Furthermore, the paper is required to use control variable method to change certain elements and investigate the changes. Besides, when there is drag force, the conditions will be more complicated. For methodology part, there are defined differentiate equations, Largent Equation, Taylor Expansion and second-order derivation.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper delves into the numerical simulation of pendulum motion, focusing on the second-order linear ordinary differential equation that models pendulum swings. The study addresses the non-uniqueness of solutions and the dependence on initial conditions, which are crucial for accurate system modeling. The paper discusses the implications of non-uniqueness in moving average models and their resolution strategies. Through stability analysis and empirical testing with Python, we validate our numerical solutions and observe the effects of different parameters on pendulum motion. The research aims to enhance understanding of pendulum dynamics, which has applications in engineering, robotics, and aerospace.

 View pdf
View pdf


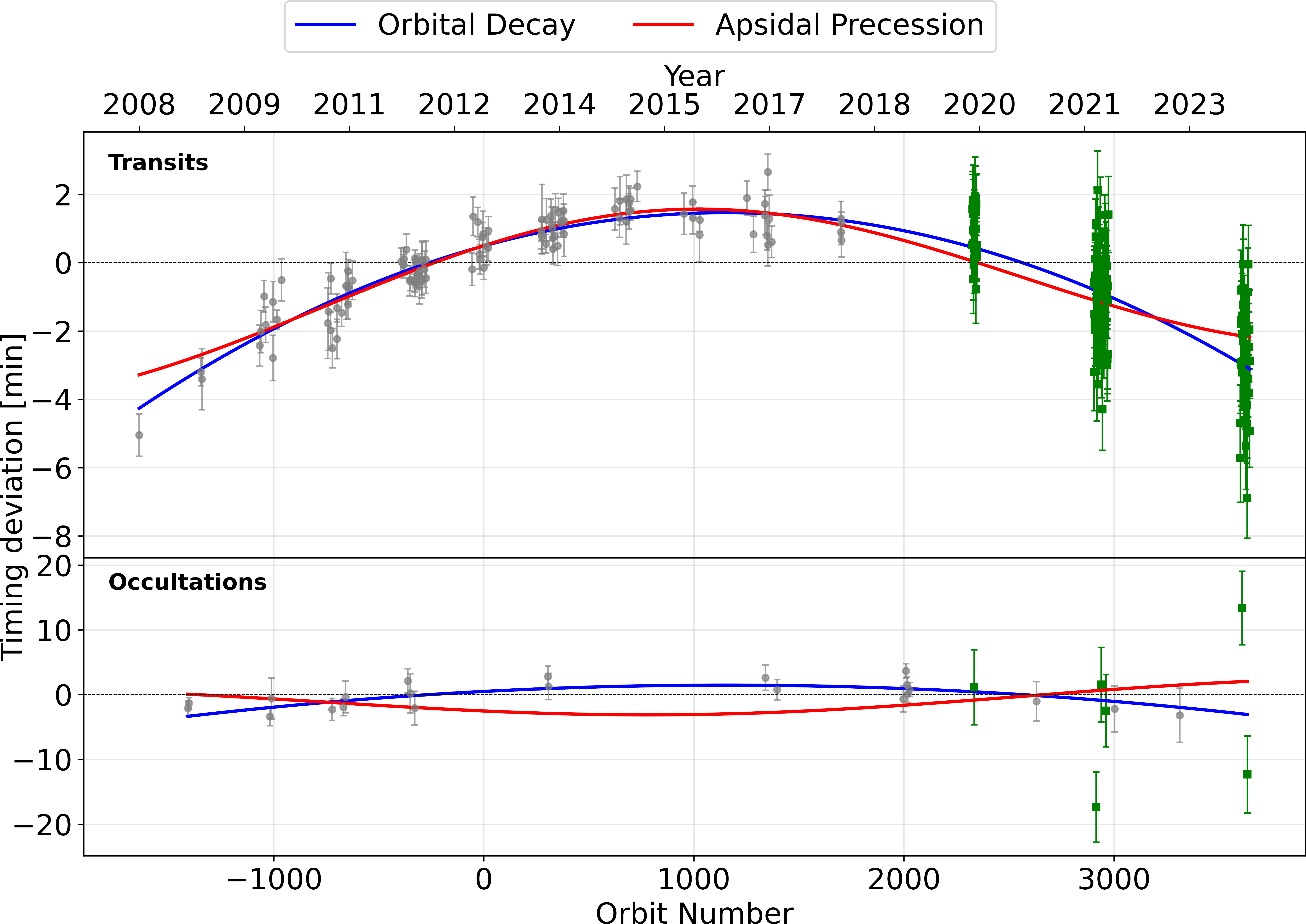
WASP-12b is the first reported hot Jupiter whose orbital period appears to be decreasing with time. This phenomenon can be interpreted using two models from earlier research: the decay of its orbit or the apsidal precession. This work chose the latest 118 transit and 6 occultation photometric observations conducted by TESS in Sectors 20, 43, 44, 45, 71, 72. They were combined with previous data to analyze the relationship between the orbit number, the mid-time of transit, and the mid-time of occultations (averaged over entire sectors to boost the signal-to-noise ratio), which favored the decay model with ∆BIC = 104.09. Our value of decay rate , and the reduced tidal quality factor when interpreting the decay as tidal orbital decay, are both aligned with earlier studies and suggest that the orbit of WASP-12b is in a state of rapid decay. Future observations and theoretical work are necessary to further explain the physical processes driving this decay and to predict the end of life of WASP-12b.

 View pdf
View pdf




