

Volume 87
Published on April 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Computing Innovation and Applied Physics
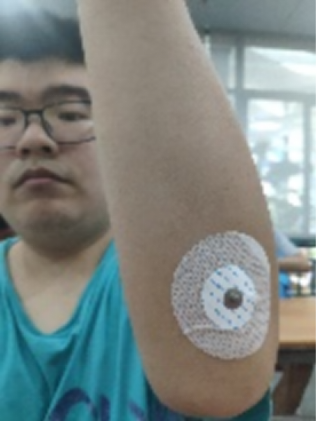
This study explores the integration of surface electromyography (sEMG) signals for precise servo control in real-time hand movement detection. It also further utilizes the feedback system designed to measure effects of workout exercises on forearm sEMG signals and delves into how different time and types of workouts affect forearm muscle response. Medical electrodes captured sEMG signals from forearm muscles and converted them into digital signals using an Arduino UNO R3 microcontroller board and an Olimex EMG shield to monitor hand pose variations. The digital signals were then processed to calculate the root mean square (RMS) voltage, which was then used to control the position of a servo motor. The implementation of a proportional-derivative (PD) controller further enhanced the accuracy and stability of the servo movements. Then the feedback system was used to measure how sEMG signals vary due to hand opening and closing before and after a range of workout exercises with varying time and workout types, and the results were compared to reach the conclusion that both workout time and type influences how forearm muscles respond to hand closing and opening. Future work may explore the effect of more time and types of workouts on muscle response, expand the range of test subjects, and improve the accuracy and stability of the test system

 View pdf
View pdf


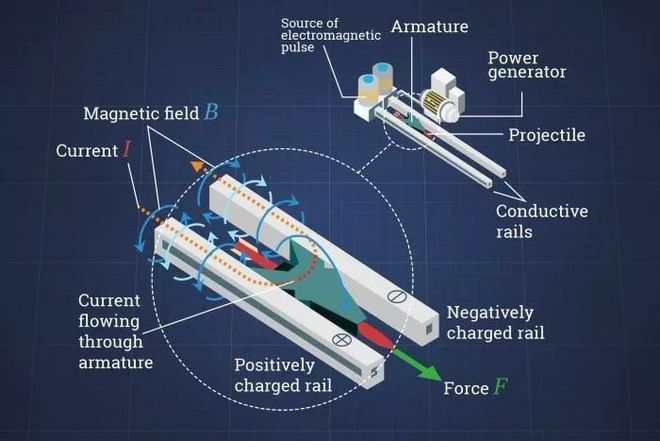
This research is mainly to provides a report and summary of the production and experimental principle of our last electromagnetic gun Electromagnetic guns use the basic principle in physics that moving charges or current-carrying conductors are subjected to the electromagnetic force (i.e., the Lorentz force) in a magnetic field to accelerate projectiles. According to the acceleration method, electromagnetic guns can be divided into rail guns and coil guns . An electromagnetic railgun accelerates projectiles using the fundamental principles of physics involving moving charges and current-carrying conductors interacting with a magnetic field, known as the Lorentz force. Electromagnetic Railguns accelerate projectiles to very high speeds using Lorentz force generated by strong electric pulses through parallel conductive rails . A coilgun is a device that uses electromagnetic fields to accelerate metallic projectiles. Its working principle is based on Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. By passing current through a coil, a strong magnetic field is generated, which propels the projectile along the guide rail. Coilguns offer several advantages over traditional gunpowder-based propulsion methods, including higher initial velocities, extended ranges, reduced recoil, and lower launch noise. However, despite these potential benefits, our experimental setup revealed several limitations.This report summarizes the challenges encountered and Outlines suggested strategies for improving the design and addressing the identified deficiencies, analyzing the problem through a qualitative perspective. To provide readers with effective information

 View pdf
View pdf


Mechanics is one of the most fundamental subfields of physics. Founded primarily by Isaac Newton, mechanics has strong relations with astronomy, one of the oldest sciences. It has astronomical origins and exhibits significant applications in astronomical problems. A historical perspective is necessary to grasp the big picture of physics, so this paper traces back to the very beginning of classical mechanics to discover its development through the literature review method. Starting from Kepler’s planetary motion laws and Newton’s theories, then moving to two-body and three-body problems, this essay demonstrates the delicacy of classical mechanics and how it effectively solves different issues. Also, after centuries of development, the implications of Newtonian mechanics have been greatly expanded upon, serving as the foundation for numerous subsequent theories. In the end, this essay provides an outlook for other theories that either derive from or relate to Newtonian mechanics, like chaos theory and analytical mechanics. The paper finds that Newtonian mechanics is essential because it not only provided solutions to many of the modern astronomical difficulties but also encouraged the emergence of other important ideas

 View pdf
View pdf


By employing a specific class of smooth functions to study a space, Morse theory establishes deep connections between analysis and topology. It is a classical subject of pure mathematics, originally pioneered by Marston Morse in the 1920s. In this article, we use Morse theory to present a proof of an interesting result on the knots, known as the Fáry-Milnor theorem. We also discuss discrete Morse theory, a subject of applied mathematics developed by Robin Forman in the 1990s, and its application. We focus on elucidating especially the inherent similarity between classical Morse theory and discrete Morse theory

 View pdf
View pdf


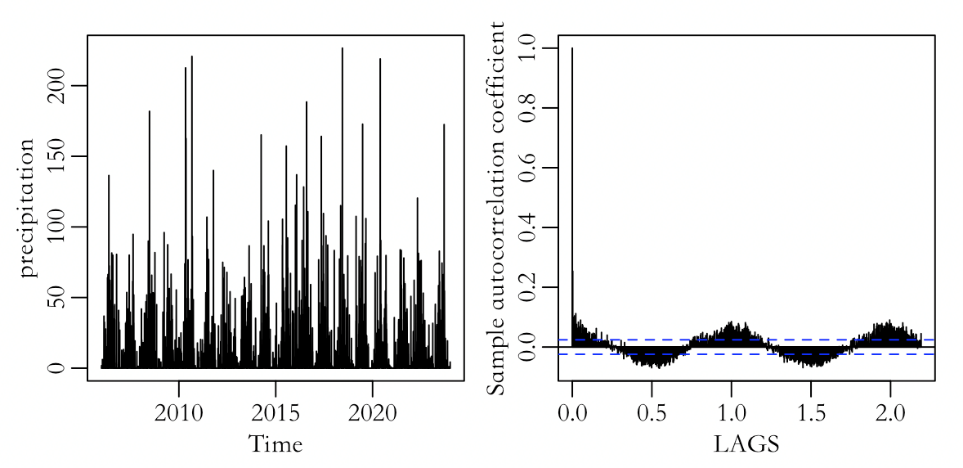
This article obtains nearly 18 years of precipitation data for Guangzhou from the National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI) under the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and conducts visualization analysis and modeling predictions using R software.Using the classic SARIMA model (the ARIMA model with seasonal components) as well as regression and residual ARIMA models to build and simulate the precipitation series.We also used Basic-bootstrap prediction, which involves resampling the residuals of the fitted model with replacement, using historical values to predict the future and obtain a model parameter, as well as Full-bootstrap prediction (which assumes that the residuals have uncertainty and that the estimated model coefficients themselves also have uncertainty).Therefore, not only are reasonable model residuals obtained through the bootstrap method, but multiple model parameters are also derived from this method to determine more reasonable model parameters, which are then used to forecast the next 12 periods for the fitted model. Comparing the results of the four prediction models, the Full-bootstrap model under the regression model showed the best predictive performance. The study found that there is no significant trend in precipitation changes over time, but short-term fluctuations still exist. Although some extreme values appeared, they remain within a predictable range.Therefore, the relevant city government departments prone to extreme rainfall can make reasonable adjustments to drainage facilities based on local precipitation forecasts

 View pdf
View pdf


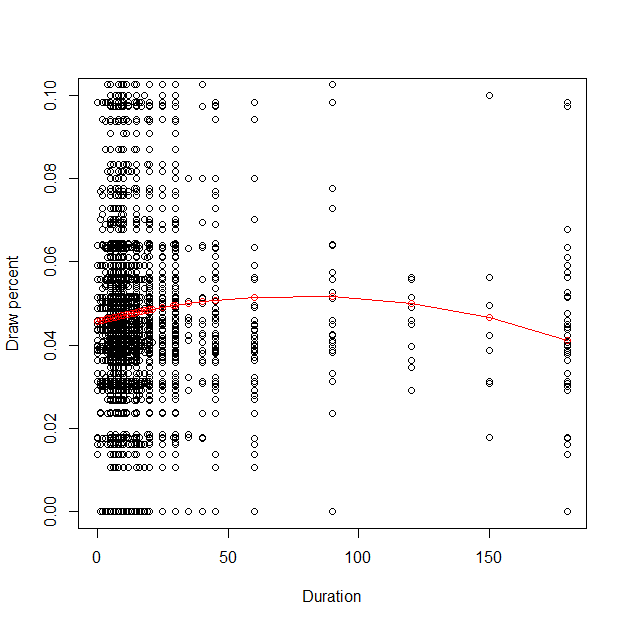
This essay explores the application of game theory in chess, focusing on the relationship between time pressure, risk, and draw probability. Game theory provides a framework for analyzing interactive decision-making processes, enabling players to understand opponents' strategies, predict moves, and formulate optimal responses. The study utilizes a dataset of 20,058 chess games to examine the impact of duration on risk behavior. The analysis reveals a nonlinear relationship between game length and draw probability, with a parabolic trend suggesting that the likelihood of a draw increases with game length up to approximately 60-70 minutes, where it peaks at around 4%-5%, and then gradually decreases for longer games. The regression model shows time pressure leads to about 10% more risk-taking, indicating a moderate fit. These findings underscore the importance of time management and risk assessment in chess, with implications for enhancing players' competitive edge and strategic planning skills in both chess and real-world decision-making scenarios

 View pdf
View pdf


This study investigates the influence of bow pretension force on the performance and tone of the violin through theoretical modeling, finite element analysis, and experimental verification. Theoretical modeling was used to establish the initial shape and bending characteristics of the bow. Through a multi-objective genetic algorithm, the material properties of the bow, particularly the Young's modulus, were optimized to closely match actual measurements. Experimental tests were conducted to analyze the effects of different pretension forces on the violin's sound quality, showing that higher pretension increases harmonic amplitude and alters the timbre. However, both excessive and insufficient pretension forces negatively impact bow controllability and performance stability. The research concludes that a moderate pretension force balances timbre and playing stability, ensuring optimal performance. This study provides valuable insights into the acoustic characteristics of the bow and offers a scientific basis for players when selecting and adjusting their bows

 View pdf
View pdf


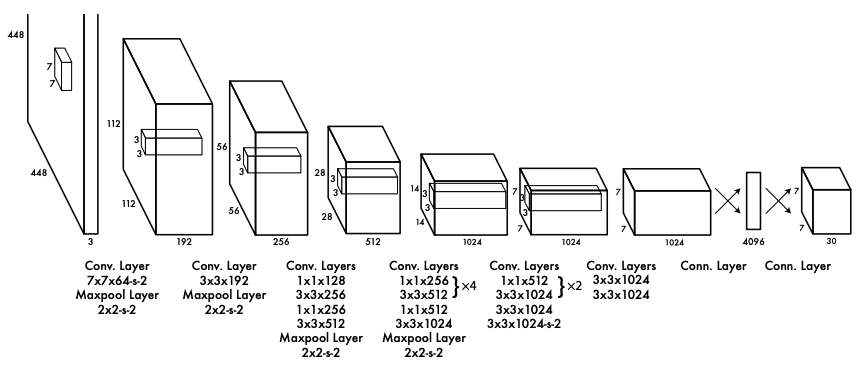
Throughout the evolution of You Only Look Once (YOLO) series, staring from base YOLO to latest YOLOv11, each version takes advantages of different techniques and mechanism, incorporating innovations that enhance object detection capabilities by improving both speed and accuracy. From introduction of anchor boxes in YOLOv2 to multi-scale predictions in YOLOv3 and Cross-Stage Partial Networks in YOLOv4, each iteration has brought unique improvements. In YOLOv7, two major advancements, Extended Efficient Layer Aggregation Network and Planned Re-parameterized Convolution, were introduced to address challenges in feature aggregation and parameter utilization, while maintaining optimal gradient flow. Additionally, advanced label assignment strategies, such as lead head guided label assigner and coarse-to-fine label assigner, further improve learning efficiency. These innovations enable YOLOv7 to set new standards in object detection, especially for applications in autonomous driving, video surveillance, medical imaging, and beyond

 View pdf
View pdf


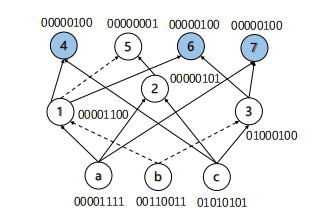
Combinational Equivalence Checking (CEC) is a critical process in digital circuit design, ensuring that two versions of a circuit are functionally equivalent. Functionally Reduced And-Inverter Graphs (FRAIGs) are a data structure extensively used in CEC, representing Boolean functions as directed acyclic graphs with AND gates and inverters. The main advantage of FRAIGs is their ability to integrate structural hashing with functional reduction, allowing for the elimination of functionally equivalent nodes during graph construction. However, conventional FRAIG approaches face challenges with scalability in complex circuits. To overcome these limitations, we propose three novel methods: improved sampling techniques that refine random simulation and SAT-based methods for early identification of equivalent nodes; advanced graph partitioning strategies that enable parallel processing and localized equivalence checking to accelerate computation; and support node analysis combined with probability distribution modeling to reduce unnecessary checks. Extensive experiments show the effectiveness and efficiency of our proposed methods

 View pdf
View pdf


In this paper, we consider some Poisson-type equations arising from the study of electromagnetic wave propagation in metals and metamaterials, where sign-changing coefficients in these equations lead to challenges that fall outside standard frameworks. We apply the T-isomorphism method, expanding on the approach in [1], to analyze Poisson-type equations in fully asymmetric configurations. These configurations require a new construction of isomorphism T. Finally, we obtain the well-posedness of these problems under certain parameters

 View pdf
View pdf




